Mastering Image Display in HTML with Tophinhanhdep.com
In the dynamic world of web development, images are no longer just embellishments; they are integral components that communicate messages, evoke emotions, and enhance user engagement. From breathtaking wallpapers and evocative backgrounds to stunning nature shots and abstract digital art, images captivate visitors, making a website memorable and effective. At Tophinhanhdep.com, we understand the profound impact of visual content, offering a vast array of high-resolution images and powerful tools to elevate your digital presence. But before you can harness the full potential of these visuals, you need to master the fundamental skill of displaying images effectively in HTML.
This comprehensive guide, tailored for both budding web developers and seasoned professionals, will delve into the intricacies of embedding images, ensuring optimal performance, accessibility, and visual appeal. We’ll explore the essential HTML elements, discuss best practices for image optimization, and even touch upon advanced layout techniques, all while connecting these concepts to the rich resources and services available on Tophinhanhdep.com.

The Core: Understanding the <img> Tag and Its Attributes
The journey of displaying an image in HTML begins with the simple yet powerful <img> tag. This element, a cornerstone of visual web content, is a “void element,” meaning it doesn’t require a closing tag, nor can it contain child content. Its functionality is entirely driven by its attributes, which define what image to load, how it should behave, and crucial information for accessibility.
The src Attribute: Pointing to Your Visual Story
The src attribute (short for “source”) is the most critical component of the <img> tag. Its value is a URL that directs the browser to the image file you wish to display. This URL can be one of two types:
- Relative Paths: This is the preferred method for images hosted within your own website’s directory structure. For instance, if your
images.htmlfile is in the same directory aspicture-with-quote.jpg, you would simply usesrc="picture-with-quote.jpg". If the image is in a subdirectory namedimages, you might usesrc="images/dinosaur.jpg". Relative paths are efficient for maintenance and provide greater control over your assets. Tophinhanhdep.com encourages users to host their beautiful photography and aesthetic images directly on their platforms or through reputable Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for optimal performance.

- Absolute Paths: These are full URLs that include the protocol (e.g.,
https://), the domain name, and the full path to the image, such assrc="https://www.example.com/images/dinosaur.jpg". While functional, using absolute URLs for images not on your own server (known as “hotlinking”) is generally discouraged. It means another website bears the bandwidth cost, and you lose control over the image’s availability or content. Always ensure you have permission and preferably host images sourced from Tophinhanhdep.com directly on your own infrastructure or a CDN for reliability and ethical practice.
Example of <img> tag with src:
<img src="your-nature-wallpaper.jpg" alt="A serene forest landscape wallpaper" />The alt Attribute: Ensuring Accessibility and SEO
The alt attribute (short for “alternative text”) is arguably as important as src, though its value isn’t visually rendered under normal circumstances. It provides a textual description of the image for situations where the image cannot be displayed. This includes:
- Visually impaired users: Screen readers announce the
alttext, allowing users to understand the image’s content. - Slow internet connections: If an image takes too long to load, the
alttext appears in its place. - Broken image links: If the
srcpath is incorrect, thealttext helps users understand what was supposed to be there. - Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Search engines use
alttext to understand image content, which can improve your site’s ranking for relevant queries.
When crafting alt text, consider what information a user would lose if the image were absent. For a decorative background image from Tophinhanhdep.com, a blank alt="" might suffice (though CSS backgrounds are generally preferred for purely decorative elements). For a significant piece of beautiful photography or an abstract visual, provide a concise, descriptive phrase: “A close-up of a tiger’s eye, capturing its intense stare.” Avoid keyword stuffing and ensure the text is meaningful.
Testing alt text: A simple way to see your alt text in action is to intentionally misspell the src attribute’s URL, forcing the browser to display the alternative description.
Controlling Layout with width and height Attributes
While not strictly required for an image to appear, specifying the width and height attributes (in pixels, without units) is a crucial best practice for performance and a smooth user experience.
