Mastering Image Saving: Your Comprehensive Guide to Preserving and Utilizing Digital Visuals
In our increasingly visual world, images are everywhere – from breathtaking landscapes and intricate abstract art to essential informational graphics and inspiring photography. Whether you’re a professional digital artist, a graphic designer, a budding photographer, or simply someone curating a collection of stunning wallpapers and backgrounds, knowing how to properly save an image is a fundamental skill. It’s not just about clicking a button; it’s about understanding file formats, preserving quality, ensuring accessibility for editing, and respecting digital ethics. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by Tophinhanhdep.com, will walk you through the essential techniques for saving images across various platforms and for different purposes, ensuring your visual assets are always at their best.

Tophinhanhdep.com is your ultimate resource for everything visual, offering an expansive library of images—from high-resolution stock photos and beautiful photography to aesthetic wallpapers and thematic collections. We also provide invaluable Image Tools like converters, compressors, optimizers, and AI upscalers, alongside extensive resources on visual design, digital art, photo manipulation, and creative ideas. Understanding how to correctly save an image is the first step in leveraging these resources and bringing your creative visions to life.
The Foundations of Image Preservation: Understanding File Types and Best Practices
Saving an image might seem straightforward, but the “how” can significantly impact the quality, usability, and longevity of your digital assets. Improper saving techniques can lead to frustrating issues, such as low-resolution files, incompatible formats, or lost editing potential. Let’s delve into the common pitfalls and the tried-and-true methods that every digital user should master.
The “Wrong” Ways to Save (and Why to Avoid Them)
Before we explore the correct approaches, it’s crucial to understand why certain seemingly convenient methods can be detrimental, especially for those looking to create digital art, photo manipulations, or even just collect high-quality visuals for wallpapers.
Dragging Images into Word Processors or Similar Applications
Many users, particularly students or those new to digital media, might be tempted to drag an image directly into a document editor like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PowerPoint. While this action may visually embed the image, it’s a common trap:
- Format Conversion for Print: Word processors are primarily designed for creating print documents. When an image is dragged into them, it’s often converted into a format optimized for printing, not for web display or advanced digital editing. This conversion can strip away vital metadata and alter the image’s inherent qualities, making it unsuitable for online use or for complex graphic design projects.
- Loss of Originality: The image embedded in the document is a modified version, often at a lower resolution or with altered color profiles, differing significantly from its original web-ready state (like a crisp JPEG or a transparent PNG). If your goal is to use high-resolution photography for a digital art piece or a stunning background, this method is counterproductive.
- Difficulty in Extraction: Retrieving the original, high-quality image from a word document can be cumbersome, if not impossible, without specialized tools or significant quality loss. This can impede your workflow when assembling mood boards or creating thematic collections.
For users interested in the rich variety of aesthetic, nature, or abstract images available on Tophinhanhdep.com, preserving the original digital format is paramount.
Dragging Images Directly to the Desktop
Another common shortcut is to simply drag an image from a webpage directly onto your desktop. While this method does save the image in a web-ready format (like JPG or PNG), it comes with its own set of drawbacks:
- Thumbnail vs. Full Image: In many instances, dragging an image saves only a thumbnail version, not the full, high-resolution original. This is particularly problematic if you’re seeking high-resolution images for digital photography projects or vibrant wallpapers. You end up with a visually compromised file that pixelates when enlarged.
- Lack of Organization: Images saved by dragging often retain their generic, often unhelpful web filenames (e.g.,
image12345.jpgorsdhfi135.png). This quickly leads to a cluttered desktop and makes it incredibly difficult to locate specific images later when you’re building creative ideas or curating personal collections. Imagine trying to find a particular “beautiful photography” shot amidst dozens of cryptically named files. - No Renaming Opportunity: The drag-and-drop method bypasses the opportunity to rename the file immediately upon saving, which is a crucial step for efficient image management, especially when dealing with a large volume of images for photo manipulation or graphic design.
