Mastering Image Resizing in HTML for Stunning Visuals on Tophinhanhdep.com
In the dynamic world of web development, images are no longer just decorative elements; they are central to user engagement, visual storytelling, and overall website aesthetics. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, which thrives on showcasing a rich array of visual content—from breathtaking “Nature” and “Abstract” “Wallpapers” to meticulously curated “Beautiful Photography” and evocative “Sad/Emotional” images—the ability to precisely control image dimensions is paramount. Proper image sizing ensures that “High Resolution” “Stock Photos” are presented optimally, “Digital Art” retains its intended impact, and “Aesthetic” collections truly resonate with visitors.
While the core functionality of embedding images in HTML is straightforward, mastering their sizing involves a nuanced understanding of HTML attributes and CSS properties. This guide will delve into the various techniques for adjusting image sizes, focusing on both client-side display control and the critical role of server-side optimization, all within the context of delivering an unparalleled visual experience on Tophinhanhdep.com. We’ll explore how to achieve responsive designs, preserve aspect ratios, and mitigate common performance pitfalls, ultimately helping you present your “Image Inspiration & Collections” with maximum impact.
Methods to Change Image Size in HTML
The journey to perfectly sized images begins with the fundamental tools provided by HTML and CSS. There are several approaches to modify image dimensions, each with its own advantages and ideal use cases, particularly when managing diverse image types like those found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
The width and height Attributes for Direct Control
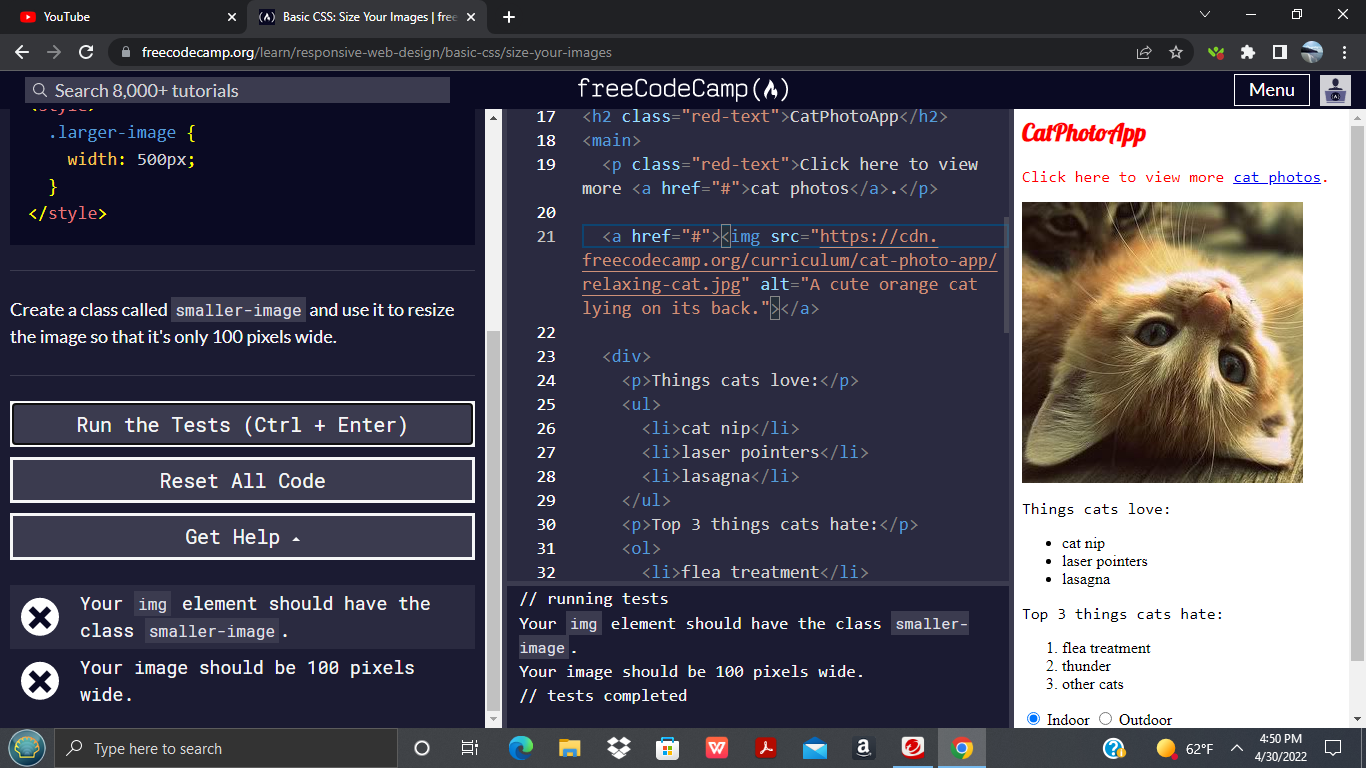
The most direct way to specify an image’s size in HTML is by using the width and height attributes directly within the <img> tag. These attributes tell the browser the exact dimensions (in pixels) the image should occupy.
