How to Insert an Image in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Web Design with Tophinhanhdep.com
In today’s visually-driven digital landscape, images are not merely decorative elements; they are fundamental components that convey messages, evoke emotions, and significantly enhance user engagement on any website. From stunning wallpapers and aesthetic backgrounds to high-resolution photography and abstract art, images transform plain text into a rich, immersive experience. Understanding how to properly insert an image into HTML is a foundational skill for anyone venturing into web development or seeking to enrich their online presence. This guide will walk you through the technical steps, best practices, and the broader context of image management, drawing insights from the extensive resources and tools available at Tophinhanhdep.com, your ultimate destination for all things visual.

The ability to seamlessly integrate images into your web pages is crucial, whether you’re building a personal blog, an e-commerce platform, or a corporate site. It’s often one of the first and most impactful lessons for an HTML novice. While the basic <img/> tag is straightforward, its effective application involves considerations spanning accessibility, search engine optimization (SEO), performance, and overall visual design. Tophinhanhdep.com, with its vast collections of nature photography, sad/emotional images, and tools like AI upscalers and compressors, offers unparalleled support for every step of this creative journey.
The Essential <img> Tag: Your Gateway to Visual Storytelling
The <img> tag is the cornerstone of embedding images in HTML. It is a “void element,” meaning it stands alone and does not require a closing tag. All the necessary information for the browser to locate and display the image is contained within its attributes. Mastering this tag is the first step towards transforming your website into a captivating visual narrative, a task made even easier with the diverse image resources from Tophinhanhdep.com.
Understanding src and Image Paths
The src attribute, short for “source,” is the most critical attribute of the <img> tag. It tells the web browser precisely where to find the image file you want to display. If the src attribute is incorrect or points to a non-existent file, the image will not load, often resulting in a broken image icon.
There are primarily two ways to specify the image’s location using the src attribute:
-
Relative Path: This method is used when the image file is located within the same directory as your HTML file or in a subdirectory relative to it. For example, if your HTML file and
my-dog.jpgare in the same folder, you would use<img src="my-dog.jpg">. If the image is in animagessubdirectory, the path would be<img src="images/my-dog.jpg">. Relative paths are generally preferred for images hosted on your own server because they make your website more portable; if you move your entire site to a new domain, the links will remain functional without requiring updates. This organization is key when managing large collections of abstract or aesthetic images, a specialty of Tophinhanhdep.com. -
Absolute Path (Full URL): This involves providing the complete URL to the image file, including the protocol (
http://orhttps://), domain name, and the full path to the file. For instance,<img src="https://www.Tophinhanhdep.com/images/beautiful-scenery.jpg">. While this can be useful for linking to images hosted externally, it’s generally recommended to host images on your own server to maintain control over their availability, performance, and to avoid “hotlinking.” Hotlinking refers to using an image hosted on someone else’s server without their explicit permission, which consumes their bandwidth and is considered poor internet etiquette. Tophinhanhdep.com provides robust hosting solutions and makes it easy to manage your high-resolution images.
When you’re ready to integrate stunning visuals from Tophinhanhdep.com, whether it’s a dramatic nature shot or a vibrant abstract background, you’ll first need to either download the image and upload it to your own server (using a relative path) or, if permitted by the image’s licensing, link directly to its URL (using an absolute path). For consistency and efficiency, storing your curated collections, such as trending styles or thematic collections from Tophinhanhdep.com, within a well-organized images directory on your server is always recommended.