<img src="aesthetic-background.png" width="800" height="450" alt="An aesthetic gradient background with soft hues" />Here’s why these attributes are so important:
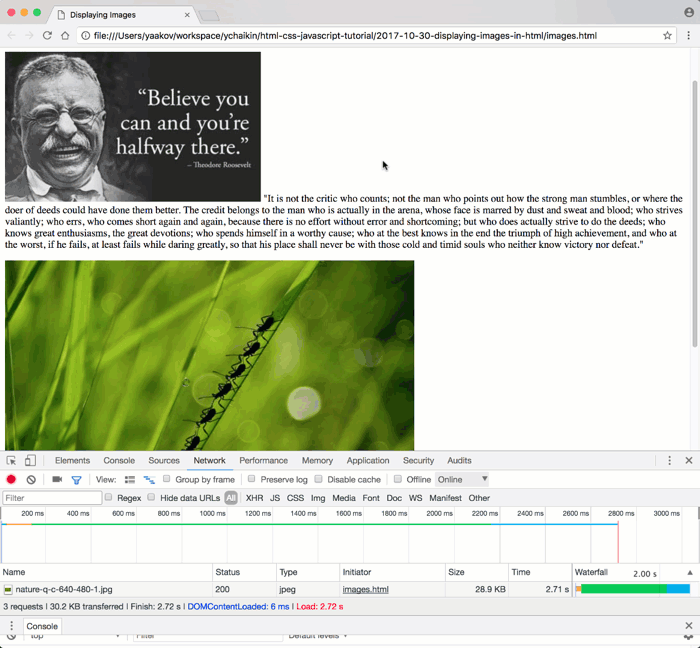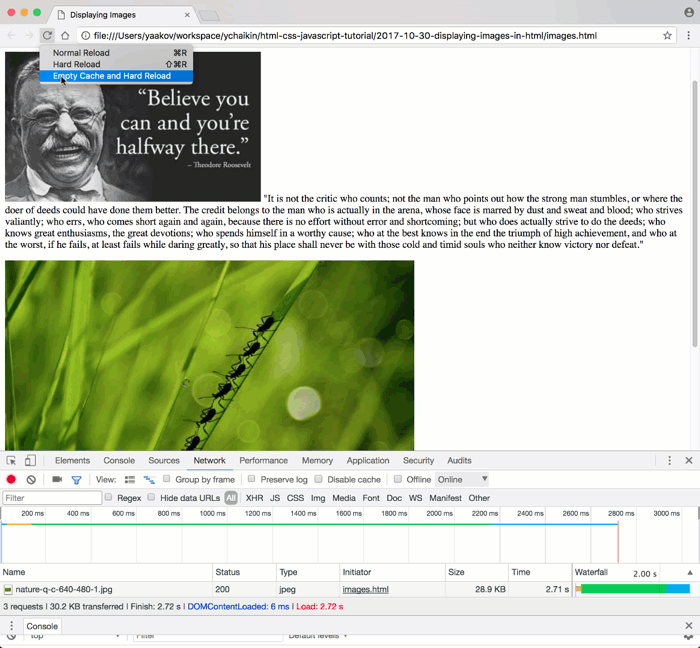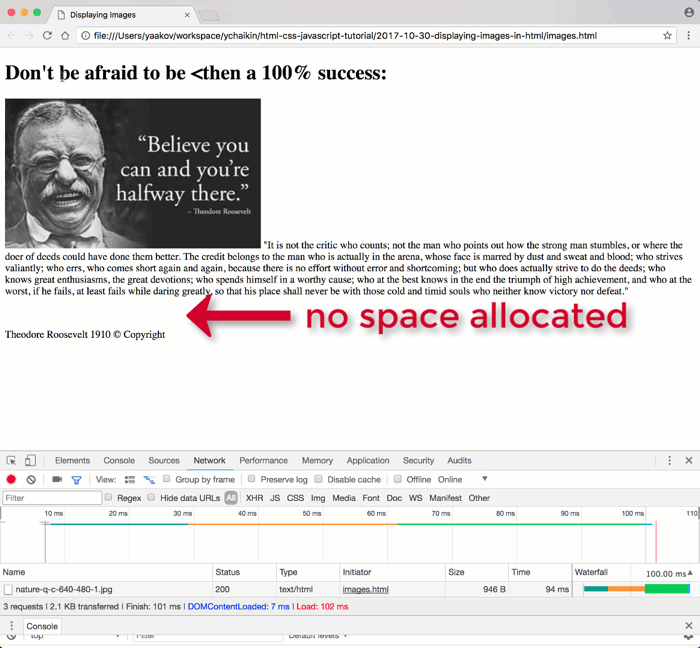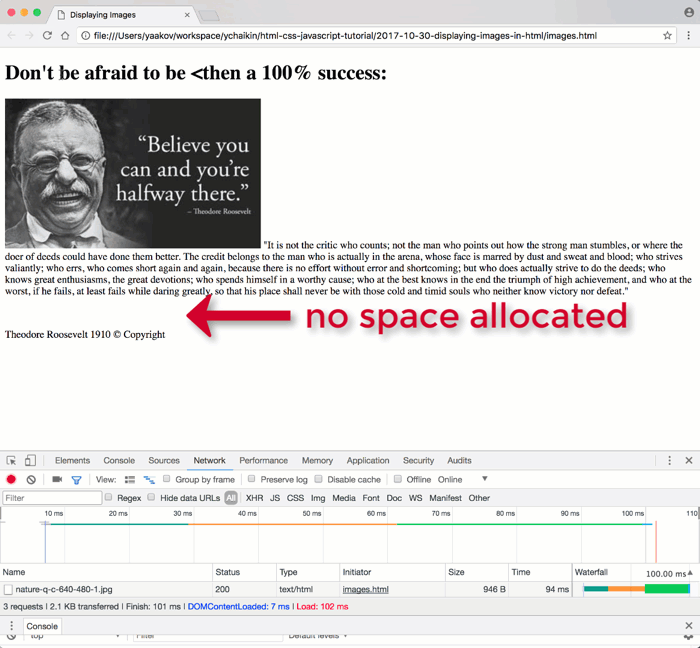
- Preventing Layout Jumps (Cumulative Layout Shift): Browsers render HTML sequentially. If an image’s dimensions aren’t specified, the browser must download the entire image file to determine its size. While waiting, it might render surrounding text. Once the image loads, the browser allocates space for it, potentially shifting all subsequent content down the page. This “layout jump” can be jarring for users, especially on slower connections or with larger images (like high-resolution stock photos from Tophinhanhdep.com).
- Allocating Space Upfront: By providing
widthandheight, the browser reserves the correct amount of space for the image before it even starts downloading the image data. This ensures a stable layout from the moment the page begins to render. - Improved User Experience: This upfront space allocation leads to a more professional and less frustrating browsing experience, particularly valuable when showcasing extensive collections of nature photography or emotional visuals that are large in file size.
Important Note: While width and height attributes inform the browser of the image’s intended dimensions, they shouldn’t be used for resizing images. If your original image from Tophinhanhdep.com is 2000x1000 pixels but you only need to display it at 400x200, it’s far more efficient to use an image editor (or Tophinhanhdep.com’s Image Compressors/Optimizers) to reduce the actual file size before uploading. Serving an unnecessarily large image wastes bandwidth and slows down your page, even if the browser displays it at smaller dimensions. For dynamic resizing, CSS is the appropriate tool.