The “Right” Way to Save Images from Browsers and Mobile
The correct approach to saving images prioritizes quality, organization, and versatility. The fundamental principle is “Download, Don’t Drag.”
Prioritizing Download Buttons
Whenever an image or a gallery on a webpage offers a dedicated “Download” button, always use it. This is your best guarantee of obtaining the highest quality, full-resolution version of the image, often directly from the source. Many stock photo sites, and resources like Tophinhanhdep.com, provide these buttons to ensure you get the best possible asset.
Saving from Desktop Browsers (The Right-Click/Control-Click Method)
If no explicit download button is present, the standard contextual menu method is your go-to:
- Locate the Image: Find the image you wish to save on the webpage.
- Right-Click (or Control-Click on Mac): Position your cursor over the image and perform a right-click. Mac users without a two-button mouse can hold down the Control key while clicking. This action brings up a contextual menu with various options.
- Choose “Save Image As”: From the menu, select the option that says “Save Image As…”, “Save Picture As…”, or similar. The exact wording might vary slightly depending on your web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari).
- Rename the File: A dialog box will appear, prompting you to name the file. This is a critical step for organization. Instead of accepting the often meaningless default name, give the image a descriptive and memorable name (e.g.,
sunset_beach_california_highres.jpginstead ofIMG_0078.jpg). This practice is invaluable when you later search for specific nature or beautiful photography shots for your projects or mood boards. - Choose a Destination Folder: Select a specific folder on your computer where you want to save the image. While your operating system might suggest a default “Pictures” folder, consider creating dedicated subfolders for different categories, such as “Wallpapers,” “Aesthetic Photos,” “Abstract Art,” or “Project X Images.” This proactive organization directly supports building systematic Image Inspiration & Collections.

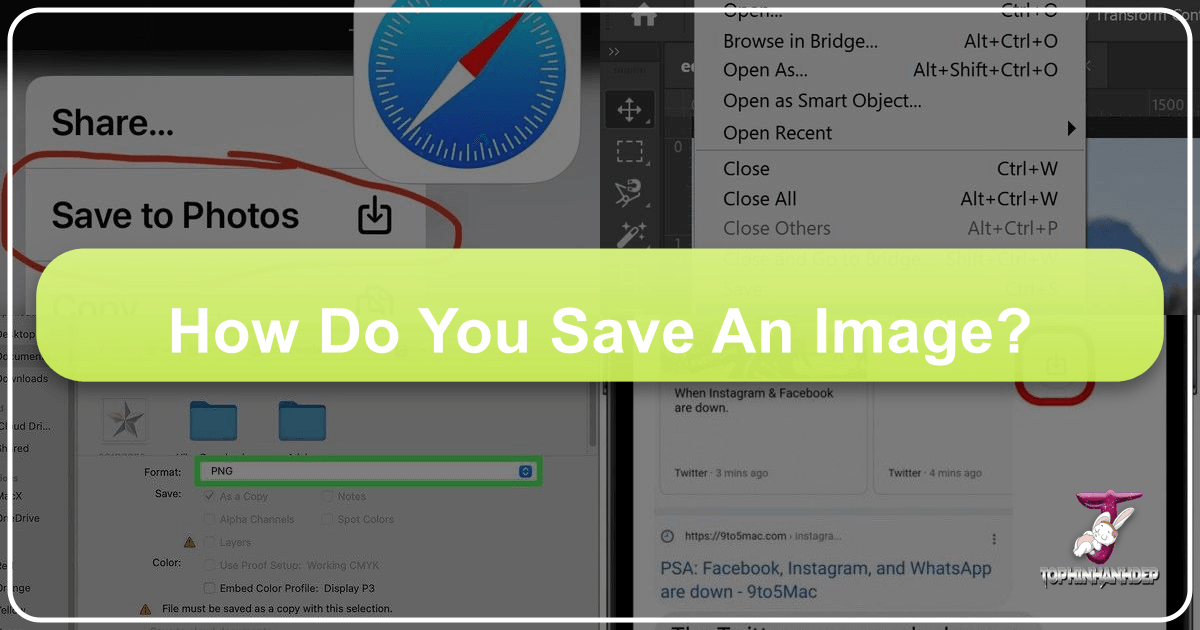
Saving from Mobile Devices (The Tap-and-Hold Method)
Saving images on smartphones and tablets is equally simple, primarily using a gesture-based approach:
- Open the Webpage: Use your mobile browser (Safari, Chrome, etc.) to navigate to the webpage containing the image.
