How to Change the Size of an Image in CSS: A Comprehensive Guide for Visual Storytellers
In the dynamic world of web design and digital content, images reign supreme. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, which thrives on delivering an unparalleled visual experience—from stunning Wallpapers and captivating Backgrounds to exquisite Beautiful Photography and inspiring Digital Art—mastering the art of image sizing with CSS is not merely a technicality; it’s a cornerstone of success. Effective image resizing ensures that every pixel serves its purpose, enhancing user engagement, optimizing performance, and preserving the artistic integrity of the visual assets.

This guide will delve deep into the various methods of changing image sizes using CSS, exploring core properties, advanced techniques, and best practices. We’ll examine how these techniques integrate seamlessly with the diverse categories and tools offered on Tophinhanhdep.com, ensuring that every image, whether a High Resolution stock photo or an Abstract piece of digital art, is presented flawlessly across all devices and screen sizes.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Image Sizing in CSS
Before diving into specific CSS properties, it’s crucial to grasp the distinction between an image’s intrinsic size and its rendered size. The intrinsic size refers to the image’s actual dimensions (width and height in pixels) as it exists in its file. The rendered size, on the other hand, is how the browser displays the image on the screen, which can be manipulated through CSS. For Tophinhanhdep.com, often dealing with large, high-quality files from Digital Photography, understanding this difference is paramount to balancing visual fidelity with web performance.