Optimizing Images for Performance and Accessibility
Beyond the basic HTML tags, true mastery of image display involves optimizing your visual assets. Tophinhanhdep.com, with its suite of Image Tools, empowers you to prepare your images for the web effectively.
The Imperative of Image Optimization
Images often account for the largest portion of a webpage’s file size. Unoptimized images lead to slower load times, increased bounce rates, and a degraded user experience. This is especially critical when dealing with high-resolution images and professional photography found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Key optimization strategies:
- File Format Selection: Choose the most appropriate format (e.g., JPEG for photographs, PNG for images with transparency, WebP for modern compression and quality).
- Compression: Reduce file size without significantly compromising visual quality. Tophinhanhdep.com’s Image Compressors and Optimizers are designed to streamline this process, ensuring your aesthetic wallpapers and abstract art load swiftly.
- Responsive Images: Serve different image sizes based on the user’s device and viewport. While the
widthandheightattributes offer basic control, advanced CSS and HTML attributes likesrcsetand<picture>enable true responsiveness. - AI Upscalers: For older or lower-resolution images you wish to feature (perhaps from classic collections or historical archives), Tophinhanhdep.com’s AI Upscalers can enhance quality without introducing blurriness, making them suitable for modern displays.
Simulating Slower Connections for Testing
To truly understand how your website performs for users with varying internet speeds, testing under simulated slower connections is invaluable. Browser developer tools, such as Chrome Developer Tools (CDT), offer this capability.