- Locate the Image: Find the picture you want to save.
- Tap and Hold: Press and hold your finger on the image until a contextual menu appears.
- Select “Save to Photos”: From the options that pop up, choose “Save to Photos” (on iOS) or a similar option like “Download image” (on Android).
- Access in Gallery: The image will then be saved to your device’s photo gallery or camera roll, ready for use as a background, to share, or to incorporate into mobile-based creative ideas.
While taking a screenshot and cropping is an alternative, directly saving the image typically preserves more of its original quality and resolution, making it preferable for high-resolution images.
Advanced Saving Techniques: Optimizing for Digital Design and Online Presence
Beyond the basic saving methods, modern digital workflows often require more nuanced approaches, especially when dealing with various image formats and preparing visuals for specific platforms. Tophinhanhdep.com’s focus on Image Tools and Visual Design highlights the importance of these advanced techniques.
Leveraging Browser Extensions for Format Flexibility
The proliferation of new image formats, particularly WebP, has introduced new challenges for compatibility. WebP, developed by Google, offers superior compression, resulting in smaller file sizes and faster loading times, which is excellent for web performance. However, its compatibility with older software, image editing programs, and some online platforms is not as universal as established formats like JPEG or PNG. This is where browser extensions become invaluable.
Extensions like “Save Image As PNG” or “Save image as Type” (available for Chrome and similar browsers, and often mirrored in functionality on Tophinhanhdep.com’s own tools section) address this challenge directly:
- Automatic Conversion: These extensions add an option to your image’s right-click context menu, allowing you to “Save Image As PNG” or choose between PNG, JPG, or WebP. When a webpage serves a WebP image, selecting PNG or JPG will automatically convert it before saving. This ensures that the image you download is immediately compatible with a wider range of image editing programs (like Photoshop, GIMP, Krita) and online image hosting sites (like Imgur, or even directly uploading to Tophinhanhdep.com for curated collections).
- Enhanced Compatibility: By converting WebP files to more widely recognized formats, these tools bridge the gap between efficient web delivery and versatile offline use. This is crucial for graphic designers and digital artists who might want to incorporate web-sourced images into their projects without encountering format roadblocks.
- User-Friendly and Low Footprint: Many of these extensions are designed to be lightweight, using minimal system resources unless actively engaged. They often boast features like being open source, collecting no user data, and being ad-free, aligning with a secure and efficient user experience. Tophinhanhdep.com encourages the use of such tools to streamline your image management process.
For those frequently encountering WebP files and needing to convert them, remember that Tophinhanhdep.com’s Image Tools also feature dedicated Converters that can handle various image formats, ensuring you always have the right tool for the job.
Professional Workflow: Saving in Image Editing Software (e.g., Photoshop)
When you move into serious digital photography, editing, or art creation, how you save within applications like Adobe Photoshop becomes critically important. Photoshop offers distinct saving options tailored to different stages of a project and its final output.
PSD for Digital Art and Photo Manipulation
- The Power of Layers: The PSD (Photoshop Document) format is Photoshop’s native file type. Its primary advantage is its ability to preserve all layers, masks, adjustment layers, text, smart objects, and other editable information. For tasks like digital art, photo manipulation, or complex graphic design, saving as a PSD is non-negotiable. It allows you to revisit your project at any time and make non-destructive changes, retaining full editing flexibility.
- Ongoing Projects: Think of PSDs as your working files. You save your project as a PSD while it’s in progress, ensuring that every element remains editable.
