Mastering Image Alignment: How to Center Your Visuals in HTML for Stunning Web Design
At Tophinhanhdep.com, we understand that exceptional visual content, from breathtaking “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds” to captivating “Aesthetic” and “Beautiful Photography” pieces, is the cornerstone of a truly engaging online experience. The power of an image lies not just in its inherent beauty or “High Resolution” quality, but also in its presentation. A perfectly aligned image can transform a simple webpage into a gallery, guiding the viewer’s eye and enhancing the overall “Visual Design.” One of the most fundamental yet often perplexing aspects of web development for visual content creators is “how to center an image in html.”
The journey to perfectly centered images has evolved significantly over the years. What was once a simple, though often inflexible, task using basic HTML tags has transformed into a sophisticated art powered by Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). For a website like Tophinhanhdep.com, which showcases diverse “Images” ranging from “Nature” and “Abstract” to “Sad/Emotional” and professional “Stock Photos,” mastering image alignment is not merely a technical detail; it’s a critical element of “Graphic Design” and “Digital Art” that directly impacts the user’s perception of quality and professionalism. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the evolution of image centering, from outdated HTML attributes to modern, robust CSS techniques like Flexbox and Grid, ensuring your visuals always take center stage.
The Evolution of Image Centering in HTML: From Simplicity to Sophistication
The early days of HTML were characterized by a focus on document structure. Designers and developers often intertwined styling directives directly within HTML tags, leading to less maintainable and flexible code. While convenient at the time, this approach became a hindrance as the web grew more complex and the demand for dynamic, responsive “Visual Design” increased. Image alignment, including the straightforward task of “how to center an image in html,” was no exception to this early paradigm.
As web standards matured, the principle of “separation of concerns” gained prominence. This meant HTML was strictly for content and structure, while CSS was designated for presentation and styling. This fundamental shift led to the deprecation of many HTML attributes that dictated visual appearance, paving the way for the powerful and versatile styling capabilities of CSS. Understanding this evolution is key to appreciating why modern methods are superior for presenting your “Photography,” “Digital Art,” and “Image Collections” on Tophinhanhdep.com.
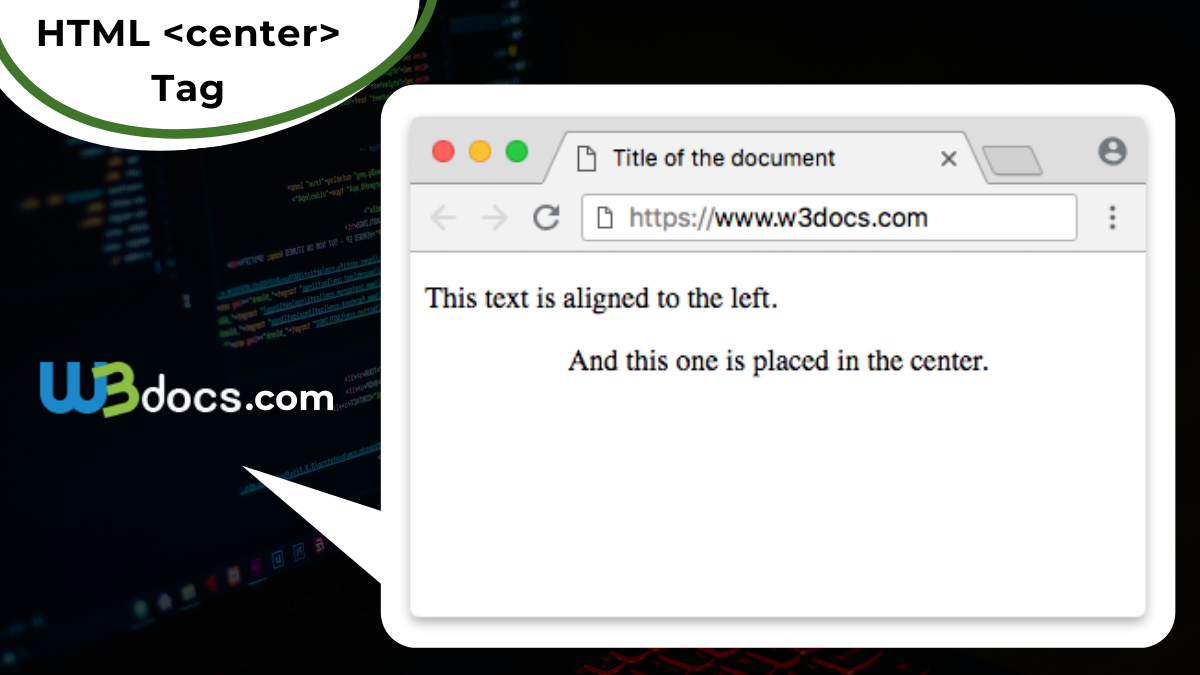
The <center> Tag: A Relic of the Past
In the infancy of the web, the <center> tag was the go-to solution for horizontal alignment. If you wanted to center a piece of text or an image, you would simply wrap it within these tags. For instance, to center an image of a “Nature” scene:
<center><img src="nature-scene.jpg" alt="Beautiful Nature Photography"></center>While seemingly straightforward, the <center> tag is now deprecated in HTML5. This means it has been removed from web standards and its use is strongly discouraged. Modern browsers might still render content wrapped in <center> tags centrally for backward compatibility, but there’s no guarantee this will continue indefinitely. Relying on it is risky, as it can lead to inconsistent rendering across different browsers and future web platforms.
