How to Master Google Image Search: A Comprehensive Guide for Visual Discovery and Verification
In an increasingly visual world, the ability to find, understand, and utilize images effectively is paramount. While keyword-based searches remain a cornerstone of online exploration, the technique of “how to Google image”—or more accurately, performing a reverse image search—unlocks a powerful new dimension of visual discovery. This guide delves into the mechanics of reverse image search, its diverse applications, and how it complements a rich visual resource like Tophinhanhdep.com, which excels in offering everything from stunning wallpapers and aesthetic backgrounds to high-resolution photography and innovative image tools.

Tophinhanhdep.com serves as a vibrant hub for visual content, encompassing categories like Nature, Abstract, Sad/Emotional, and Beautiful Photography, alongside resources for Digital Art, Graphic Design, and Photo Manipulation. Understanding how to leverage Google’s image search capabilities can profoundly enhance your experience, whether you’re sourcing high-resolution stock photos, verifying an image’s backstory, or seeking inspiration for creative ideas and mood boards.
Unlocking Visual Information: The Core of Reverse Image Search
At its heart, reverse image search allows you to use an image as your search query, rather than descriptive text. Instead of typing “Eiffel Tower at sunset,” you can upload or link to a picture of the Eiffel Tower at sunset and ask Google to find related information. This seemingly simple inversion of the traditional search process opens up a world of possibilities for verification, discovery, and creative exploration.
What is Reverse Image Search? Beyond Keywords

Unlike searching for images using keywords, reverse image search focuses on searching by an image. This distinction is crucial. When you input an image, Google’s sophisticated algorithms analyze its visual characteristics—colors, shapes, textures, objects, and composition—to identify similar images and provide context. This capability is invaluable in many scenarios, from journalistic fact-checking to simply satisfying curiosity about an unknown object or location.
For instance, a photojournalist might use it to track where their work has been published online, while a researcher could uncover the earliest appearance of a particular image to verify its authenticity. Everyday users, too, benefit immensely, whether they’re trying to identify a plant from a holiday photo or seeking more examples of a specific aesthetic for a personal project, much like the diverse “Image Inspiration & Collections” found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Key Benefits and Applications
The utility of reverse image search extends across various domains:
Image Verification and Fact-Checking
In an era rife with digital misinformation, verifying the authenticity and context of an image is more important than ever. Reverse image search provides critical tools for fact-checkers and critical thinkers alike. By tracing an image’s publication history, you can:
- Determine its origin: Find the original source of an image, which is crucial for understanding its context. Was it taken recently, or is it an old photo recirculating?
- Identify manipulation: Detect if an image has been altered or used out of context, helping to expose misleading content.
- Track usage over time: See where and when an image has appeared across the web, revealing how its narrative might have evolved. This is particularly important for images that go viral, as their backstories often get distorted. Tophinhanhdep.com, with its curated “Beautiful Photography” and “High Resolution” sections, understands the importance of image integrity and quality.
Finding Sources and Creators
For copyright holders or simply those curious about the creator of a captivating photograph, reverse image search is a powerful tool. It can help you:
- Locate the original photographer: Pinpoint the individual or organization that first published the image.
- Discover licensing information: Find out if an image is available for reuse or if specific permissions are required, invaluable for those looking for “Stock Photos” for commercial or personal use.
- Trace image attribution: Ensure proper credit is given to artists and photographers, fostering a respectful visual ecosystem.
Discovering Similar Visual Content
Beyond verification, reverse image search excels at visual discovery. If you find an image you love, it can lead you to a treasure trove of related visuals:
- Find higher-resolution versions: Upgrade the quality of an image, perfect for use as “Wallpapers” or “Backgrounds.” Tophinhanhdep.com’s “AI Upscalers” tool can further enhance these discoveries.
- Explore similar styles and themes: If you appreciate an “Aesthetic” image, reverse searching can unearth other photos with a similar mood, color palette, or composition. This is directly aligned with Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Thematic Collections” and “Trending Styles” sections.
- Locate related products or objects: See a piece of furniture or clothing you like in a photo? Reverse search can help you find where to buy it or discover similar items.
Product and Object Identification
This application is incredibly practical for everyday life. Whether you’re traveling, shopping, or just curious, an image can become your query:
- Identify landmarks or locations: Upload a photo of an unknown building or natural wonder to instantly learn its name and history.
- Recognize plants, animals, or art: A quick snap with your phone can reveal the species of a flower or the artist behind a painting.
- Find manuals or information for devices: Take a picture of an appliance, and Google can lead you to its user manual or troubleshooting guides.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Reverse Image Searches
Google has continuously refined its reverse image search functionality, making it accessible and intuitive across various devices. Here’s how you can harness this power.