Why does CSS sizing matter so much? Firstly, for performance. Loading excessively large images, even if scaled down by CSS, can drastically slow down a webpage, leading to a poor user experience. Secondly, for responsiveness. With users accessing Tophinhanhdep.com on a myriad of devices—from vast desktop monitors to compact smartphones—images must adapt seamlessly to different viewports without distortion or loss of detail. Thirdly, for visual integrity and aesthetic presentation. A poorly sized image can appear pixelated, stretched, or cut off, detracting from the carefully curated Aesthetic, Nature, or Sad/Emotional collections that Tophinhanhdep.com offers.
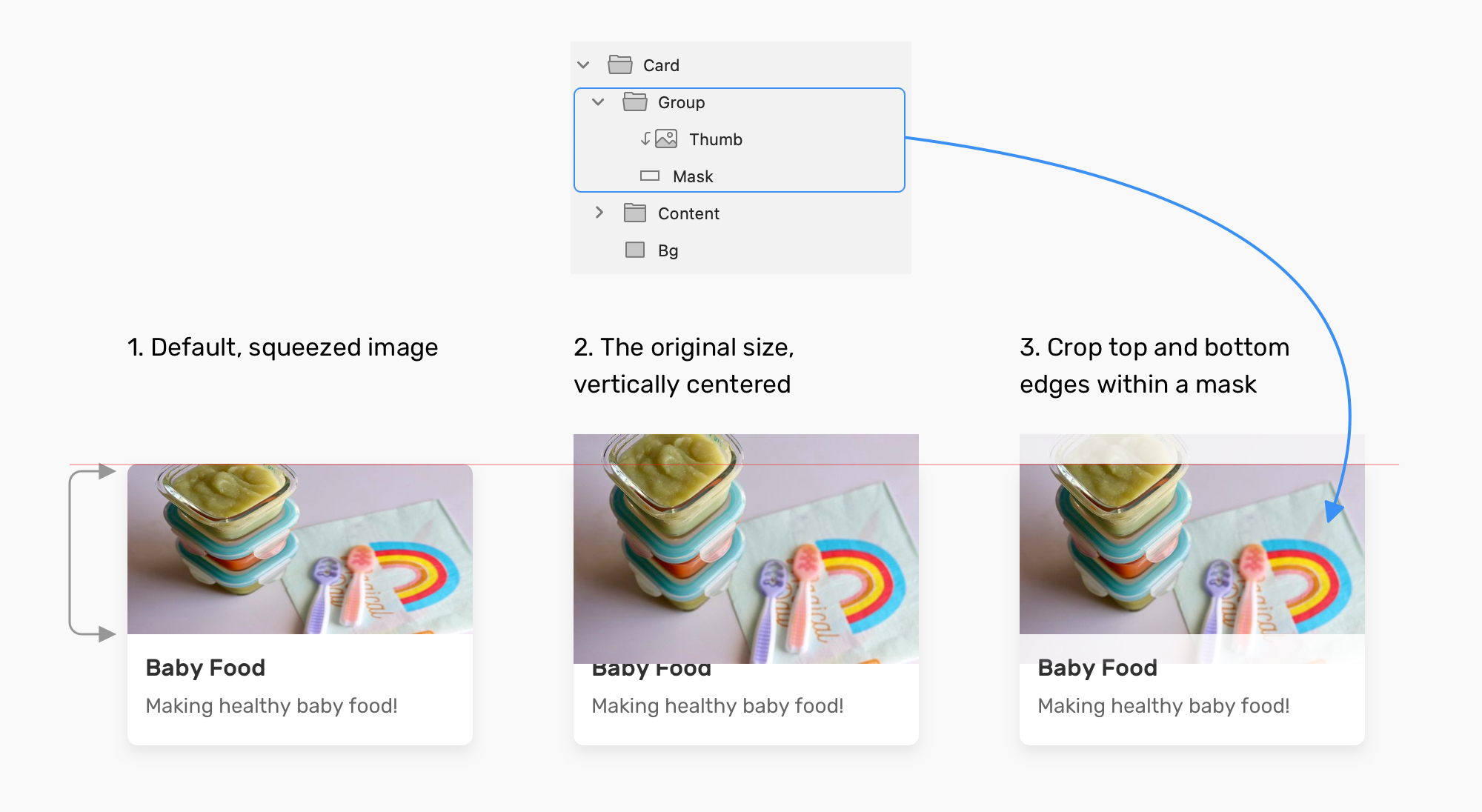
Setting Fixed Dimensions: The width and height Properties
The most straightforward way to change an image’s size in CSS is by directly setting its width and height properties. These properties allow you to define the exact dimensions for an image, using various units such as pixels (px), percentages (%), em units (em), or rem units (rem).
img {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}In this example, every img element will be rendered at 300 pixels wide and 200 pixels high. This method is useful for specific scenarios on Tophinhanhdep.com, such as:
- Fixed-size thumbnails: For image galleries or “Image Inspiration & Collections” sections, where a consistent visual grid is desired.
- Specific UI elements: Like logos or small decorative icons where precise dimensions are critical.
- Pre-defined banner ads: Where the space allocated for the image is fixed.
However, relying solely on fixed width and height has significant drawbacks, especially for responsive design. If the aspect ratio of the original image doesn’t match the specified width and height, the image will appear stretched or squashed, severely compromising the quality of Beautiful Photography or any meticulously crafted Digital Art. Furthermore, fixed pixel dimensions do not adapt to different screen sizes, leading to images that are either too large on mobile or too small on desktop. This is where more flexible sizing techniques become indispensable.