Syntax:
<img src="path/to/your/image.jpg" alt="Description of image for accessibility" width="X" height="Y">Where:
src: The file path or URL to your image. On Tophinhanhdep.com, this would link to your “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” or specific “Beautiful Photography” assets.alt: An essential attribute providing alternative text for the image. This is crucial for accessibility (screen readers) and SEO, helping search engines understand the content, especially for thematic “Image Collections” on Tophinhanhdep.com.width: The desired width of the image in pixels.height: The desired height of the image in pixels.
Example:
Let’s say Tophinhanhdep.com wants to display a “Nature” image at a specific size:
<img src="forest-wallpaper.jpg" alt="Lush green forest wallpaper from Tophinhanhdep.com" width="800" height="450">In older HTML 4.01, height could also be defined as a percentage of the containing element. However, in HTML5, the standard dictates that these values must be in pixels. When width and height are explicitly set, the browser reserves the required space for the image before it fully loads. This prevents a jarring “layout shift” as images pop into place, ensuring a smoother user experience, which is vital when browsing extensive “Photo Ideas” and “Trending Styles” on Tophinhanhdep.com.

Considerations for width and height attributes:
While straightforward, directly setting both width and height requires careful attention to the image’s original aspect ratio. If the specified width and height do not match the image’s inherent proportions, the browser will stretch or compress the image to fit, leading to distortion and compromised visual quality. This is particularly detrimental for “High Resolution” or “Digital Photography” where fidelity is key. For creative flexibility and maintaining image integrity, CSS often provides more robust solutions.
Resizing an Image with CSS
CSS offers a more powerful and flexible approach to image resizing, allowing for greater control over aesthetics, responsiveness, and maintaining aspect ratios. This is especially beneficial for managing the diverse visual elements inherent to Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Visual Design” and “Graphic Design” principles.
Using the Inline style Attribute
Similar to direct HTML attributes, you can apply CSS rules directly to an <img> tag using the style attribute. This is essentially embedding CSS styling inline with your HTML.
Syntax:
<img src="path/to/image.jpg" alt="Image description" style="width: Xpx; height: Ypx;">Example:
To display an “Abstract” image with specific dimensions:
<img src="abstract-design.jpg" alt="Modern abstract design from Tophinhanhdep.com" style="width:500px; height:300px;">The inline style attribute takes precedence over external or internal stylesheets, essentially overriding any conflicting declarations. This method is useful for one-off styling where a specific image requires a unique treatment that doesn’t fit broader design rules. However, for a website with extensive “Image Collections” like Tophinhanhdep.com, relying heavily on inline styles can lead to difficult-to-manage code and lack of consistency.
External and Internal CSS Styling for Scalability
For a more maintainable and scalable approach, especially for a content-rich site like Tophinhanhdep.com, using internal or external CSS stylesheets is highly recommended. These methods allow you to define styles once and apply them across multiple images or even entire categories of images.
- Internal CSS: Defined within
<style>tags in the<head>section of your HTML document. - External CSS: Stored in a separate
.cssfile and linked to your HTML document. This is the industry standard for large projects.