On Desktop Computers (PC/Mac)
Performing a reverse image search on a desktop or laptop offers the most comprehensive options.
Accessing Google Images
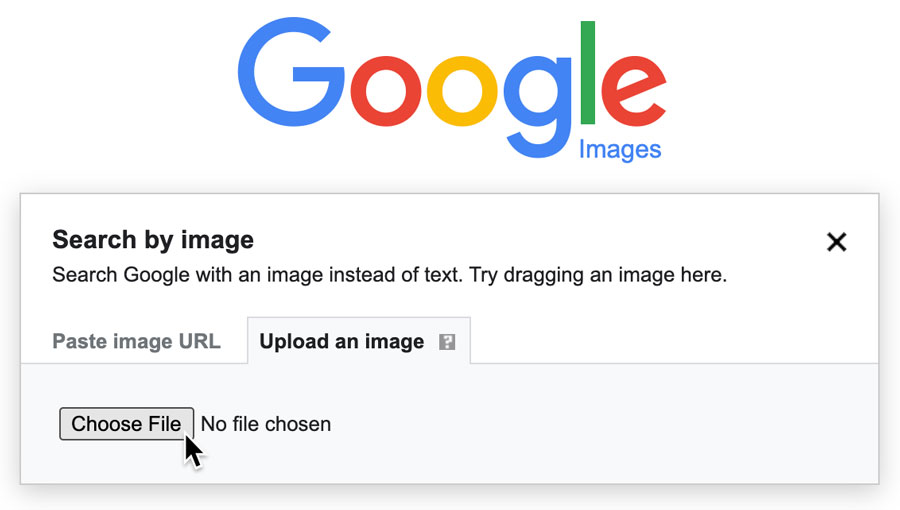
The primary gateway is through images.google.com. Once there, you’ll notice a camera icon within the search bar. This is your key to visual search.
The Camera Icon: Uploading or Pasting
Clicking the camera icon presents two main methods for inputting your image:
- Paste image URL: If the image you want to search is already online, right-click it (or control-click on Mac) and select “Copy Image Address” (wording might vary slightly by browser). Then, paste this URL into the provided text box on images.google.com and click “Search.”
- Upload an image: If the image is saved on your computer, select the “Upload an image” tab, then click “Choose file” to browse your local storage and select the desired picture. The search will typically initiate automatically upon upload.
Right-Click Search: A Convenient Shortcut
For Google Chrome users, the process is even simpler. When you encounter an image on any webpage:
- Right-click on the image.
- Select “Search Google for this image” from the context menu. This bypasses the need to visit images.google.com directly or copy the image URL, making for a seamless experience. Similar functionality can be added to other browsers like Firefox via extensions.
Interpreting Results
The search results page will look familiar, displaying not only visually similar images but also websites where that image or related images appear. You’ll often find:
- Keywords that Google identifies in the image, helping you refine your search if needed.
- Websites that contain the image, allowing you to trace its origins or find more context.
- Visually similar images, useful for discovering more “Aesthetic” or “Nature” themed pictures for Tophinhanhdep.com’s vast collections.
- Image size information, which is helpful if you are looking for higher resolution versions to use as “Wallpapers” or for professional “Digital Photography” projects.
On Mobile Devices (iPhone & Android)
Mobile reverse image search has evolved significantly, offering both browser-based and app-centric solutions.
Using the Google Images Website (via Desktop Site Request)
For both iOS and Android, you can access the desktop version of Google Images on your mobile browser:
- Open your mobile browser (Safari on iOS, Chrome on Android) and go to images.google.com.
- Request the desktop site:
- iOS (Safari): Tap the “Aa” icon in the address bar and select “Request Desktop Website.”
- Android (Chrome): Tap the three dots in the upper-right corner and select “Desktop site.”
- Once the desktop version loads, you will see the familiar camera icon, allowing you to “Upload an image” from your device’s photo library or “Paste image URL.”
Leveraging the Google App / Google Lens
The Google app and Google Lens provide the most integrated and powerful reverse image search experience on mobile:
- Google Lens: This standalone app (or integrated feature within the Google app/Chrome browser on Android) is designed for visual search. It’s particularly adept at identifying live objects using your camera.
- Open the Google app or Chrome.
- Tap the camera icon (representing Google Lens) in the search bar.
- You can then either:
- Point your camera at a live object: Tap the shutter button to analyze what you see. Google Lens can identify everything from plants to products, offering rich information.
- Upload an image from your gallery: Tap the image icon (usually a square with mountains) to select a picture you’ve already saved on your phone.
Specific Steps for iOS
- Google App: Download the Google app from the App Store. Open it, tap the camera icon in the search bar, allow camera/photo access, then either scan a live object or select an image from your Photos library.
