How Do I Do an Image Search? Unlocking the Power of Visual Discovery
In an increasingly visual world, images are more than just pixels on a screen – they are stories, inspiration, information, and a vital part of our digital lives. From breathtaking nature photography that sparks awe to abstract art that challenges perception, the digital landscape is brimming with visual content. But what happens when you encounter an image and want to know more about it? Perhaps you’ve seen a stunning wallpaper and want to find a high-resolution version, identify the subject of a beautiful photograph, trace the origin of a piece of digital art, or simply understand the context of an aesthetic background. This is where the powerful technique of reverse image search comes into play, transforming the way we interact with visual information online.
Reverse image search allows you to use a picture itself as your search query, rather than relying on descriptive text. Instead of typing “red panda animal cute,” you can simply upload an image of a red panda, and the search engine will return visually similar results, identify the subject, or even lead you to its original source. This innovative approach is invaluable not only for everyday curiosities but also for professionals in photography, graphic design, and digital art, and anyone looking to enhance their collection of images, backgrounds, and aesthetic elements.
The Power of Visual Search: Beyond Keywords

At its core, reverse image search is a technology that analyzes the visual characteristics of an image – its colors, shapes, textures, patterns, and even objects within it – to find matching or similar images across the vast expanse of the internet. It flips the traditional search paradigm, making an image the starting point of your discovery journey. This capability has profound implications for various aspects of visual content:
- Identifying the Original Source: For content creators and curators on platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, understanding an image’s origin is crucial for proper attribution and avoiding copyright issues. Reverse image search can pinpoint the first instance an image appeared online, revealing the photographer, artist, or publisher.
- Finding High-Resolution Versions: You might fall in love with a striking landscape wallpaper, an abstract background, or a piece of beautiful photography, only to find it in low quality. Reverse image search can help you locate higher-resolution versions suitable for large screens, prints, or digital projects. This is especially useful for maintaining the integrity of wallpapers and backgrounds, ensuring they look crisp and clear.
- Discovering Similar Images and Aesthetics: Whether you’re building a mood board for a graphic design project, looking for more images in a particular aesthetic style, or seeking variations of a nature or abstract theme, reverse image search is an excellent tool for inspiration and expanding thematic collections. It can unveil a world of related visual ideas and trending styles you might not find with text-based queries.
- Product Identification and Shopping: See a sad or emotional image featuring a unique prop? Spotted an item of clothing or a piece of furniture in a photo and want to buy it? Reverse image search can instantly connect you to online retailers selling that exact product or similar items, complete with price comparisons.
- Detecting Plagiarism and Copyright Infringement: For artists, photographers, and content creators, protecting their digital art and photography is paramount. Reverse image search allows you to monitor where your work is being used online, helping you identify unauthorized usage and take necessary action. This empowers creators to protect their images, whether they are high-resolution stock photos or unique digital artworks.
- Gathering Information About a Photo: Beyond just identifying objects, a reverse image search can often provide context about an image – where it was taken, who is in it, or what event it depicts. This is particularly useful when encountering unfamiliar digital photography or artistic pieces.
Essentially, if you have an image and a question, a reverse image search is often the quickest way to find an answer, turning visual ambiguity into clear information.
Mastering Reverse Image Search on Any Device
The accessibility of reverse image search has grown significantly, with major search engines and specialized tools offering straightforward methods across mobile and desktop platforms. Google, particularly with its Lens technology, leads the way in intuitive visual search.
On Mobile Devices: Android and iOS
Performing a reverse image search on your smartphone or tablet is incredibly convenient, leveraging the device’s camera and gallery.
Using the Google App (Google Lens)
Google Lens is Google’s primary visual search tool, seamlessly integrated into the Google app and Google Chrome on both Android and iOS devices.
From your Photo Gallery:
- Open the Google App: Download and open the Google app (or Google Chrome app) on your Android or iPhone/iPad. Safari on iOS typically doesn’t support direct reverse image search in the same way, making Google Chrome or the Google app essential.
- Access Google Lens: In the search bar, you’ll find a camera icon – this is your portal to Google Lens. Tap it. You may need to grant the app permission to access your camera and photo gallery.
- Select an Image: Your device’s gallery or camera roll will appear. Browse and select the image you wish to search.