The primary reason for its deprecation lies in the philosophy of separating structure from presentation. HTML should describe what content is (an image, a heading, a paragraph), not how it looks. Styling, including alignment, belongs to CSS. For intricate “Visual Design” elements, detailed “Graphic Design” layouts, or striking “Digital Art,” the <center> tag offered minimal control and hindered the ability to create truly responsive and adaptable layouts. Websites like Tophinhanhdep.com, committed to showcasing “High Resolution” and “Aesthetic” visuals, require far more granular control than this archaic tag could ever provide.

The align Attribute: An Outdated Approach
Another method prevalent in older HTML versions for image alignment was the align attribute, used directly within the <img> tag. You might have seen examples like:
<img src="abstract-art.jpg" alt="Abstract Digital Art" align="middle">This attribute allowed for various alignments, including left, right, top, bottom, and middle (which often had effects similar to centering or vertical alignment relative to surrounding text). However, much like the <center> tag, the align attribute for <img> is also deprecated in HTML5. It represented another instance of mixing presentational styling with structural HTML, a practice that modern web development strives to avoid.
For displaying professional “Photography” or meticulously crafted “Photo Manipulation,” the limitations of the align attribute quickly become apparent. It provided limited options for precise positioning and no inherent responsiveness, making it ill-suited for the dynamic layouts required for modern web galleries or “Image Collections.” The community’s shift away from these attributes underscored the need for a dedicated styling language that could offer robust, flexible, and future-proof solutions for “Visual Design.” This is where CSS stepped in, providing a powerful toolkit to precisely control “how to center an image in html” and achieve stunning visual layouts.
Modern Approaches: Leveraging CSS for Precision Alignment
With the advent and widespread adoption of CSS, web developers gained unprecedented control over the presentation of HTML elements. CSS allows for styles to be defined separately from the document’s structure, promoting cleaner code, easier maintenance, and significantly greater flexibility. For Tophinhanhdep.com, harnessing modern CSS is essential for rendering “High Resolution” images and diverse “Thematic Collections” with pixel-perfect accuracy and responsive adaptability. These modern techniques provide not just methods for “how to center an image in html,” but a foundation for truly sophisticated “Visual Design.”
Centering Inline Images with text-align: center
The <img> tag is inherently an inline element, meaning it flows with the text content, similar to a word in a sentence. The text-align CSS property is designed to horizontally align inline-level content (like text or inline images) within its block-level parent container. Therefore, to center an image using text-align: center, the image itself must be placed inside a block-level element, such as a <div> or <p> tag, and the text-align: center; style applied to that parent container.