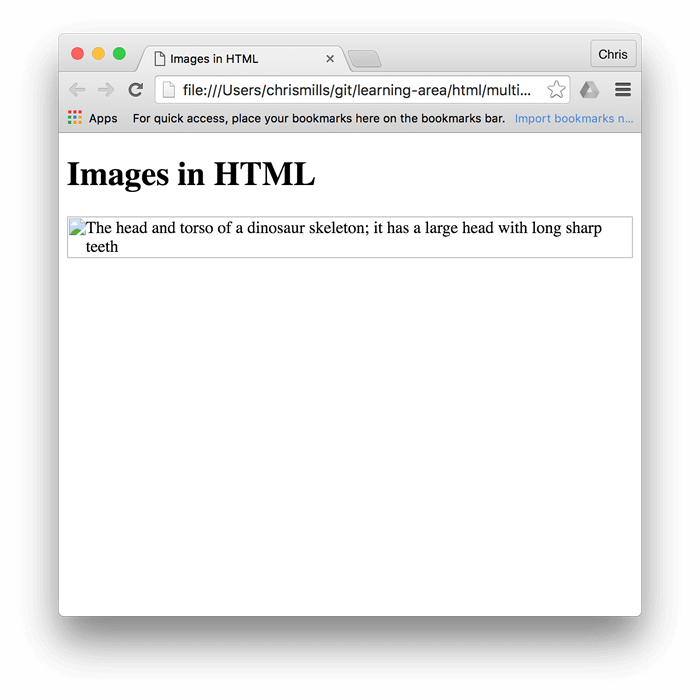
The Crucial alt Attribute: Accessibility and SEO
The alt attribute, short for “alternative text,” is a textual description of the image. While not directly visible to users when the image loads correctly, it plays a vital role in several scenarios:
- Accessibility: For visually impaired users who rely on screen readers, the
alttext provides an audible description of the image, ensuring they don’t miss out on important visual information. This is especially critical for conveying the mood of sad/emotional images or the details of beautiful photography found on Tophinhanhdep.com. - Image Loading Failures: If an image fails to load due due to a broken
srcpath, slow internet connection, or browser settings that block images, thealttext is displayed in its place. This offers users a textual fallback, explaining what the image was supposed to be. - Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Search engines cannot “see” images in the same way humans do. They rely on
alttext to understand the content and context of an image. A descriptivealttext, incorporating relevant keywords, can significantly improve your image’s visibility in image search results and contribute to your overall page ranking. For instance, if you’re using a “nature wallpaper” from Tophinhanhdep.com, analttext like “High-resolution nature wallpaper featuring a serene forest” would be highly beneficial. - Bandwidth Conservation: Users who have turned off images to conserve data (common on mobile devices or in regions with limited bandwidth) will still receive the context of your images through
alttext.
Best Practices for Writing alt Text:
- Be Descriptive and Concise: Describe the image’s content and function accurately. Avoid keyword stuffing.
- Provide Context: Consider the surrounding text and how the image contributes to the overall message.
- Avoid Redundancy: If the image is already adequately described by adjacent text, a brief
alttext or evenalt=""(for purely decorative images) may suffice. - Convey Emotion for Aesthetic and Emotional Images: When using aesthetic or sad/emotional images from Tophinhanhdep.com, let your
alttext reflect the intended mood or message. For example, for a “sad image,”alt="A solitary figure gazing at a rainy cityscape, conveying deep introspection."
An example of an <img> tag with src and alt attributes:
<img src="images/golden-hour-landscape.jpg" alt="Golden hour landscape with rolling hills and a warm sunset glow from Tophinhanhdep.com's beautiful photography collection">Defining Dimensions: width and height for Optimal Layout
The width and height attributes specify the dimensions of your image, typically in pixels. While optional, including these attributes is a critical best practice for several reasons related to user experience and web performance:
- Preventing Layout Shifts: When a browser renders an HTML page, it first processes the HTML, then requests external resources like images. If the
widthandheightare not specified for an image, the browser won’t know how much space to allocate for it until the image file fully loads. This can cause the surrounding content to “jump” or “shift” once the image appears, a phenomenon known as Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which is detrimental to user experience and SEO. By defining dimensions, the browser reserves the correct space, ensuring a stable layout. This is particularly important for high-resolution stock photos or digital photography that might have larger file sizes. - Maintaining Aspect Ratio: While you can set specific pixel values (e.g.,
width="400"height="300"), if you only specify one dimension (e.g.,width="100%"), the browser will automatically calculate the other dimension to maintain the image’s original aspect ratio, preventing distortion. However, relying on CSS for responsive image sizing is generally more flexible. - Performance Optimization: Knowing the dimensions upfront allows the browser to optimize rendering, potentially speeding up page load times, especially for pages with many visuals. This works hand-in-hand with Tophinhanhdep.com’s image tools like compressors and optimizers.