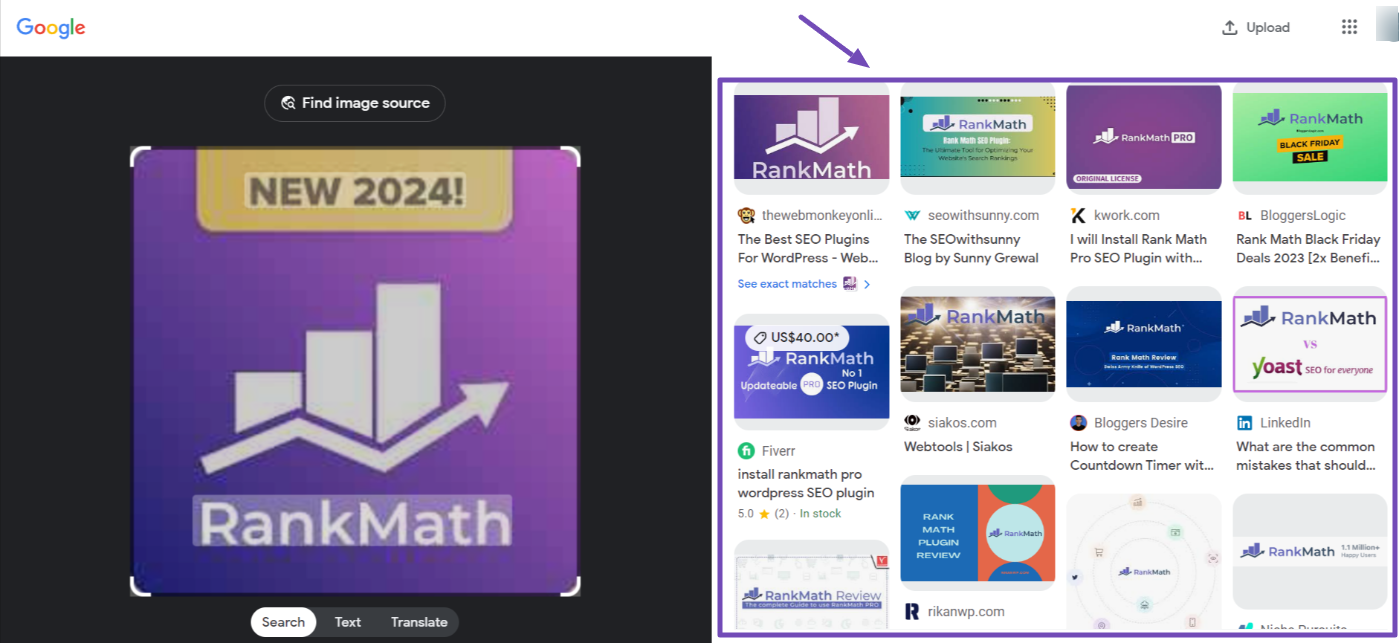
- Analyze and Refine: Google Lens will analyze the image, highlighting key objects or elements. For instance, if you’ve uploaded a picture of an aesthetic nature scene, it might identify specific flora or geographical features. You can often tap on specific areas of the image or drag bounding boxes to focus the search on a particular item, like a unique piece of abstract art within a larger composition.
- View Results: The app will then display a list of visually similar images, websites featuring the image, product links (if applicable), and related information. You might discover where to find high-resolution wallpapers, learn about the species in your nature photo, or find galleries showcasing similar abstract art. You can also tap “Add to your search” to append text keywords for more refined results.
Taking a Picture with your Camera:
- Open Google Lens: Similar to above, open the Google app or Google Chrome and tap the camera icon.
- Point and Shoot: Select the “Search with your camera” option (or similar wording) and point your phone’s camera at any real-world object you want to identify. This could be a plant, a piece of clothing, or even a book cover.
- Capture and Search: Tap the shutter button. Google Lens will immediately process the image, providing instant information, shopping links for products, or details about landmarks. This is fantastic for identifying elements for mood boards or quickly finding visual inspiration on the go.
On Desktop Computers: Unlocking Deeper Insights
Desktop reverse image search offers more flexibility, particularly when dealing with files saved on your computer or images found on websites where you can easily copy URLs.