Consider a beautiful “Aesthetic” image you wish to center within a paragraph or a dedicated section:
<div class="image-container">
<img src="aesthetic-wallpaper.jpg" alt="Aesthetic Wallpaper">
</div>And the corresponding CSS:
.image-container {
text-align: center;
/* Optional: Add padding, margin, or max-width for better control */
max-width: 90%; /* For responsive width */
margin: 0 auto; /* To center the container itself if it has a max-width */
}This method is highly effective for centering images where the parent container might also contain other inline content (like captions or text descriptions) that also needs to be centered. It’s a common and reliable technique, especially suitable for “Backgrounds” or “Wallpapers” that are contained within a specific content block. It’s even frequently used in environments where full CSS flexibility is limited, such as in basic HTML email templates, as noted by web development resources like Tophinhanhdep.com’s guides.
Mastering Block-Level Image Centering with margin: auto
Another incredibly powerful and widely used technique for horizontal centering involves treating the image as a block-level element and then leveraging auto margins. This method is particularly robust for ensuring images, especially “High Resolution” ones or those intended to stand alone, are perfectly centered within their available horizontal space.
Since <img> tags are inline by default, the first step is to explicitly change their display property to block:
<img class="block-centered-image" src="beautiful-photography.jpg" alt="High Resolution Photography">And the crucial CSS:
.block-centered-image {
display: block; /* Make the image a block-level element */
margin-left: auto; /* Push the image to the right as much as possible */
margin-right: auto; /* Push the image to the left as much as possible */
/* Shorthand for margin: 0 auto; for top/bottom margin 0, left/right auto */
/* It's often good practice to define a width for block-level images for responsiveness */
max-width: 100%; /* Ensure it doesn't overflow its parent */
height: auto; /* Maintain aspect ratio */
}When a block-level element has a defined width (or max-width that creates an intrinsic width) and its margin-left and margin-right properties are set to auto, the browser will automatically distribute the available horizontal space equally on both sides of the element, thereby centering it perfectly. This technique is fundamental for creating responsive layouts for “Digital Photography” galleries or “Image Inspiration & Collections” where images need to scale and remain centered on various screen sizes. It provides a clean, elegant solution for presenting any “Editing Styles” or “Photo Manipulation” with a strong central focus.
Advanced Techniques: Dynamic Layouts with CSS Flexbox and Grid
As web design evolved to embrace more complex and adaptive layouts, CSS introduced powerful layout modules like Flexbox and Grid. These tools go far beyond simple horizontal centering, offering comprehensive control over two-dimensional and one-dimensional content alignment. For Tophinhanhdep.com, which strives for cutting-edge “Visual Design” and presents diverse “Trending Styles” in “Digital Art” and “Photography,” Flexbox and Grid are indispensable for crafting sophisticated and responsive image layouts.
Effortless Centering with CSS Flexbox
Flexbox (Flexible Box Layout Module) is a one-dimensional layout system that excels at distributing space among items in a container, primarily for aligning items along a single axis (either row or column). It simplifies centering both horizontally and vertically with remarkable efficiency.
To center an image using Flexbox, you first need a parent container that will act as the flex container, and the image itself will be a flex item:
<div class="flex-center-container">
<img src="abstract-wallpaper.jpg" alt="Abstract Wallpaper">
</div>The CSS implementation is wonderfully concise:
.flex-center-container {
display: flex; /* Turn the container into a flex container */
justify-content: center; /* Center content horizontally along the main axis */
align-items: center; /* Center content vertically along the cross axis */
/* Optional: Define a height for vertical centering to be apparent */
height: 300px; /* Example height */
background-color: #f0f0f0; /* For visibility */
}Flexbox is ideal for single images or small groups of images (like a “Mood Board” component) that need to be centered precisely within a defined area. It’s particularly useful when you need to align content both horizontally and vertically, making it perfect for “Aesthetic” layouts, showcasing “Photo Ideas” with a clean, centralized presentation, or even for centering dynamically sized “Stock Photos” within a flexible wrapper. Its simplicity and power make it a top choice for “Creative Ideas” in web layout.