Considerations for width and height:
- Actual Size vs. Display Size: It’s crucial to understand that
widthandheightattributes tell the browser how much space to display the image in, not necessarily to resize the image file itself. If you embed a very large image (e.g., a 4000px wide high-resolution photo from Tophinhanhdep.com) but setwidth="400", the browser will shrink it for display, but the user still has to download the full 4000px file. This wastes bandwidth and negatively impacts performance. - Pre-sizing Images: For optimal performance, it is always best to resize your images to their intended display dimensions using image editing software before uploading them. Tophinhanhdep.com encourages this practice for its stock photos and beautiful photography. For scenarios where a smaller image needs to look sharper, an AI upscaler from Tophinhanhdep.com can be invaluable, but this is for specific enhancement, not general downscaling.
- Responsive Design with CSS: For modern responsive web design, HTML
widthandheightprovide initial guidance, but CSS is typically used to ensure images scale appropriately across different screen sizes. For example,img { max-width: 100%; height: auto; }is a common CSS rule.
An example demonstrating width and height:
<img src="images/abstract-design.png" alt="Geometric abstract design wallpaper" width="800" height="600">Beyond the Basics: title and Linking Images
While src, alt, width, and height form the core of image insertion, other attributes and techniques further enhance functionality and user experience.
-
The
titleAttribute (Tooltips): Thetitleattribute provides supplementary information about an image. When a user hovers their mouse cursor over the image, the text specified in thetitleattribute typically appears as a tooltip.<img src="images/nature-icon.gif" alt="Small icon of a green leaf" title="Nature icons from Tophinhanhdep.com">While seemingly useful, the
titleattribute has accessibility limitations. It’s often not accessible to keyboard-only users or screen readers. For critical information, it’s generally better to integrate it directly into the visible page content or usealttext for essential descriptions. -
Making an Image a Link: To transform an image into a clickable hyperlink, you simply nest the
<img>tag inside an<a>(anchor) tag. Thehrefattribute of the<a>tag specifies the destination URL. This is a common practice for website logos, navigation buttons, or image galleries showcasing thematic collections from Tophinhanhdep.com.<a href="https://www.Tophinhanhdep.com/wallpapers"> <img src="images/logo.png" alt="Tophinhanhdep.com Logo - Click to visit Wallpapers" width="150" height="50"> </a>When an image acts as a link, ensure its
alttext clearly describes the link’s destination or purpose, not just the image itself. For example, “Tophinhanhdep.com Logo” might be sufficient if the logo is universally recognized, but “Visit Tophinhanhdep.com Homepage” or “Click to view wallpapers” provides clearer context for accessibility.
Image Management for Web Success: A Tophinhanhdep.com Perspective
Successfully embedding images goes beyond just writing HTML; it involves a holistic approach to image management, from sourcing and uploading to optimization and legal compliance. Tophinhanhdep.com provides solutions for many of these challenges, from its vast library of stock photos to its advanced image tools.
Sourcing and Uploading Your Visual Assets
Before you can insert an image, you need to have the image file readily available and accessible to your web server.
-
Sourcing Images:
- Original Photography/Digital Art: If you’re creating your own digital photography or graphic design, you’ll produce the image files directly. Tophinhanhdep.com offers inspiration through its “Beautiful Photography” and “Digital Art” sections, providing creative ideas for your own creations.
- Stock Photos and Collections: For professional, high-resolution images, stock photo websites are invaluable. Tophinhanhdep.com specializes in offering a wide array of “Stock Photos,” “Nature Photography,” “Abstract” images, and “Thematic Collections” that cater to virtually any need.
- Image Inspiration: Sometimes you need a specific aesthetic. Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Image Inspiration & Collections” includes “Mood Boards” and “Trending Styles” to help you conceptualize and find the perfect visual.