Using Google Images (Google Lens)
Google Images is the most popular platform for desktop reverse image searches.
- Navigate to Google Images: Open your web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, etc.) and go to
images.google.com. - Access Google Lens: Click the camera icon (Google Lens icon) in the search bar.
- Upload an Image File:
- Drag and Drop: The easiest method is to drag an image file directly from your computer’s folders (e.g., from your “Wallpapers” or “Photography” folders) and drop it into the “Drag an image here” section.
- Upload a File: Alternatively, click “Upload a file” and navigate to the image you want to search for on your computer. This is ideal for high-resolution photography or digital art pieces you’ve stored locally.
- Paste an Image URL: If the image you want to search is already online, you can right-click it on the webpage, select “Copy image address” (or “Copy image link”), and then paste that URL into the “Paste image link” field in the Google Lens window. This is especially useful for checking the origin of stock photos or images used on other sites.
- View Results: Google will process your image and display a new page with visually similar results, the image’s source, related search terms, and options to search for specific elements within the image.
Searching Directly from a Website (Google Chrome)
Google Chrome offers a powerful built-in functionality for quick reverse image searches.
- Right-Click the Image: When you encounter an image on any webpage in Google Chrome, simply right-click it.
- Select “Search image with Google Lens”: From the context menu that appears, choose this option.
- Instant Sidebar Results: A Google Lens sidebar will open on the right side of your browser, displaying immediate results. This method is incredibly fast for identifying elements within an aesthetic or trending image, or for finding more details about a specific piece of beautiful photography without leaving your current page.
Advanced Applications for Creatives and Professionals
Beyond general curiosity, reverse image search offers specialized benefits for anyone working with or appreciating visual content, aligning perfectly with the core topics of a website like Tophinhanhdep.com.
Enhancing Visual Design and Photography
For graphic designers, digital artists, and photographers, reverse image search is a powerful tool in their creative arsenal:
- Sourcing and Attribution for Digital Art and Stock Photos: When creating graphic designs or photo manipulations, it’s often necessary to use external elements. Reverse image search ensures you can properly attribute sources or confirm that stock photos are genuinely free to use. It’s a critical step in ethical visual design, safeguarding against unintentional copyright violations.
- Discovering Editing Styles and Photo Manipulation Techniques: If you come across a photograph with a particularly striking editing style or a creative photo manipulation, a reverse image search can sometimes lead you to the artist, their portfolio, or even tutorials on how similar effects were achieved. This fuels creative ideas and helps refine your own digital photography and editing styles.
- Curating Thematic Collections and Mood Boards: Visualizing creative ideas often starts with a mood board. Reverse image search can help you rapidly gather images that fit a specific theme – whether it’s abstract patterns, serene nature scenes, or highly aesthetic compositions. By searching a base image, you can quickly find an entire collection of related visuals, streamlining the inspiration process for any visual project.
Protecting Your Digital Art and Discovering Inspiration
Artists and creators are constantly battling unauthorized use of their work. Reverse image search offers a proactive defense, while also being a wellspring of new ideas.
- Detecting Copyright Violations for Images and Digital Art: Imagine you’ve poured hours into creating a unique piece of digital art or capturing a stunning high-resolution photograph. A reverse image search allows you to input your original work and see everywhere it appears online. If you find your work used without permission or proper credit, it’s a clear indication of a copyright violation, enabling you to take action. This is vital for protecting your intellectual property, whether it’s an abstract painting or a deeply emotional photograph.
- Finding Inspiration and Trending Styles for Wallpapers and Backgrounds: Beyond protection, reverse image search is a fount of inspiration. See a captivating wallpaper or background that speaks to a current trend? Search it to discover the broader artistic movement, find similar aesthetic backgrounds, or explore how leading designers are incorporating trending styles into their work. This helps keep your visual content fresh and relevant.
- Exploring Different Renditions and Photo Ideas: Sometimes, you might have a core photo idea but want to see how others have interpreted it, or find different angles, lighting, or compositions. Searching your concept image can reveal diverse renditions of similar subjects, offering new perspectives and enriching your personal collection of photo ideas. For instance, searching an image of a sad or emotional scene might lead to various artistic interpretations of similar feelings.