- Safari (Desktop Site): Follow the “Desktop Site Request” steps above to upload an image or paste a URL.
Specific Steps for Android
- Google App / Chrome (Google Lens): On Android, Google Lens is often deeply integrated. Open the Google app or Chrome, tap the camera icon, and proceed to scan a live object or upload from your gallery. Permissions for camera and storage access will be prompted if not already granted.
- Chrome (Long-press): When browsing a website in Chrome, you can often long-press on an image to bring up a context menu that includes “Search Google for this Image” or “Search image with Google Lens.”
Optimizing Your Visual Content for Google Images and Tophinhanhdep.com’s Reach
For content creators, photographers, and website owners (like Tophinhanhdep.com), understanding how to optimize images for Google Images is crucial for discoverability. A strong presence in image search results can significantly increase visibility and drive traffic.
Understanding Google’s Image Search Algorithm
Google’s image search algorithm is incredibly sophisticated. When you upload an image, Google analyzes numerous elements:
- Visual characteristics: Colors, shapes, lines, textures, and the overall composition of the image.
- Metadata: Information embedded within the image file itself.
- Contextual cues: The surrounding text on the webpage, the page’s title, and other elements that provide meaning to the image. These factors combine to create a comprehensive understanding of the image, allowing Google to match it accurately with relevant search queries.
Best Practices for Image SEO
To ensure your images, especially the high-quality “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” and “Beautiful Photography” offered on Tophinhanhdep.com, are easily found, consider these optimization strategies:
Enhancing User Experience (UX)
Google prioritizes websites that offer a great user experience. For image content, this means:
- Relevant Context: Ensure images are highly relevant to the surrounding text content. A beautiful nature photo on Tophinhanhdep.com should accompany an article about natural landscapes or be clearly categorized.
- Proper Placement: Place images near relevant text on the page. Critical images, especially for key topics, should be positioned early in the content.
- Avoid Text in Images: While visually appealing, don’t embed crucial information (like titles or calls to action) solely within an image. Use HTML text instead, complemented by descriptive alt text, to ensure accessibility for all users and search engines.
- Overall Page Quality: A high-quality webpage with rich, informative content provides a better context for your images and improves your site’s overall authority, benefiting all your visual assets.
- Mobile Responsiveness: A vast number of image searches occur on mobile devices. Ensuring Tophinhanhdep.com is fully responsive across all screen sizes is vital for retaining users and improving search rankings.
Descriptive File Names and URLs
Google uses file names and URLs to understand image content.
- Logical File Names: Use descriptive, keyword-rich file names (e.g.,
golden-gate-bridge-sunset-high-resolution.jpginstead ofIMG00123.jpg). - Structured URLs: Organize image files in a logical directory structure (e.g.,
tophinhanhdep.com/wallpapers/nature/mountains/mountain-wallpaper.jpg).
Strategic Titles and Descriptions
Google automatically generates titles and snippets for image search results.
- Compelling Titles: Ensure your page titles are clear, descriptive, and accurately reflect the image content.
- Rich Snippets: The description accompanying the image in search results should be informative and enticing, helping users decide whether to click.
Implementing Structured Data
Structured data helps Google understand your images in greater detail, enabling them to appear as rich results with special badges or formats:
- Schema Markup: Apply schema markup (e.g., for products, videos, recipes, or creative works) to your image-containing pages. This can make your images eligible for “rich snippets” in image search, drawing more attention. Tophinhanhdep.com can leverage this for its “Stock Photos,” “Digital Art,” or even for specific “Image Inspiration & Collections” if they relate to products or events.
- Required Properties: Ensure the
imageproperty in your structured data is correctly specified to enable these enhanced displays.
High-Quality Imagery
This is foundational for Tophinhanhdep.com. Images must be not only present but also visually appealing and technically sound:
- Clarity and Resolution: High-resolution, clear, and sharp images are more likely to attract clicks and perform better in search. Tophinhanhdep.com’s focus on “High Resolution” and “Beautiful Photography” directly addresses this.
- Visual Appeal: Engaging and aesthetically pleasing images naturally draw more attention. This ties into the “Aesthetic” and “Nature” categories, showcasing the site’s commitment to visual excellence.
Optimizing Page Load Speed
Images are often large files and can slow down page loading times, negatively impacting UX and SEO.
- Compression: Use image compression tools (like Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Compressors” and “Optimizers”) to reduce file size without significant loss of quality.
- Responsive Images: Serve different image sizes based on the user’s device and screen resolution to ensure faster loading on mobile.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading, so images only load when they are scrolled into view, improving initial page load times.
Effective Alt Text Usage
Alternative text (alt text) is a descriptive tag added to an image that serves multiple purposes:
- Accessibility: It’s read by screen readers for visually impaired users, providing a textual description of the image.