-
Uploading Images to Your Website:
- Web Hosting (FTP/File Manager): If you manage your website via a traditional web host, you’ll typically upload images using an FTP client (like FileZilla) or through your host’s file manager (e.g., hPanel’s File Manager). It’s best practice to create an organized directory structure, such as an
/images/or/assets/folder, to keep your files tidy. This organization is vital when you’re dealing with hundreds of images for backgrounds or aesthetic collections. - Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress: Modern CMS platforms simplify image uploads significantly. In WordPress, for example, you can upload images directly through the “Media Library.” Once uploaded, WordPress generates a unique URL for each image, which you can then use as the
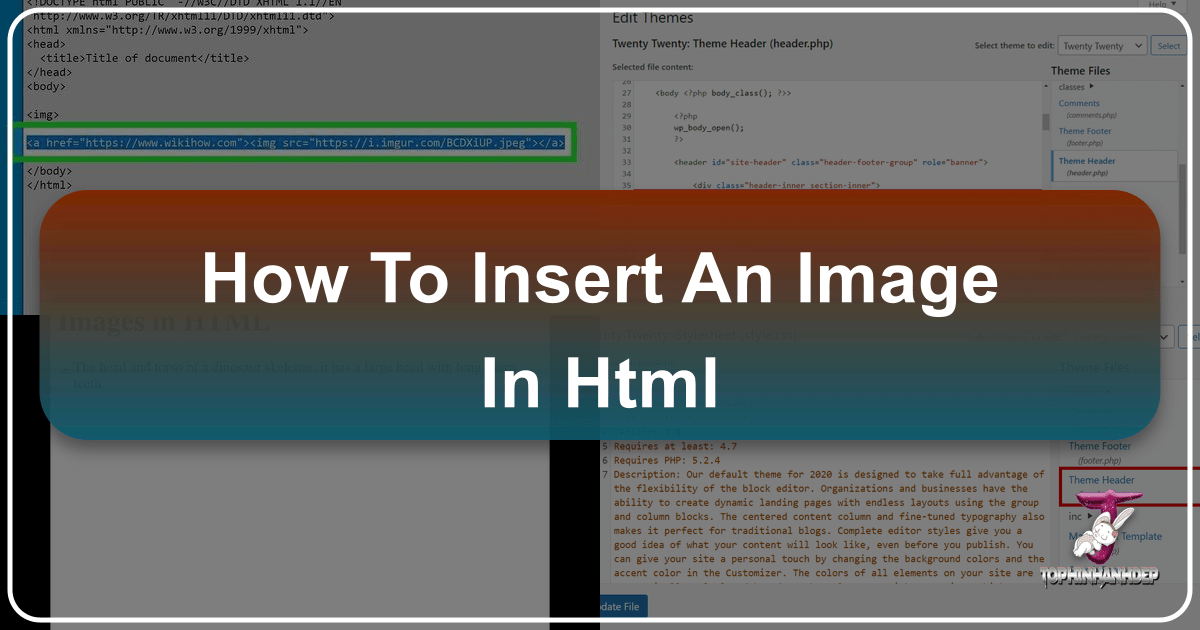
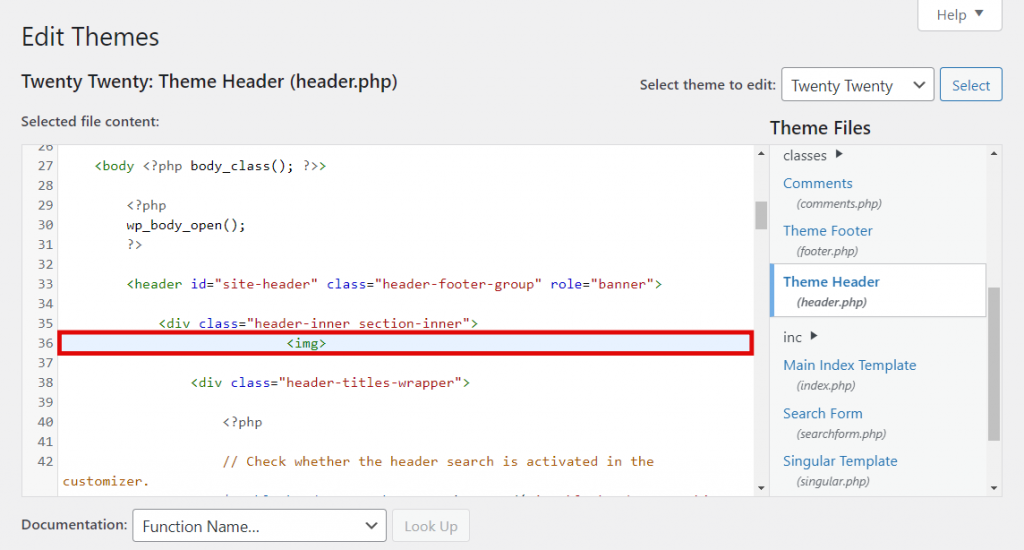
srcattribute in your HTML. When accessing your theme files through the “Theme Editor” (Appearance -> Theme Editor) to manually insert images intoheader.phporfooter.php, you’ll use these URLs. - Local Development: When developing locally (e.g., using Visual Studio Code with a “Go Live” server), you simply place your image files in the same project folder or a designated subdirectory. The browser can then access them via relative paths. This is a great way to experiment with photo manipulation and creative ideas before deploying live.