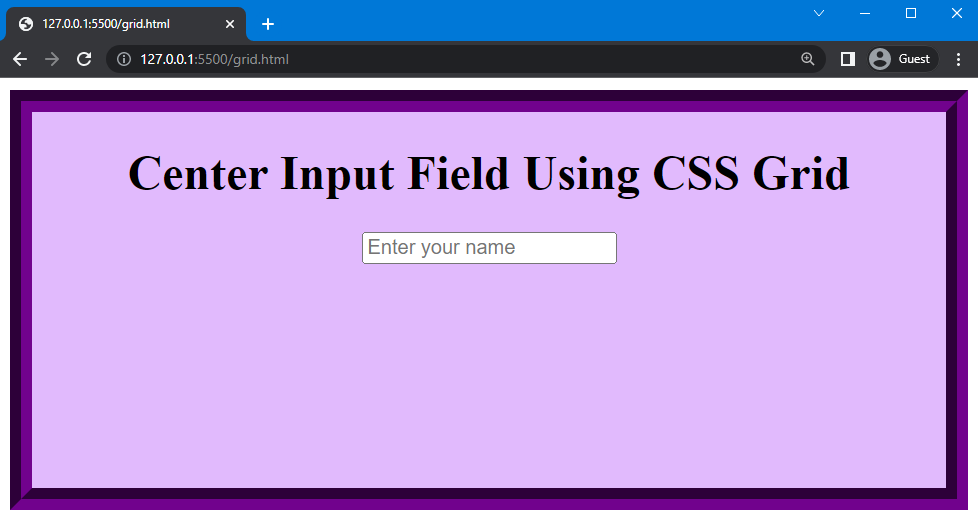
Precision Positioning with CSS Grid
CSS Grid Layout is a two-dimensional layout system, offering unparalleled control over both rows and columns simultaneously. This makes it incredibly powerful for intricate “Graphic Design” and complex page structures, allowing images to be placed and centered within specific grid areas with high precision.
To center an image using CSS Grid, similar to Flexbox, you’ll need a parent container for your image:
<div class="grid-center-container">
<img src="nature-photography.jpg" alt="High Resolution Nature Photography">
</div>The CSS provides direct control over item placement within the grid:
.grid-center-container {
display: grid; /* Turn the container into a grid container */
place-items: center; /* Shorthand for justify-items: center; and align-items: center; */
/* Optional: Define dimensions for the grid area */
min-height: 400px; /* Example height */
background-color: #e9e9e9; /* For visibility */
/* Example: define grid columns/rows if needed for complex layouts */
/* grid-template-columns: 1fr; */
/* grid-template-rows: 1fr; */
}The place-items: center; property is a powerful shorthand that will center all grid items (in this case, our image) both horizontally and vertically within their respective grid areas. Grid is particularly advantageous when dealing with “Image Collections” or “Thematic Collections” arranged in complex layouts, where individual “Digital Photography” pieces or “Photo Manipulation” results need to be precisely centered within their designated cells. It offers the highest degree of control for responsive “Backgrounds” and sophisticated “Visual Design” that goes beyond simple one-axis alignment.
Achieving Vertical and Horizontal Harmony
While the previous sections focused on horizontal centering (and Flexbox/Grid inherently offer both), there are specific scenarios where explicit vertical alignment might be needed or combined with other techniques.
For block-level elements centered with margin: auto, achieving vertical centering often requires Flexbox or Grid on the parent. However, for a more traditional approach, one can simulate table-cell behavior:
<div class="vertical-align-container">
<img src="sad-emotional-image.jpg" alt="Emotional Photography">
</div>.vertical-align-container {
display: table-cell; /* Treat container as a table cell */
vertical-align: middle; /* Align content vertically in the middle */
text-align: center; /* Align content horizontally in the center */
height: 400px; /* Must have a defined height */
width: 100%; /* Must have a defined width */
}
.vertical-align-container img {
display: block; /* Important for margin:auto, otherwise redundant with text-align */
margin: 0 auto; /* Horizontal centering if image is block */
}This method can be a bit more cumbersome and less flexible for responsive design compared to Flexbox or Grid. However, understanding its mechanics can be useful for specific legacy contexts or for fine-tuning. For Tophinhanhdep.com, ensuring that every “Beautiful Photography” piece, regardless of its “Editing Styles” or emotional impact, is perfectly positioned within its frame is paramount. Mastering these centering techniques provides the foundation for consistent and compelling visual storytelling.