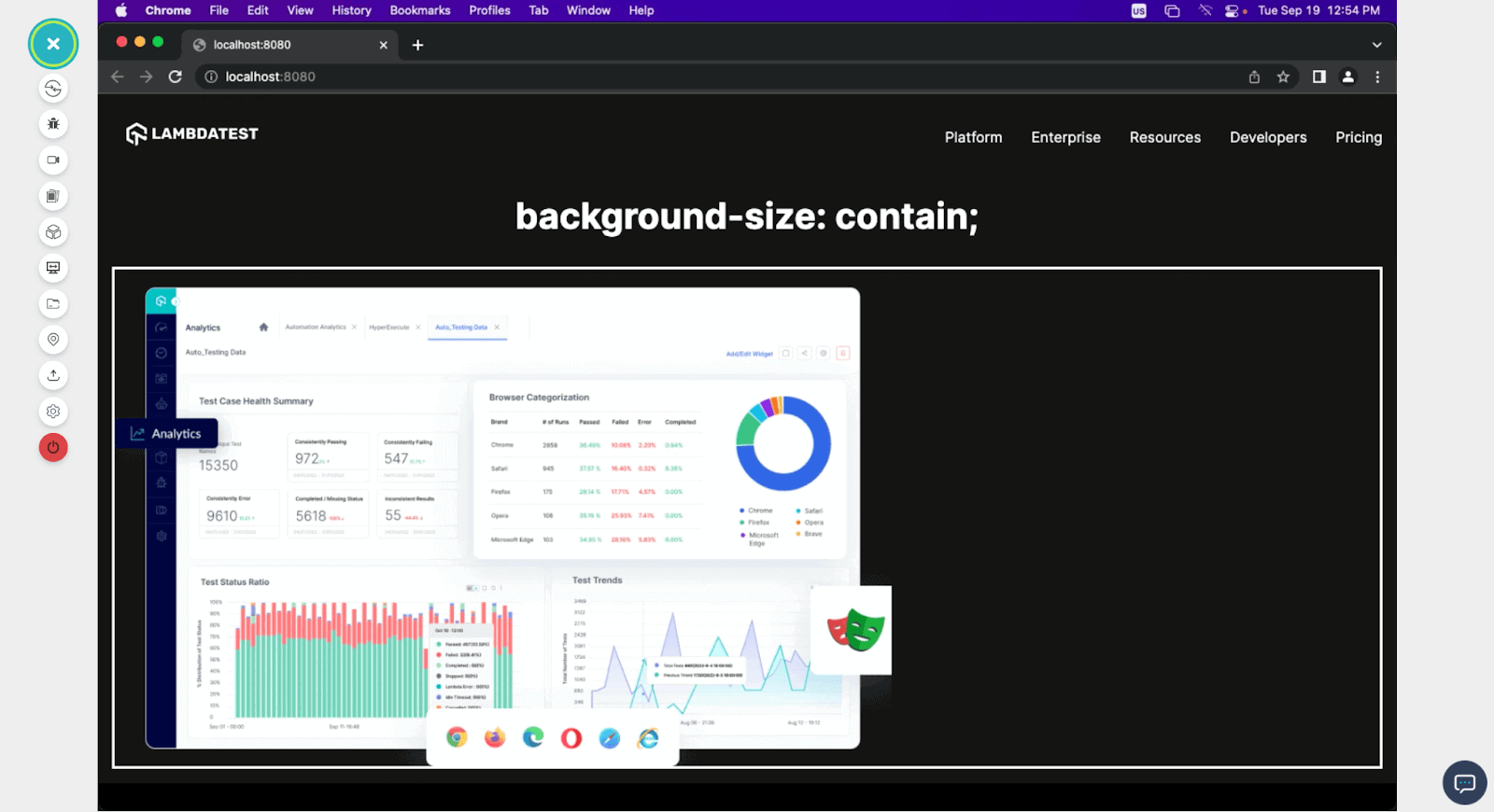
Maintaining Aspect Ratio: The Power of max-width and max-height
To overcome the limitations of fixed dimensions and ensure images retain their visual integrity while being responsive, the max-width property is a game-changer. It’s often paired with height: auto; to automatically adjust the height proportionally based on the width, thereby preserving the image’s original aspect ratio.
img {
max-width: 100%; /* Ensures the image never exceeds its parent container's width */
height: auto; /* Automatically adjusts height to maintain aspect ratio */
display: block; /* Optional: removes extra space below the image */
}This CSS snippet is the cornerstone of responsive image design. When applied to images on Tophinhanhdep.com:
- For Wallpapers and Backgrounds: It ensures that these large, often High Resolution images scale down gracefully on smaller screens without appearing cropped or distorted, fitting perfectly within their container.
- For Nature and Abstract Photography: The original composition and artistic intent are preserved, as the image shrinks or expands proportionally.
- For Stock Photos and Digital Photography: Professionals can be confident that their work will be displayed correctly, regardless of the user’s device.