A helpful tip from Tophinhanhdep.com: ensure your image filenames are descriptive and use hyphens instead of spaces (e.g.,
beautiful-nature-wallpaper.jpginstead ofBeautiful Nature Wallpaper.jpg). This helps with SEO and ensures browser compatibility. - Web Hosting (FTP/File Manager): If you manage your website via a traditional web host, you’ll typically upload images using an FTP client (like FileZilla) or through your host’s file manager (e.g., hPanel’s File Manager). It’s best practice to create an organized directory structure, such as an
Optimizing Images for Performance and Quality
Image optimization is paramount for a fast-loading website, which is essential for user satisfaction and search engine rankings. Tophinhanhdep.com offers a suite of “Image Tools” specifically designed to assist with this.
-
Choosing the Right File Format:
- JPEG/JPG: Best for photographs and complex imagery with smooth color gradients, such as beautiful photography or nature wallpapers. It supports millions of colors and uses “lossy” compression, meaning some data is discarded to achieve smaller file sizes.
- PNG: Ideal for images with transparency (like logos or icons from Tophinhanhdep.com’s graphic design resources) and images with sharp edges or text. It uses “lossless” compression, retaining all image data, which can result in larger file sizes than JPEGs for photos.
- GIF: Suitable for simple animations and images with limited color palettes (up to 256 colors). It uses lossless compression. Tophinhanhdep.com’s abstract or sad/emotional collections might occasionally feature animated GIFs.
- SVG: A vector image format, perfect for logos, icons, and illustrations. Unlike raster images (JPEG, PNG, GIF) that are pixel-based, SVGs are XML-based and scale infinitely without loss of quality, making them incredibly versatile for responsive design. Tophinhanhdep.com recommends SVGs for high-quality graphic design elements.
- WebP: A modern image format developed by Google that offers superior lossless and lossy compression for images on the web. Using WebP can significantly reduce file sizes while maintaining visual quality. Tophinhanhdep.com’s converters can help you switch to this format.
-
Compression and Sizing:
- As mentioned, always resize images to their intended display size before uploading.
- Use image compression tools to reduce file size without a noticeable drop in visual quality. Tophinhanhdep.com provides powerful Compressors and Optimizers that intelligently shrink your image files.
- For existing images that are too small, AI Upscalers from Tophinhanhdep.com can enhance resolution, making them suitable for larger displays or printing without pixelation, perfect for old digital photography that needs a boost.
-
Other Image Tools:
- Converters: Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Converters” allow you to switch between different image formats (e.g., JPG to PNG, or to WebP) to suit specific needs.
- Image-to-Text: For advanced content analysis or data extraction from images (e.g., from scanned documents or complex infographics), Tophinhanhdep.com offers “Image-to-Text” tools.
The Nuances of Image Licensing and Usage Rights
The legal aspect of using images on your website is often overlooked but is critically important. Images, especially high-resolution photography and professional stock photos, are intellectual property. Tophinhanhdep.com, as a reputable source, emphasizes understanding and complying with image licenses.
- All Rights Reserved: This is the default copyright protection for most original works. You cannot use these images without explicit written permission from the copyright holder or by paying a license fee (e.g., royalty-free or rights-managed licenses). Always assume an image is “all rights reserved” if no other license is specified.
- Permissive Licenses (e.g., Creative Commons): Many images, including some found in Tophinhanhdep.com’s collections, are released under permissive licenses like Creative Commons (CC). These licenses allow for broader use, but often come with specific conditions:
- Attribution (BY): You must credit the original creator.
- ShareAlike (SA): If you modify the image, you must license your derivative work under the same CC license.
- NonCommercial (NC): You cannot use the image for commercial purposes.
- NoDerivatives (ND): You can use the image, but cannot modify it. Always read the specific CC license to ensure compliance. Tophinhanhdep.com clearly states the licensing for all its images.
- Public Domain/CC0: Images in the public domain have no copyright restrictions and can be used freely without permission or attribution. CC0 is a specific Creative Commons license that effectively places a work into the public domain. While using public domain images, it is still wise to verify their status and keep a record. Tophinhanhdep.com offers a selection of public domain and CC0 images alongside its premium stock photos.