Beyond Centering: Optimizing Images for a Visually Rich Experience
While knowing “how to center an image in html” is fundamental, it’s merely one piece of the puzzle in creating a truly exceptional visual website like Tophinhanhdep.com. Optimal image presentation involves a holistic approach that integrates technical alignment with thoughtful image preparation and advanced “Image Tools.” After all, a perfectly centered image loses its impact if it loads slowly or appears pixelated.
Enhancing Visuals for Wallpapers and Backgrounds
For “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds,” proper centering is crucial for establishing visual balance and immersive user experiences. A high-resolution background, for instance, must adapt seamlessly to various screen dimensions while keeping its focal point central.
- Responsiveness is key: Centering techniques must work fluidly with responsive design principles. Images intended as backgrounds often use
background-position: center center;andbackground-size: cover;in CSS, combined with media queries, to ensure they look great on any device. - Aesthetic Impact: A well-aligned “Aesthetic” background creates a cohesive look, free from awkward cropping or distracting shifts. For “Nature” or “Abstract” wallpapers, perfect centering can enhance the artistic intent, allowing the viewer to fully appreciate the composition without distraction.
The Role of Alignment in Professional Photography Presentation
For “Digital Photography” and professional “Stock Photos,” alignment transcends mere aesthetics; it speaks to the quality and professionalism of the presentation.
- Highlighting the Subject: If a “Beautiful Photography” piece features a strong central subject, perfect centering ensures that this subject is the immediate focus, as intended by the photographer’s “Editing Styles.” This is particularly true for symmetrical compositions or specific “Photo Manipulation” techniques that rely on precise balance.
- Consistency in Galleries: In “Image Collections” or “Thematic Collections,” consistent alignment (even if it’s consistently off-center for artistic effect) creates a harmonious flow, making the entire collection feel curated and polished. Imagine a gallery of “High Resolution” images where each one shifts slightly left or right; it quickly becomes distracting and unprofessional. Centering provides the stability needed for an engaging visual journey.
Integrating Image Tools for Flawless Display
The best centering techniques in the world can’t compensate for poorly prepared images. This is where “Image Tools” become invaluable, working hand-in-hand with alignment to deliver a superior visual experience on Tophinhanhdep.com.
- Compressors and Optimizers: Before an image is even considered for centering, it must be optimized. “Compressors” reduce file size without significant loss of quality, ensuring faster load times. “Optimizers” fine-tune various aspects for web delivery. A perfectly centered, but slow-loading, “High Resolution” image will frustrate users.
- AI Upscalers: For older or lower-resolution images, perhaps “Sad/Emotional” photographs that hold sentimental value but lack modern display quality, “AI Upscalers” can dramatically improve their resolution. Once upscaled, these images can then be perfectly centered and showcased without pixilation, reviving their impact.
- Converters: Tools like “Converters” (e e.g., converting JPEGs to modern formats like WebP) further enhance performance. A centered WebP image will load faster and often look better than a centered JPEG, contributing to a seamless user experience.
- Image-to-Text: While not directly related to visual presentation, the “Image-to-Text” capability of image tools is crucial for accessibility. The
altattribute in the<img>tag, often set up using “Image-to-Text” descriptions, provides context for screen readers and search engines, ensuring that your perfectly centered image is understood by all users and discovered effectively.
Creative Ideas and Future Trends in Image Layout
The ability to precisely control “how to center an image in html” opens up a world of “Creative Ideas” for “Visual Design.” Centering is not a static concept; it evolves with “Trending Styles” and new approaches to “Graphic Design” and “Digital Art.” For Tophinhanhdep.com, staying ahead of these trends means leveraging alignment not just for functional display, but as an integral part of artistic expression.
Visual Design Principles and Centered Aesthetics
Centering is a foundational principle in “Visual Design” for several reasons:
- Balance and Harmony: A centered element naturally feels balanced and stable. This creates a sense of calm and order, which is highly desirable for presenting “Beautiful Photography” or serene “Nature” scenes.
- Focus and Emphasis: Placing an image or a key element directly in the center draws immediate attention. This is a powerful technique for highlighting a featured “Digital Art” piece, a pivotal “Photo Manipulation,” or a crucial message accompanying “Sad/Emotional” imagery.