The max-width: 100%; rule dictates that the image will never be wider than its parent container. If the container is smaller than the image’s intrinsic width, the image will scale down. If the container is larger, the image will retain its intrinsic width, preventing it from appearing pixelated by being forced to scale up beyond its natural resolution (unless its container also has a fixed width or width: 100% is used, which can cause pixelation if the intrinsic size is smaller than the container).
Similarly, max-height can be used, often when you want an image to fit vertically within a container, again usually paired with width: auto;. This is less common for general responsive images but highly effective for specific layout challenges, such as fitting images into a row where vertical space is constrained.
Advanced CSS Techniques for Dynamic Image Sizing and Control
While max-width: 100%; height: auto; provides a solid foundation for responsive images, modern CSS offers more granular control and sophisticated methods for handling image sizing, especially when dealing with complex layouts, variable content, and diverse user expectations.
Mastering object-fit for Flexible Image Presentation
The object-fit property is a powerful tool for controlling how an <img> or <video> element should resize to fit its container. It behaves similarly to background-size but applies directly to replaced elements like images. This property is invaluable for Visual Design and Photo Manipulation, allowing designers on Tophinhanhdep.com to achieve specific visual effects without altering the image’s intrinsic file.
It takes several values:
fill: The image is resized to fill the entire content box. If the aspect ratio doesn’t match, the image will be stretched or squashed. (Generally avoided for photographic content).contain: The image is scaled down to fit entirely within the content box, maintaining its aspect ratio. If the aspect ratio of the image doesn’t match the container, empty space (letterboxing or pillarboxing) will be visible. Ideal for showcasing complete images within a defined frame, such as displaying full-bleed images in a mood board on Tophinhanhdep.com without cropping.cover: The image is scaled to fill the entire content box, maintaining its aspect ratio. If the aspect ratio doesn’t match, the image will be cropped to fit. This is excellent for hero images, gallery thumbnails, or section backgrounds where the image should always fill the available space, like presenting a beautiful Nature scene or an Aesthetic wallpaper.none: The image is not resized. It maintains its intrinsic size and will be clipped if it’s larger than the container.scale-down: The image is sized as ifnoneorcontainwere specified, whichever results in a smaller concrete object size. This can be useful for preventing large images from overflowing.
Example:
.gallery-thumbnail {
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
object-fit: cover; /* Images will fill the thumbnail area, cropping as needed */
}
.hero-image {
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
object-fit: cover; /* Hero image fills banner, great for Wallpapers and Backgrounds */
object-position: center; /* Centers the image within the frame */
}For Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Image Inspiration & Collections” or “Thematic Collections,” object-fit: cover; is perfect for creating uniform gallery layouts while using images of varying intrinsic dimensions. Conversely, object-fit: contain; might be used when users click on a thumbnail to view the full image without any part being cropped.
Sizing Background Images with background-size
When images are used as backgrounds for elements rather than as direct <img> tags, the background-size CSS property comes into play. This is particularly relevant for Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Backgrounds” and “Wallpapers” categories, where images are often used to adorn entire sections or pages.
Common values for background-size:
auto: The default value. The background image’s intrinsic size is used.cover: Scales the background image to be as large as possible, so that the background area is completely covered by the image. Some parts of the image may be cut off if the aspect ratio differs. Ideal for full-screen backgrounds.contain: Scales the background image to the largest size possible without cropping or stretching the image. If the background area has a different aspect ratio than the image, the image will not cover the entire area (leaving empty space). Useful for showcasing a complete image within a section.- Percentages (
%): Scales the background image relative to the background positioning area.background-size: 50% 50%;would make the image half the width and half the height of the element. - Lengths (
px,em,rem, etc.): Sets a fixed width and height for the background image. E.g.,background-size: 200px 150px;.
Example:
.hero-section {
background-image: url('path/to/my-wallpaper.jpg');
background-size: cover; /* Ensures the background covers the entire section */
background-position: center; /* Centers the image within the background area */
background-repeat: no-repeat; /* Prevents tiling */
min-height: 500px; /* Ensures section has some height */
}This technique is fundamental for creating engaging visual sections on Tophinhanhdep.com, such as hero banners featuring “Beautiful Photography” or sections dedicated to “Aesthetic” design. It ensures that regardless of screen size, the background image provides a consistent and immersive experience, adapting fluidly while maintaining its overall aesthetic impact.