- SEO: Google uses alt text to understand the image’s subject matter, especially when combined with machine vision and surrounding text.
- Context: If an image fails to load, the alt text appears in its place.
- Best Practices: Write concise, descriptive alt text that includes relevant keywords naturally, avoiding keyword stuffing. For a “Sad/Emotional” image on Tophinhanhdep.com, an alt text might be “Close-up of a single tear falling down a cheek, conveying deep sadness.”
Image Sitemaps
An image sitemap is a dedicated XML sitemap that helps Google discover and index images on your site, especially those that might not be found through standard crawling methods (e.g., images loaded via JavaScript).
- Enhanced Discovery: This is particularly beneficial for large image repositories like Tophinhanhdep.com, ensuring all “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” and “Stock Photos” are visible to search engines.
- Multi-Domain Support: Image sitemaps can list image URLs from different domains, which is useful if Tophinhanhdep.com uses a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for image hosting.
Beyond Google: Expanding Your Visual Search Horizons and Tophinhanhdep.com’s Complementary Role
While Google remains the dominant player, other platforms and specialized apps offer unique approaches to reverse image search, which can complement your visual journey on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Alternative Reverse Image Search Engines
Several other search engines provide visual search capabilities, often with slightly different features or result sets:
Bing Visual Search
Microsoft’s Bing offers “Visual Search,” a robust alternative that goes beyond mere image matching. It can help users:
- Backtrack products: Find similar products or where to purchase items seen in images.
- Discover landmarks: Identify famous locations or geographical features.
- Solve problems: In some cases, it can even assist with identifying math problems or text within an image. Bing Visual Search is accessible via the camera icon in Bing’s search bar, both on desktop and mobile.
Dedicated Reverse Image Search Apps
For smartphone users, several third-party apps provide specialized or enhanced reverse image search experiences:
- Reversee (iOS/Android): Often powered by Google Images, Reversee simplifies the mobile reverse search process. Its Pro version may even integrate results from other engines like Bing and Yandex, providing a broader scope of results. It’s user-friendly for uploading saved pictures or pasting image URLs.
- CamFind (iOS/Android): This app focuses on visual search by taking photos with your camera. Powered by CloudSight, it boasts high accuracy in identifying objects, landmarks, and even QR codes. CamFind is ideal for real-time identification and can speak the name of the object it identifies aloud.
These alternatives can sometimes yield different results, providing a more comprehensive visual investigation, especially when combined with the vast resources available on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Tophinhanhdep.com as a Hub for Visual Exploration
Tophinhanhdep.com plays a vital role in the larger visual ecosystem by not only curating diverse “Image Inspiration & Collections” (including Photo Ideas, Mood Boards, Thematic Collections, and Trending Styles) but also by providing essential “Image Tools.”
- Curated Collections: After discovering an image via reverse search, users can turn to Tophinhanhdep.com to find entire collections of similar “Aesthetic,” “Nature,” or “Abstract” images, enriching their creative projects or simply expanding their visual enjoyment.
- Complementary Image Tools: The site’s “Image Tools” – such as “Converters,” “Compressors,” “Optimizers,” and “AI Upscalers” – are invaluable for users who have found an image through reverse search but need to modify it for specific uses. For example, an image found at a low resolution can be upscaled using Tophinhanhdep.com’s AI Upscaler, or a large file can be compressed for web use. The “Image-to-Text” tool can help extract information from discovered images, further enhancing their utility.
- Fueling Visual Design: Tophinhanhdep.com provides a foundational resource for “Visual Design” enthusiasts, graphic designers, and digital artists. High-quality “Stock Photos” and inspiration for “Digital Art” and “Photo Manipulation” can be sourced, enhanced, and creatively manipulated using the site’s offerings, fostering new “Creative Ideas.”
In essence, while Google Images provides the gateway to visual discovery and verification, Tophinhanhdep.com offers the curated content, inspiration, and practical tools to take that discovery further, making it a complete resource for anyone engaged with the world of images.
Conclusion
Mastering how to Google image, or perform a reverse image search, is an indispensable skill in today’s visually-driven digital landscape. It empowers individuals to verify information, uncover origins, discover similar content, and identify unknown elements within photographs. Whether you are a professional researcher, a casual browser, or a creative designer, the ability to effectively search by image expands your understanding and interaction with the digital world.
Combined with a comprehensive platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, which offers a rich array of “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” “Aesthetic” collections, “High Resolution” photography, and essential “Image Tools” for optimization and enhancement, the potential for visual exploration and creative output is limitless. By integrating these powerful search techniques with curated resources, you can transform how you find, use, and appreciate the vast ocean of imagery available online. Embrace the visual journey, and let images guide your search.