Optimizing Your Image Search Strategy
While reverse image search is intuitive, a few strategic approaches can significantly enhance the accuracy and breadth of your results, helping you extract the most value from this powerful tool.
Tips for Unlocking Precise Results
Not all image searches are created equal. Fine-tuning your approach can make a world of difference.
- Use High-Quality Images for Better Results: The clearer your input image, the more precise the search engine’s analysis will be. Blurry, pixelated, or heavily compressed images (even if they started as high-resolution photography) can lead to irrelevant or inaccurate results. Search algorithms rely on distinct visual data points – colors, patterns, specific details – which are lost in low-quality images. Always aim to use the best possible version of the image you have. For example, if you’re looking for a specific nature background, start with the sharpest available photo.
- Crop and Focus on the Main Subject: Often, an image contains multiple elements. If you’re interested in a specific part of a complex scene – say, a particular flower in a busy garden photo, or an abstract pattern on a piece of furniture – cropping the image to isolate that subject can yield much more targeted results. Google Lens often tries to intelligently identify main subjects, but manual cropping gives you ultimate control, preventing the search engine from getting “distracted” by irrelevant background elements or text within the image. This technique is invaluable for discovering specific design elements or particular items within aesthetic imagery.
- Utilize Additional Filters and Keywords: Most reverse image search engines, especially Google Lens, offer options to refine your search. After an initial visual search, you might be able to add text keywords to narrow down the results further. For example, if you searched an image of a vintage camera, you could add “price” or “model number” to find shopping results. Some platforms also allow filtering by image size (e.g., “large,” “medium,” or “icon-sized”), which is perfect for finding high-resolution versions for wallpapers or digital photography projects.
Beyond Google: Exploring Alternative Search Engines and Image Tools
While Google is a dominant player, exploring other reverse image search engines can often provide diverse perspectives and uncover results that Google might miss. Each engine uses its own algorithms and indexed databases, leading to varying outcomes.
- Bing Visual Search: Microsoft’s Bing offers a robust “Visual Search” feature, accessible directly from
bing.comvia a camera icon. It performs similarly to Google Lens, allowing image uploads, URL pastes, or direct camera input (on mobile). Bing is particularly good at identifying landmarks and shopping for products. - TinEye: Known for its focus on finding exact matches and variations, TinEye is excellent for copyright detection. It specializes in tracking the same image across the web, making it a go-to tool for artists and photographers looking to protect their work. It can also find different sizes of an image, which is useful for sourcing high-resolution images.
- Yandex Image Search: The Russian search engine Yandex provides a powerful reverse image search, often yielding different results than Google. It’s known for its strong facial recognition and ability to suggest related content, including identifying elements in a picture and offering a “For sale” tab for product matches. Yandex can also be very effective for discovering unique abstract images or niche artistic photography.
- Specialized Mobile Apps (Reversee, CamFind): Apps like Reversee (for iOS/Android) and CamFind (iOS/Android) offer mobile-first reverse image search experiences. Reversee integrates Google, Bing, and Yandex searches, while CamFind utilizes CloudSight for highly accurate object recognition, even speaking the name of identified objects aloud. These can be particularly handy for quick, real-time searches of objects for photo ideas or product sourcing.
- AI Chatbots (ChatGPT, Gemini): The new wave of AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, are integrating multimodal capabilities that allow you to upload an image and ask questions about it. While not traditional reverse image search engines, they can analyze an image and provide descriptive information, identify objects, and even suggest text-based search queries to find related content. For example, you could upload an image of a digital art piece and ask Gemini to describe its style or suggest similar artists. However, remember that AI chatbots can sometimes “hallucinate” or provide inaccurate information, so always cross-reference critical findings with traditional search engines. These AI tools are fantastic for image-to-text functionality, extracting descriptions or concepts from visuals.
By combining these different tools and applying smart search strategies, you can unlock the full potential of reverse image search. Whether you’re a casual user looking for aesthetic backgrounds or a professional artist ensuring the originality of your digital art, mastering visual search is an indispensable skill in today’s image-rich online environment. It’s a key component in a comprehensive approach to managing, appreciating, and creating stunning visual content, from high-resolution wallpapers to inspired photography collections.