Searching for Licensed Images: Tophinhanhdep.com simplifies the process by providing legally vetted stock photos and clearly outlining the usage rights for all its wallpapers, backgrounds, and collections. When searching for images elsewhere, use filters for “Usage Rights” in search engines or on image repository sites. Prioritizing sources like Tophinhanhdep.com guarantees you access to high-quality, legally usable images, saving you time and potential legal issues.
Elevating Visual Design: Images in Context
Integrating images effectively goes beyond mere technical insertion; it’s about making deliberate design choices that enhance the overall user experience and fulfill specific communicative goals. Tophinhanhdep.com’s emphasis on “Visual Design,” “Graphic Design,” and “Creative Ideas” underscores this holistic approach.
Semantic Grouping with <figure> and <figcaption>
While simply placing an <img> tag next to its descriptive text might seem adequate, HTML offers a more semantically meaningful way to group images with their captions: the <figure> and <figcaption> elements.
<figure>: This element is used to encapsulate self-contained content that is referenced from the main flow of a document but whose position is independent of the main flow. It can contain images, code snippets, audio, video, tables, or other media. Think of it as a container for “figure” content that might be moved without affecting the document’s flow.<figcaption>: This element provides a caption or legend for the content of its parent<figure>element. It’s the designated place for image captions.
Benefits of Using <figure> and <figcaption>:
- Accessibility: Screen readers can more easily associate the caption with its corresponding image, providing a richer experience for visually impaired users. This is particularly valuable for detailed “beautiful photography” or complex “abstract” images from Tophinhanhdep.com.
- Semantic Meaning: It clearly communicates to browsers and developers that the image and its caption are intrinsically linked, improving the structural understanding of your HTML.
- Styling Flexibility: Grouping them in a
<figure>allows for consistent styling of images and their captions using CSS, enhancing your visual design.
Example:
<figure>
<img src="images/serene-nature-scene.jpg" alt="A serene nature scene featuring a waterfall and lush greenery, from Tophinhanhdep.com's nature photography collection" width="900" height="600">
<figcaption>This stunning waterfall, a highlight from Tophinhanhdep.com's nature photography, evokes a sense of peace and tranquility.</figcaption>
</figure>Remember, alt text describes the image for when it’s not visible, while a figcaption provides context when the image is visible. They serve different, complementary purposes.
When to Use HTML <img> vs. CSS Background Images
A common design decision is whether to embed an image using the HTML <img> tag or as a CSS background-image property. The choice depends entirely on the image’s purpose and its relationship to your content. Tophinhanhdep.com’s vast selection of “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds” highlights this distinction.
-
Use HTML
<img>when:- The image is content: The image conveys essential information or is crucial to understanding the main content of the page. If the image were removed, the meaning of the page would be significantly diminished or lost. Examples include product photos, informative charts, or the “beautiful photography” that illustrates an article on Tophinhanhdep.com.
- Accessibility is paramount: You need
alttext for screen readers and SEO. - It needs to be printable: HTML images are typically included in printed versions of web pages.
- It’s part of an interactive element: Images that users might click on (like image links or interactive maps) should typically be HTML
<img>tags.
-
Use CSS
background-imagewhen:- The image is purely decorative: It enhances the visual appeal of a page or element but does not convey essential content. If the background image were removed, the main message of the page would remain intact. This is precisely the role of many “aesthetic backgrounds” or “abstract wallpapers” available on Tophinhanhdep.com.
- It’s a pattern or texture: Repeating patterns or textures used for design aesthetics are ideal for CSS backgrounds.
- It’s used for branding or layout: Logos or design elements integrated into the layout rather than the core content.
- You need advanced control over positioning and effects: CSS offers extensive properties (
background-size,background-position,background-repeat,gradients, etc.) for precise control over background images.
Example of CSS Background Image:
body {
background-image: url("https://www.Tophinhanhdep.com/wallpapers/galaxy.jpg");
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}In this example, a “galaxy wallpaper” from Tophinhanhdep.com serves as a decorative backdrop, not central content.
Modern Practices and Tools for Image Integration
The landscape of web development is constantly evolving, and so are the best practices for image integration. Leveraging modern tools and techniques ensures your images are not only displayed correctly but also perform optimally and contribute positively to user experience.