Example (Internal CSS):
<head>
<style>
.gallery-thumbnail {
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#hero-banner-image {
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
object-fit: cover; /* More on this later */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="nature-photo-1.jpg" alt="Scenic nature photo" class="gallery-thumbnail">
<img src="abstract-art-2.jpg" alt="Vibrant abstract art" class="gallery-thumbnail">
<img src="beautiful-landscape.jpg" alt="Beautiful landscape banner" id="hero-banner-image">
</body>Using CSS classes and IDs allows for highly granular control. You could have .wallpaper-preview for smaller versions of “Wallpapers,” img.nature-collection for all “Nature” images, or #trending-photo-of-the-day for a unique “Trending Styles” showcase. This separation of HTML structure from visual presentation is a cornerstone of good “Visual Design” and crucial for efficiently updating “Image Inspiration & Collections” on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Preserving the Aspect Ratio While Resizing Images
One of the most common challenges in image resizing is maintaining the image’s original proportions to prevent distortion. For “Beautiful Photography” or “Digital Photography” on Tophinhanhdep.com, an altered aspect ratio can completely ruin the artistic intent.
The solution is elegant: specify only one dimension (either width or height) and set the other to auto. The browser will then automatically calculate the auto dimension to preserve the image’s original aspect ratio.
Example:
/* All images on Tophinhanhdep.com should maintain their aspect ratio */
img {
width: 100%; /* Take up 100% of the parent container's width */
height: auto; /* Automatically adjust height */
}
/* Or for a fixed height, such as in a grid of aesthetic images */
.aesthetic-grid-item img {
height: 250px;
width: auto; /* Automatically adjust width */
}Most modern web layouts are primarily constrained by width, making width: 100%; height: auto; a very common and effective pattern for ensuring images scale proportionally within their containers. This guarantees that “High Resolution” images, whether “Abstract” or “Nature,” always look correct, regardless of the available screen space.
Responsive Image Which Adjusts Based on Available Width
Creating a truly responsive website, where content adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes (desktops, tablets, phones), is essential for Tophinhanhdep.com’s diverse audience. Image resizing plays a crucial role here, especially for “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds” that need to look good on any device.
-
width: 100%;: This property forces the image to take up 100% of its parent element’s width. While great for responsiveness, it comes with a significant caveat: if the parent container is larger than the original image, the image will be upscaled. Upscaling raster images (like JPEG, PNG) inevitably leads to pixelation and blurriness, degrading the quality of “Digital Photography” or “Stock Photos.” -
max-width: 100%;: This is generally the preferred approach for responsive images. By settingmax-width: 100%;(along withheight: auto;), the image will:- Scale down if its container becomes smaller than its original width.
- Never scale up beyond its original dimensions, thus preventing pixelation and maintaining visual clarity.
Example:
.responsive-image {
max-width: 100%; /* Image will scale down, but not up beyond its natural size */
height: auto; /* Maintain aspect ratio */
display: block; /* Helps prevent extra space below images */
}This approach ensures that “Trending Styles” and “Thematic Collections” images on Tophinhanhdep.com are displayed beautifully and sharply across all devices, providing an optimal viewing experience without sacrificing image quality.
How to Resize & Crop Image to Fit an Element Area
Sometimes, simply resizing an image isn’t enough. For sophisticated “Visual Design,” “Graphic Design,” or “Photo Manipulation” on Tophinhanhdep.com, you might need an image to fill a specific container area, even if it means parts of the image are cropped, or the image is upscaled. This is where object-fit and background-image come into play.
Utilizing object-fit CSS Property for Precise Cropping
The object-fit CSS property, applied directly to the <img> element, controls how the image’s content should fit into its container. It’s an incredibly powerful tool for ensuring “Aesthetic” layouts and “Creative Ideas” are executed flawlessly.
Possible values for object-fit (along with inherit, initial, unset):
fill(default): The image will stretch or squeeze to fill the entire container, ignoring its aspect ratio. This can lead to distortion.contain: The image is resized to fit entirely within the container, preserving its aspect ratio. It will be “letterboxed” (empty space will appear) if the aspect ratios don’t match.cover: The image is resized to cover the entire container, preserving its aspect ratio. Parts of the image might be cropped if the aspect ratios don’t match. This is ideal for hero images or banner sections displaying “Wallpapers” or “Backgrounds.”none: The image is not resized at all. It retains its original size, and only the portion that fits within the container is visible (it’s cropped).scale-down: The image is scaled down as ifcontainwere applied, but only if the image’s natural size is larger than the container. Otherwise, it behaves likenone.
Additionally, the object-position property can be used with object-fit to specify which part of the image should be prioritized when cropping occurs (e.g., object-position: center;, object-position: right;).