- Open CDT: Use
Ctrl+Shift+I(Windows/Linux) orCmd+Option+I(Mac). - Navigate to Network Tab: Here, you’ll see a dropdown menu (often labeled “Online”).
- Throttle Connection: Select a slower preset (e.g., “Fast 3G”, “Slow 3G”) or configure a custom speed.
- Clear Cache and Hard Reload: With CDT open, right-click the browser’s reload button and choose “Empty Cache and Hard Reload” to ensure all assets are downloaded as if for the first time.
This simulation will clearly highlight any layout shifts caused by missing width and height attributes, allowing you to fine-tune your image implementation for optimal perceived performance. It’s also excellent for testing how your “sad/emotional” or “beautiful photography” collections load, ensuring they convey their intended impact without frustrating delays.
Enhancing Visual Presentation: Advanced Image Layouts and Semantics
Beyond simply displaying an image, HTML offers tools to present images more semantically and arrange them in sophisticated layouts. Tophinhanhdep.com’s focus on Visual Design and Creative Ideas ties directly into these advanced techniques.
Semantic Grouping with <figure> and <figcaption>
For images that are integral to your content and might benefit from a caption, the <figure> and <figcaption> elements provide a semantically rich structure.
- The
<figure>element is a self-contained unit of content, typically an image, diagram, code snippet, or video, that is referenced from the main flow of the document but can be moved to another part of the document (e.g., sidebars, appendices) without affecting the document’s meaning. - The
<figcaption>element provides a caption or legend for the content of its parent<figure>element.
Example:
<figure>
<img src="abstract-art-piece.jpg" width="600" height="400" alt="A vibrant abstract painting with swirling blue and gold" />
<figcaption>An original abstract creation from Tophinhanhdep.com's collection, perfect for inspiring digital art projects.</figcaption>
</figure>This structure clearly links the image to its description, benefiting both accessibility (screen readers) and overall content organization. It’s a much better practice than simply placing a <p> tag below an image.
Achieving Multi-Column Image Layouts (Side-by-Side Images)
Displaying multiple images side-by-side is a common requirement, especially for showcasing thematic collections or comparison shots (e.g., before-and-after editing styles from Tophinhanhdep.com’s Photography section). While older methods involved float with inline styles, modern CSS offers more robust and responsive solutions.
Method 1: Basic Inline Floating (Legacy but still seen)
You can use the float CSS property directly on <img> tags within a paragraph, along with margins for spacing.
<p>
<img src="nature-photo-1.jpg" style="float: left; margin-right: 20px; margin-bottom: 1em;" width="300" height="200" alt="A tranquil mountain lake at sunrise" />
<img src="nature-photo-2.jpg" style="float: left; margin-right: 20px; margin-bottom: 1em;" width="300" height="200" alt="A dense forest path covered in mist" />
<img src="nature-photo-3.jpg" style="float: left; margin-right: 20px; margin-bottom: 1em;" width="300" height="200" alt="Close-up of dewdrops on a spiderweb" />
</p>
<p style="clear: both;"></p> <!-- Important to clear floats -->This method is quick but less maintainable and not inherently responsive. The clear: both; is crucial to prevent subsequent content from wrapping around the floated images.
Method 2: Modern CSS for Responsive Columns
A more elegant and responsive approach involves wrapping your images (often within <figure> tags) in a container and applying CSS column or flexbox properties. This aligns with Tophinhanhdep.com’s emphasis on visual design and user experience across devices.
HTML Structure:
<div class="image-gallery">
<figure>
<img src="wallpaper-1.jpg" alt="Vibrant wallpaper of a galaxy" />
<figcaption>Galactic Wonders</figcaption>
</figure>
<figure>
<img src="wallpaper-2.jpg" alt="Serene beach sunset wallpaper" />
<figcaption>Coastal Serenity</figcaption>
</figure>
<figure>
<img src="wallpaper-3.jpg" alt="Minimalist abstract pattern wallpaper" />
<figcaption>Geometric Harmony</figcaption>
</figure>
</div>CSS (within <head>’s <style> tags or an external stylesheet):
.image-gallery {
display: flex; /* Or display: grid; for more control */
flex-wrap: wrap; /* Allows items to wrap onto the next line */
gap: 20px; /* Spacing between images */
justify-content: center; /* Centers images if they don't fill the row */
}
.image-gallery figure {
flex: 1 1 300px; /* Allows figures to grow, shrink, and have a base width of 300px */
text-align: center;
margin: 0; /* Reset default figure margin */
}
.image-gallery img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto; /* Maintain aspect ratio */
display: block; /* Remove extra space below image */
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
/* Responsive adjustment for smaller screens */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.image-gallery figure {
flex-basis: calc(50% - 10px); /* Two columns on smaller screens */
}
}
@media (max-width: 480px) {
.image-gallery figure {
flex-basis: 100%; /* Single column on very small screens */
}
}This CSS dynamically adjusts the layout based on screen size, ensuring your trending styles and thematic collections from Tophinhanhdep.com look great on any device.