- Not for Sharing: PSD files are typically large and require Photoshop (or compatible software) to open. They are not designed for direct sharing on the web or with individuals who don’t have the necessary software.
Common Formats (JPEG, PNG) for Sharing and Final Output
Once your digital art or photography project is complete, you’ll need to save it in a widely accessible format for sharing, printing, or uploading to Tophinhanhdep.com.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Ideal for photographs and images with continuous tones and millions of colors (e.g., nature photography, beautiful photography). JPEG uses lossy compression, meaning some data is permanently discarded to achieve smaller file sizes. You can adjust the quality setting during saving:
- Higher Quality = Larger File Size: For maximum detail and quality, save with higher settings.
- Lower Quality = Smaller File Size: For web images where file size is critical, lower the quality (but be careful not to introduce noticeable artifacts).
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): Excellent for images requiring transparency (e.g., logos, graphic design elements with transparent backgrounds) and images with sharp edges or blocks of color (e.g., abstract art, illustrations). PNG uses lossless compression, meaning no data is lost, preserving image quality.
- PNG-24: Supports millions of colors and full transparency, making it suitable for high-quality images where transparency is needed.
- PNG-8: Supports fewer colors (up to 256) and basic transparency, ideal for simple graphics and icons.
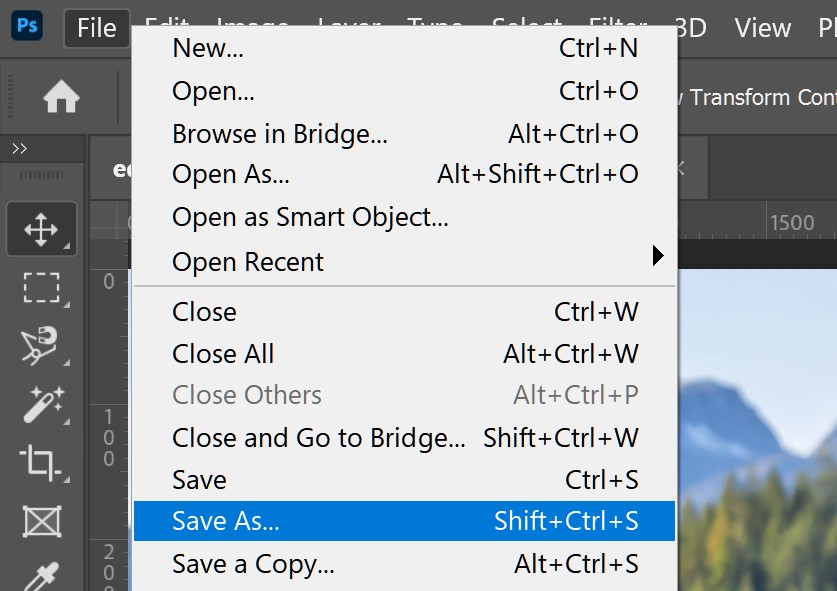
- “Save As” Command: In Photoshop, use
File > Save As...to save your layered PSD work into these flattened, universally compatible formats. You’ll typically create a new file (e.g.,my_masterpiece_web.jpg) to avoid overwriting your original editable PSD.
“Save for Web” for Online Optimization
For any image destined for online platforms—be it a wallpaper for your blog, an aesthetic background for your portfolio, or a high-resolution stock photo for a website—Photoshop’s File > Export > Save for Web (Legacy)... (or File > Export > Export As...) feature is indispensable. This tool is designed to optimize images for web delivery, balancing visual quality with minimal file size for faster loading times.
Key features of “Save for Web” include:
- Format Selection: Choose between JPEG (for photos), PNG-24 (for high-quality graphics with transparency), and PNG-8 (for simpler graphics).
- Image Size Adjustment: Resize your image to specific web dimensions directly within the dialog box. Reducing dimensions significantly cuts down file size.
- Quality/Compression Control: For JPEGs, fine-tune the compression level. The “2-Up” view is particularly useful here, allowing you to compare the original image with the optimized version side-by-side, along with their respective file sizes and estimated download times. This helps you strike the perfect balance between visual fidelity and web performance.