Example for a “Featured Image” section on Tophinhanhdep.com:
<div class="featured-image-container">
<img src="beautiful-flower.jpg" alt="Close-up of a beautiful flower" class="featured-image">
</div>.featured-image-container {
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
overflow: hidden; /* Ensure content outside bounds is hidden */
border: 1px solid #eee;
}
.featured-image {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
object-fit: cover; /* Cover the container, cropping if necessary, preserve aspect ratio */
object-position: center; /* Center the image within the container */
}This ensures that all “Beautiful Photography” or “Thematic Collections” images within the featured container consistently fill the space without distortion, creating visually cohesive “Mood Boards.”
Utilizing Background Images for Flexible Layouts
The background-image CSS property is another versatile tool, allowing you to place images on non-<img> elements (like div, section, etc.) and precisely control their sizing and positioning. This is often used for page “Backgrounds,” header sections showcasing “Abstract” patterns, or intricate “Graphic Design” elements on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Key background properties for sizing and cropping:
background-size: Controls the size of the background image.auto: Default, image at full size.length(e.g.,200px 150px): Sets explicit width and height.percentage(e.g.,50% 50%): Sets width and height relative to the element.contain: Resizes the background image to fit entirely within the element, preserving aspect ratio. Empty space might appear.cover: Resizes the background image to cover the entire element, preserving aspect ratio, cropping if necessary. This is commonly used for full-width section “Wallpapers” or “Backgrounds.”
background-position: Sets the starting position of a background image (e.g.,center,top left,50% 50%).
Example for a “Sad/Emotional” themed section background on Tophinhanhdep.com:
<section class="emotional-background-section">
<h2>Reflections</h2>
<p>Explore images that capture profound emotions.</p>
</section>.emotional-background-section {
background-image: url('sad-emotional-image.jpg');
background-size: cover; /* Image covers the entire section */
background-position: center; /* Center the focal point */
background-repeat: no-repeat; /* Prevent tiling */
min-height: 400px;
color: white; /* Ensure text is readable */
text-align: center;
padding: 50px;
}This allows for stunning visual backdrops that enhance the “Creative Ideas” and thematic presentation of content on Tophinhanhdep.com without interfering with the primary document flow.
Downsides of Client-Side Image Resizing and Tophinhanhdep.com’s Solution
While HTML and CSS provide excellent control over how images are displayed, relying solely on these client-side methods for resizing has significant drawbacks. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, which prioritizes “High Resolution” “Photography” and a smooth user experience across a vast “Image Collections,” these downsides necessitate a more robust, server-side approach.
Performance and Quality Implications
The core problem with client-side resizing is that the browser still downloads the original, full-sized image, even if you instruct it to display a much smaller version.
-
Slow Image Rendering: Imagine a user browsing “Stock Photos” on Tophinhanhdep.com. They click on a thumbnail, which is rendered at 200x150 pixels but is actually a 4000x3000 pixel, 5MB image. The browser must download the entire 5MB file before it can even begin to display the 200x150 pixel thumbnail. This dramatically increases page load times and slows down the overall “Image Inspiration & Collections” browsing experience. This delay can be particularly frustrating for users on slower internet connections or mobile devices.
-
Poor Image Quality: Browsers use various algorithms for scaling images, and these algorithms are not always optimized for the best quality, especially when significantly downsizing or upsizing an image. The performance of these algorithms can also vary depending on the user’s hardware and operating system. This often results in noticeably blurry, pixelated, or artifact-ridden images, directly undermining the aesthetic appeal of “Beautiful Photography,” “Digital Art,” or carefully crafted “Visual Design” on Tophinhanhdep.com. The integrity of “High Resolution” images is especially compromised.
-
Bandwidth Wastage: Downloading excessively large images that are then scaled down on the client-side represents a colossal waste of bandwidth. This not only increases hosting costs for Tophinhanhdep.com but also incurs real data costs for users, especially those with limited mobile data plans. Every megabyte unnecessarily transferred adds to the load on both the server and the client.
-
Increased Client-Side Resource Usage: Resizing large images is a computationally intensive task. For users on low-end smartphones, older computers, or devices with limited memory, forcing the browser to perform extensive image scaling can lead to sluggish performance, unresponsive interfaces, and a generally poor user experience. This negates the effort put into curating appealing “Aesthetic” or “Nature” images if the user can’t smoothly interact with the page.