Responsive Images for Diverse Viewports: srcset and sizes
While CSS properties like max-width and object-fit handle how an image is displayed, the HTML attributes srcset and sizes combined with the <picture> element provide a method for the browser to choose the most appropriate image file to load based on the user’s device capabilities and viewport size. This is a critical performance optimization, especially for a site like Tophinhanhdep.com that features extensive “High Resolution” photography and “Stock Photos.” Why load a 4K image on a smartphone screen that’s only 400px wide?
srcset: Specifies a list of image files, along with their intrinsic widths or pixel densities. This allows the browser to select the most suitable image from the list.sizes: Specifies a list of media conditions (likemin-width) and the corresponding widths of the image when those conditions are met. This tells the browser how much space the image will occupy on the screen.
Example using srcset for different resolutions:
<img
src="image-small.jpg"
srcset="image-small.jpg 480w, image-medium.jpg 800w, image-large.jpg 1200w"
sizes="(max-width: 600px) 480px, (max-width: 1000px) 800px, 1200px"
alt="Description of image for Tophinhanhdep.com"
>Here:
480w,800w,1200wtell the browser the intrinsic width of each image file.(max-width: 600px) 480pxmeans “if the viewport is 600px or less, the image will take up 480px of space.”- The browser uses this information to pick the optimal image from
srcset.
The <picture> element offers even more flexibility, allowing you to specify different image files for different media queries, often used for art direction (changing the image entirely, not just its resolution, based on screen size). This is invaluable for “Visual Design” and “Creative Ideas” where a specific crop or orientation might be desired for mobile vs. desktop displays of “Digital Art” or “Photo Manipulation.”
These techniques are vital for Tophinhanhdep.com because they directly address performance concerns associated with high-quality imagery. By only loading the necessary image size, bandwidth is saved, load times are reduced, and the user experience for browsing “Image Inspiration & Collections” or specific “Thematic Collections” becomes much smoother.
Beyond Basic Resizing: Integrating CSS with Design Principles and Tophinhanhdep.com’s Ecosystem
Effective CSS image sizing isn’t just about code; it’s about integrating technical solutions with overarching design goals and leveraging available tools. Tophinhanhdep.com offers a rich ecosystem of visual content and utilities, making this integration even more critical.
The Role of Tophinhanhdep.com’s Image Tools in Pre-Optimization
Before any image even touches a CSS stylesheet, its intrinsic quality and file size can be drastically optimized using Tophinhanhdep.com’s dedicated “Image Tools.” These tools complement CSS sizing by preparing images for optimal web delivery:
- Compressors and Optimizers: These tools reduce the file size of images without significant loss of visual quality. While CSS dictates the rendered size, a smaller initial file size means faster downloads, which is crucial for collections of “High Resolution” images. An image optimized by Tophinhanhdep.com’s tools will load faster, even if CSS then scales it down or up.
- AI Upscalers: For images that might need to be displayed larger than their original intrinsic resolution, Tophinhanhdep.com’s AI Upscalers can intelligently increase resolution, adding detail that simple CSS scaling cannot. This is particularly useful for older “Digital Photography” or “Stock Photos” that need a modern, high-res presentation.
- Converters: Ensuring images are in the most web-friendly format (e.g., WebP for better compression) also contributes to performance.
The interplay is clear: Tophinhanhdep.com’s tools handle the quality and efficiency of the image file itself, while CSS handles how that file is presented and adapted to the layout. A strategy combining both yields the best results.
CSS Resizing for Visual Design and Digital Art
For categories like “Visual Design,” “Graphic Design,” “Digital Art,” and “Photo Manipulation,” CSS image sizing is an expressive tool. It allows designers to:
- Achieve specific layouts: Grid systems often rely on consistent image sizing (even if responsive) to create a harmonious flow. CSS properties like
grid-template-columnscombined withobject-fiton images within grid items allow for dynamic yet controlled layouts. - Create dynamic visual hierarchies: Larger images for key “Beautiful Photography” or “Trending Styles” can draw attention, while smaller, consistently sized images can guide the user through “Thematic Collections.”