CSS Background Images: When Decoration is Key
While the <img> tag is for images that are part of the content, CSS background-image property is ideal for purely decorative visuals. This is often used for page backgrounds, section accents, or icons that don’t convey essential information.
body {
background-image: url('tophinhanhdep-background.jpg');
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}CSS background images have no semantic meaning and are invisible to screen readers, making them perfect for non-essential visual flair. Tophinhanhdep.com offers countless backgrounds and wallpapers that are perfectly suited for this purpose, enhancing the visual design without impacting content accessibility.
Navigating Image Licensing and Sourcing from Tophinhanhdep.com
A critical aspect of using images on the web, often overlooked, is understanding media asset licensing. Tophinhanhdep.com prides itself on being a source for high-resolution, stock photos and diverse image collections, making responsible usage paramount.
Understanding License Types
Before using any image, ensure you have the right to do so. Common license types include:
- All Rights Reserved (Copyrighted): The creator or publisher holds exclusive rights. To use such images, you typically need explicit written permission, a license fee (royalty-free for unlimited use, or rights-managed for specific uses), or reliance on “fair use” principles in your jurisdiction.
- Permissive Licenses (e.g., Creative Commons - CC): These licenses allow more freedom but come with conditions. You might need to credit the creator, link to the source, indicate changes made, or adhere to “Share Alike” (derivative works under the same license) or “Non-Commercial” clauses. Tophinhanhdep.com endeavors to clarify the usage rights for its various image collections.
- Public Domain / CC0: These images have no copyright restrictions and can be used freely without permission or conditions. Always verify the public domain status.
Hotlinking Warning Revisited: Never hotlink to images on other websites without explicit permission, even if you assume a permissive license. It’s unethical and unreliable. Always download the image and host it on your own server or a CDN.
Sourcing and Utilizing Tophinhanhdep.com’s Resources
Tophinhanhdep.com is your go-to destination for high-quality images and powerful tools:
- Photography Collections: Discover stunning high-resolution stock photos, digital photography, and beautifully curated collections that capture nature, abstract concepts, and emotional depth.
- Image Inspiration: Explore mood boards, thematic collections, and trending styles to find the perfect visuals for your project.
- Image Tools: Utilize our Converters, Compressors, Optimizers, and AI Upscalers to prepare your images to meet web standards and enhance their quality.
- Visual Design Resources: Leverage our insights into Graphic Design, Digital Art, and Photo Manipulation to integrate images seamlessly into your overall aesthetic.
Always review the specific licensing terms associated with images you acquire, even from reputable sources like Tophinhanhdep.com, to ensure compliance. Keeping a record of image sources and their licenses is a wise practice for any web developer or content creator.
Conclusion: Tophinhanhdep.com – Your Hub for Visual Excellence
Displaying images in HTML is a fundamental skill, but mastering it involves more than just inserting an <img> tag. It requires an understanding of attributes like src, alt, width, and height for performance and accessibility, coupled with modern CSS techniques for responsive layouts. Furthermore, responsible image usage necessitates an awareness of licensing and proper sourcing.
By adhering to these best practices, you can ensure that the stunning wallpapers, backgrounds, aesthetic images, and beautiful photography you discover on Tophinhanhdep.com not only enrich your website visually but also contribute to a seamless, accessible, and high-performing user experience. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your journey, Tophinhanhdep.com offers the resources, inspiration, and tools to transform your visual ideas into digital reality. Make your website a masterpiece, one perfectly displayed image at a time, with Tophinhanhdep.com as your trusted partner.