The Power of Server-Side Optimization and Image Tools
To truly overcome these limitations and ensure Tophinhanhdep.com delivers a blazing-fast, high-quality visual experience, a server-side optimization strategy is indispensable. This involves processing images before they are sent to the user’s browser, providing images that are already perfectly sized and optimized for their display context.
Tophinhanhdep.com leverages a suite of “Image Tools” to ensure every pixel is delivered efficiently:
- Image Compressors: These tools reduce the file size of images without perceptible loss of quality. By intelligently removing redundant data, compressors ensure that “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds” load quickly while still looking pristine.
- Image Optimizers: Beyond simple compression, optimizers select the most efficient image format (e.g., converting JPEG to WebP or AVIF for browsers that support them), strip unnecessary metadata, and apply progressive loading techniques. This ensures “Digital Photography” and “Stock Photos” are delivered in their lightest possible form.
- Image Converters: Different contexts might require different image formats. Converters enable Tophinhanhdep.com to seamlessly change image formats as needed, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various devices and browsers.
- AI Upscalers: For those rare instances where an original “Photo Idea” or a piece of “Digital Art” is available in a smaller resolution than required for a specific display on Tophinhanhdep.com, AI Upscalers can intelligently enlarge the image without the typical pixelation. These sophisticated algorithms “guess” missing pixel data, providing a much higher quality enlargement than traditional scaling methods, thereby maintaining the “High Resolution” standard.
Benefits of Tophinhanhdep.com’s Integrated Approach:
By combining precise HTML/CSS display control with robust server-side image optimization, Tophinhanhdep.com achieves:
- Significantly Faster Load Times: Users can instantly view “Wallpapers,” “Thematic Collections,” and “Trending Styles” without waiting for large files to download, dramatically improving satisfaction.
- Reduced Bandwidth Consumption: Lower hosting costs for Tophinhanhdep.com and faster loading for users, especially crucial in mobile-first browsing.
- Consistently High Image Quality: Images are delivered at their ideal dimensions, preserving the fidelity of “Beautiful Photography,” “Nature,” “Abstract,” and “Sad/Emotional” content.
- Enhanced User Experience: A smooth, fast, and visually stunning browsing experience on any device, making “Image Inspiration & Collections” truly engaging.
- Improved SEO: Faster page speeds are a key ranking factor, ensuring Tophinhanhdep.com’s rich visual content is easily discoverable.
In essence, HTML and CSS resizing dictates how an image should appear, but server-side tools and optimization ensure that the correct, most efficient version of that image is delivered to begin with. This holistic strategy is critical for a visually-driven platform like Tophinhanhdep.com.
Conclusion
Effectively managing image size in HTML is a foundational skill for any web developer, especially for platforms rich in visual content such as Tophinhanhdep.com. We’ve explored the direct, yet sometimes limiting, width and height HTML attributes, and delved into the more flexible and powerful realm of CSS for image control. From using inline styles for specific instances to leveraging external stylesheets for scalable “Visual Design,” and mastering properties like max-width, object-fit, and background-size for responsive, perfectly framed visuals, the tools are abundant.
However, the true mastery of image optimization for a visually focused site like Tophinhanhdep.com extends beyond client-side display adjustments. The critical downsides of client-side resizing—slow rendering, poor quality, bandwidth waste, and increased client-side resource usage—underscore the necessity of server-side solutions. Tophinhanhdep.com’s commitment to delivering an exceptional visual experience means not only guiding images to fit their containers perfectly with HTML and CSS but also leveraging sophisticated “Image Tools” such as compressors, optimizers, converters, and AI upscalers. These technologies ensure that every “Nature” scene, “Abstract” design, “Beautiful Photography” piece, and “Stock Photo” from its vast “Image Collections” is delivered efficiently, at optimal quality, and precisely sized for every user and device.
By integrating these frontend display techniques with robust backend optimization, Tophinhanhdep.com exemplifies a comprehensive approach to image management, transforming mere pixels into stunning visual narratives that inspire and captivate. Whether you are crafting “Mood Boards,” curating “Thematic Collections,” or presenting “Trending Styles,” understanding both the art of HTML/CSS resizing and the science of image optimization is key to unlocking the full potential of your visual content.