- Minimalist Trends: Many “Trending Styles,” particularly those embracing minimalism, heavily rely on centered layouts. A single, perfectly centered “Aesthetic” image against a clean background can be incredibly impactful, conveying elegance and sophistication. This simplicity is often achieved by combining centered elements with ample whitespace, creating a visually compelling experience.
- Grids and Asymmetry with Central Focus: Even in more dynamic grid layouts or asymmetrical designs, a central element can serve as an anchor. Think of a “Mood Board” where elements are scattered, but a key image remains perfectly centered, acting as the visual core around which other “Photo Ideas” revolve.
Curating Image Collections with Intentional Alignment
For “Image Inspiration & Collections,” consistency in alignment contributes significantly to the overall aesthetic and user experience. Whether you’re presenting “Thematic Collections” of “Abstract” art or a gallery of “High Resolution” “Stock Photos,” intentional alignment elevates the presentation.
- Gallery Grids: In a grid-based gallery, ensuring each image within its cell is consistently centered provides a neat, organized look. This creates a professional framework for showcasing diverse “Photography” without visual clutter.
- Hero Sections: Websites often use a large “hero image” at the top. Centering this image, whether it’s a dramatic “Wallpaper” or a striking piece of “Beautiful Photography,” creates an immediate and powerful impression.
- Narrative Flow: Alignment, including strategic centering, can influence how viewers perceive and navigate an “Image Collection.” A series of perfectly centered images can create a deliberate, contemplative pace, whereas more dynamic, varied alignments might convey energy or movement.
Ultimately, “how to center an image in html” is more than just a coding problem; it’s a “Visual Design” decision. It’s about taking raw “Images” and transforming them into curated visual experiences that resonate with users, whether they are admiring a delicate “Nature” shot or seeking inspiration from “Trending Styles.” By mastering modern CSS techniques, Tophinhanhdep.com can continue to offer a platform where every visual, from “High Resolution” “Backgrounds” to emotionally charged “Digital Photography,” is presented with the excellence it deserves.
Conclusion
The journey of “how to center an image in html” reflects the broader evolution of web development itself, moving from rudimentary, often inefficient HTML attributes to the precise and powerful capabilities of CSS. While the <center> tag and align attribute served their purpose in earlier web eras, their deprecation in HTML5 firmly establishes modern CSS as the definitive approach for image alignment.
For content-rich platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, which thrives on delivering an unparalleled visual experience through “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” “Aesthetic” imagery, and “Beautiful Photography,” mastering these modern techniques is paramount. We’ve explored several robust CSS methods:
- Wrapping images in a block-level parent and applying
text-align: center;is a reliable solution for inline images, especially within mixed content flows or in simpler contexts like email templates. - Transforming images into block-level elements with
display: block;and utilizingmargin: 0 auto;provides an elegant and responsive way to horizontally center images of any size, a cornerstone for presenting “High Resolution” “Digital Photography.” - Leveraging CSS Flexbox with
display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center;offers a powerful and concise method for one-dimensional centering, ideal for focused elements or components within “Mood Boards” and “Image Inspiration.” - Employing CSS Grid with
display: grid; place-items: center;provides ultimate control for two-dimensional centering within complex layouts, indispensable for intricate “Graphic Design,” “Digital Art” presentations, and sophisticated “Image Collections.”
Beyond mere technical execution, effective image centering is deeply intertwined with “Visual Design” principles. It enhances the presentation of diverse “Images” from “Nature” and “Abstract” themes to “Sad/Emotional” narratives, ensuring “Stock Photos” and “Photo Manipulation” results are displayed with maximum impact. Furthermore, integrating “Image Tools” like “Compressors,” “Optimizers,” “AI Upscalers,” and “Converters” ensures that these perfectly centered visuals are also performant and accessible, enriching the entire user journey.
By embracing these modern CSS methodologies, developers at Tophinhanhdep.com can ensure that every visual asset, regardless of its “Editing Styles” or thematic content, is positioned with intentionality and precision, contributing to an overall aesthetic that is both stunning and user-friendly. The future of visual web design lies in flexible, responsive, and precisely aligned content, and mastering image centering is a fundamental step towards achieving that excellence.