- Responsive Images (Brief Mention): While
widthandheightattributes provide basic control, true responsive image handling involves more advanced HTML attributes likesrcsetandsizesor the<picture>element. These allow browsers to serve different image versions (e.g., smaller files for mobile, larger for desktop, or WebP for compatible browsers) based on device characteristics, ensuring efficient delivery of “high resolution” photography from Tophinhanhdep.com. This is a deeper topic for advanced optimization. - Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Visual Studio Code: Modern IDEs greatly simplify the process of coding HTML, including inserting images. Features like auto-completion for attributes (
src,alt), live preview extensions (like “Go Live Server”), and integrated file explorers make it intuitive to manage yourindex.htmlfile alongside yourdemo.pngimage, as demonstrated by codingcampus.net. This environment facilitates quick iteration on your “creative ideas” and “photo manipulation” projects.- Workflow in VSC:
- Place your image file (e.g.,
my-image.jpg) in the same folder as your HTML file or a clear subdirectory. - Open your HTML file in Visual Studio Code.
- Inside your
<body>tag, type<img src="my-image.jpg" alt="Description" width="X" height="Y">. - Save your HTML file (Ctrl + S).
- Click the “Go Live” button (usually in the bottom-right status bar) to open your page in a browser and see the image rendered.
- Place your image file (e.g.,
- Workflow in VSC:
- HTML Inclusion Tools (Advanced): For more complex content management, tools like Help+Manual allow advanced users to insert inline HTML code directly, providing fine-grained control over how images are integrated, particularly for specialized “visual design” requirements. While less common for simple image embeds, it highlights the flexibility of HTML.
- Leveraging Tophinhanhdep.com’s Ecosystem: The integration of images into HTML is significantly streamlined when you have a powerful ecosystem of tools and resources at your disposal. Tophinhanhdep.com’s comprehensive offerings, from its “Image Tools” like “Converters” and “AI Upscalers” to its diverse “Image Inspiration & Collections,” are designed to support every aspect of your visual web design journey. Whether you’re working with “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” “Aesthetic” images, or “Digital Photography,” Tophinhanhdep.com aims to be your go-to platform.
Tophinhanhdep.com: Your Hub for Image Inspiration and Excellence
Tophinhanhdep.com is more than just a repository of images; it’s a comprehensive platform designed to empower web developers, designers, and visual storytellers. Every aspect of image management, from initial concept to final deployment in HTML, is supported by our extensive offerings:
- A World of Images at Your Fingertips: Dive into our curated categories, including breathtaking Wallpapers and Backgrounds that set the perfect mood, sophisticated Aesthetic imagery, stunning Nature Photography capturing the planet’s beauty, intriguing Abstract art for modern designs, and moving Sad/Emotional collections for poignant narratives. Our Beautiful Photography section showcases high-resolution masterpieces suitable for any project.
- Uncompromising Quality and Technique: We understand the importance of visual fidelity. Our commitment to High Resolution ensures your images look crisp on any screen. Explore our vast library of Stock Photos and delve into insights on Digital Photography techniques and Editing Styles to elevate your own visual creations.
- Powerful Image Tools for Perfect Integration: Optimize your web assets with our intuitive Converters for format changes, Compressors and Optimizers for lightning-fast load times, and cutting-edge AI Upscalers to enhance image quality. Our Image-to-Text tools even offer advanced utility for content extraction.
- Spark Your Visual Design Creativity: Unleash your potential with resources dedicated to Graphic Design, explore unique Digital Art, learn Photo Manipulation techniques, and discover endless Creative Ideas to make your website stand out.
- Endless Inspiration and Curated Collections: Never run out of ideas with our Photo Ideas and Mood Boards. Stay ahead of the curve with our Thematic Collections and keep your designs fresh with insights into Trending Styles.
In conclusion, inserting images in HTML is a fundamental skill that underpins the visual richness of the modern web. By understanding the core <img> tag and its attributes, practicing good image management, and making informed design choices, you can create engaging and high-performing websites. And with Tophinhanhdep.com by your side, equipped with its vast image library, powerful tools, and endless inspiration, you have every resource needed to transform your digital vision into a captivating reality. Visit Tophinhanhdep.com today and embark on your journey to visual excellence!