- Ensure artistic intent is preserved: Digital artists who carefully craft every pixel of their work need to know that CSS resizing will display their creations as intended, without unwanted distortion.
object-fitand thoughtful aspect ratio management are key here. - Implement creative ideas: From parallax scrolling backgrounds (using
background-sizeandbackground-attachment) to intricate collages, CSS image sizing facilitates ambitious “Creative Ideas” in web design.
Enhancing Image Inspiration & Collections
The core mission of Tophinhanhdep.com revolves around inspiring users with vast collections of images. Proper CSS sizing directly contributes to the success of these collections:
- Mood Boards: Consistent sizing and alignment, achieved through CSS, make mood boards visually appealing and easy to digest, helping users explore “Photo Ideas.”
- Thematic Collections: Whether it’s a collection of “Nature” photography or “Abstract” art, uniform display (even if responsive) ensures that the collection feels cohesive and professional.
- Trending Styles: Presenting trending images in an optimal, fast-loading, and responsive manner makes them more accessible and engaging, encouraging users to explore further.
- User Experience: Fast-loading, properly displayed images mean users spend less time waiting and more time engaging with the content, enhancing their overall experience with Tophinhanhdep.com.
Best Practices for CSS Image Sizing on Tophinhanhdep.com
To ensure the best possible experience for users and maintain the high standards of Tophinhanhdep.com, consider these best practices when applying CSS image sizing:
- Prioritize Performance: Always optimize image files before uploading them. Use Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Compressors” and “Optimizers” to reduce file size. CSS can resize, but it cannot make a large file load faster. Combine CSS sizing with
srcset/sizesfor adaptive loading. - Maintain Aspect Ratio: Unless a specific design choice requires distortion, always strive to maintain an image’s original aspect ratio. Use
height: auto;withmax-widthorobject-fitto prevent stretched or squashed images, particularly for “Beautiful Photography” and “Digital Photography.” - Use Relative Units: Whenever possible, use relative units like percentages,
em,rem, or viewport units (vw,vh) forwidthandheightto ensure responsiveness across devices. Fixed pixel values should be reserved for very specific, non-responsive elements. - Consider
object-fitandbackground-size: These properties offer powerful control for how images fill or fit within containers, providing elegant solutions for various layout challenges without resorting to complex hacks. - Implement a Mobile-First Approach: When designing, think about how images will display on the smallest screens first, then progressively enhance for larger viewports. This ensures a solid baseline experience.
- Provide
altText for Accessibility: While not directly a sizing property, always include descriptivealttext for images. This is crucial for accessibility and SEO, providing context even if an image fails to load or for users with screen readers. - Test Across Devices: Always test image displays on a variety of devices, browsers, and screen sizes. What looks good on a desktop might be broken on a mobile phone. Browser developer tools are invaluable for this.
- Leverage Semantic HTML: Use the
<figure>and<figcaption>elements for images with captions, and always use the<img>tag for content images (not background images for content), allowing browsers to handle intrinsic sizing and accessibility more effectively.
Conclusion
Mastering CSS image sizing is an indispensable skill for anyone involved in web development and visual content delivery, especially for a platform as visually rich as Tophinhanhdep.com. From basic width and height properties to advanced techniques like object-fit, background-size, and responsive srcset/sizes, each method plays a vital role in crafting an optimal user experience.
By thoughtfully applying these CSS techniques, combined with the powerful “Image Tools” offered by Tophinhanhdep.com for pre-optimization, content creators and designers can ensure that every “Wallpaper,” “Background,” “Aesthetic” image, “High Resolution” photograph, or piece of “Digital Art” is presented beautifully, performs efficiently, and adapts seamlessly across the myriad of devices users employ today. The ultimate goal is to deliver an inspiring, engaging, and flawless visual journey for every visitor to Tophinhanhdep.com, making every pixel count in the story it tells.