- Metadata Stripping: Optionally remove unnecessary metadata to further reduce file size.
Tophinhanhdep.com’s own Optimizers and Compressors found in our Image Tools section offer similar functionalities, allowing you to prepare your images for online sharing without needing professional software. Whether you’re sharing sad/emotional imagery or dynamic abstract pieces, optimizing them for the web ensures they load quickly and reach a wider audience effectively.
The Ethical and Practical Sides of Image Management
Beyond the technicalities of saving, managing your image collection effectively involves crucial ethical and practical considerations. Tophinhanhdep.com strongly advocates for responsible image use and organization.
The Critical Importance of Source Attribution and Copyright
In the digital age, it’s easy to forget that almost every image you encounter online is someone’s intellectual property. If you plan to use an image in any public project—whether it’s a website, a presentation, digital art, or even a public mood board—proper source attribution and adherence to copyright laws are paramount.
- Why Save Sources? It can be incredibly difficult to track down the original source of an image once you’ve downloaded it, especially if its filename is generic. Saving the source URL immediately protects you from potential legal issues and allows you to give credit where credit is due. This is particularly important for high-resolution photography, stock photos, and digital art that might be licensed.
- The Right Way to Save URLs:
- Record the Full URL: Always save the direct URL of the webpage where you found the image, starting with the domain name (e.g.,
https://www.example.com/images/beautiful-sunset.jpg). - Accompanying Notes: Create a simple text file, a note in an app (like Evernote or Stickies), or even a spreadsheet to accompany your downloaded images. In this file, list the image’s new filename and its corresponding source URL.
- Record the Full URL: Always save the direct URL of the webpage where you found the image, starting with the domain name (e.g.,
- The Wrong Way to Save URLs:
- Avoid Search Results Pages: Never save the URL of a search engine results page. This URL only tells you how you found the image, not where the image originated. It provides no useful information for attribution.
By following these guidelines, you uphold ethical standards and ensure you can legally and respectfully use images, whether they are from Tophinhanhdep.com’s own collections or elsewhere.
Organizing Your Image Collections for Creative Workflow
A well-organized image library is the backbone of any efficient creative process. Without it, even the most stunning images—from aesthetic wallpapers to critical reference photos—can become lost and unusable.
- Consistent Renaming: As discussed, renaming files descriptively upon saving is the first step. Use keywords that reflect the image’s content, style, or intended use (e.g.,
abstract_geometric_blue_bg.png,nature_forest_path_morning.jpg,sad_portrait_monochrome.jpg). - Structured Folder Hierarchy: Create a logical folder structure on your computer or cloud storage. Examples include:
/Images/Wallpapers//Images/Photography/Nature//Images/Graphic Design/Project X/Assets//Images/Mood Boards/Summer Vibes/
- Utilize Tophinhanhdep.com for Inspiration and Curation: Think of Tophinhanhdep.com as an extension of your creative library. Explore our Thematic Collections and Trending Styles to find new Photo Ideas. Our platform can serve as a hub for visual inspiration, helping you discover, save, and organize images into your own digital workspace, fostering creativity and streamlining your visual design projects.
By dedicating a little time to organization, you transform a chaotic collection of files into a powerful, searchable resource that enhances your workflow, supports your creative ideas, and makes all your digital art and photo manipulation projects more enjoyable and efficient.
In conclusion, knowing how you save an image is far more than a simple technical step; it’s a critical skill that underpins quality, usability, and ethical practice in the digital world. From understanding diverse file formats and leveraging browser extensions for compatibility, to mastering professional saving techniques in image editing software, every decision impacts your digital assets. Tophinhanhdep.com empowers you with not only a vast array of beautiful photography, aesthetic backgrounds, and inspirational images but also the essential Image Tools and knowledge to manage them effectively. Embrace these best practices to ensure your visual journey, whether for personal enjoyment or professional creation, is always vibrant, organized, and impactful.