How to Make Images Smaller in HTML for Optimal Web Performance and Visual Design
In the vast and visually-driven landscape of the internet, images are paramount. They capture attention, convey emotion, and provide context, making a website truly engaging. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, which specializes in an extensive array of visual content—from stunning Wallpapers and Backgrounds to Aesthetic, Nature, Abstract, Sad/Emotional, and Beautiful Photography—the efficient management and display of these images are not merely a technical detail but a cornerstone of user experience and overall success. One of the most critical aspects of image management for web platforms is sizing. Displaying images at their appropriate dimensions directly impacts page load times, bandwidth consumption, and the overall aesthetic appeal of your Visual Design.

While it might seem straightforward, “making an image smaller in HTML” goes far beyond simply altering a couple of numerical values. It encompasses a spectrum of techniques, from direct HTML attributes and CSS styling to sophisticated server-side optimization and dynamic image delivery. This comprehensive guide will delve into these methods, highlighting best practices and showing how they integrate with the philosophy of Tophinhanhdep.com to deliver high-quality visual content efficiently. We’ll explore how to manipulate image dimensions effectively, understanding the nuances of client-side versus server-side resizing, and connecting these technicalities to the broader goals of Photography and Image Tools to enhance your website’s visual integrity and performance.
HTML & CSS Fundamentals: Resizing Images for Web Layouts
The journey of making an image smaller in HTML typically begins with the foundational tools provided by HTML and CSS. These client-side methods allow developers to dictate how an image should appear within the browser, influencing its dimensions relative to the surrounding content. While easy to implement, it’s crucial to understand their implications, especially when dealing with a rich image library like that of Tophinhanhdep.com.

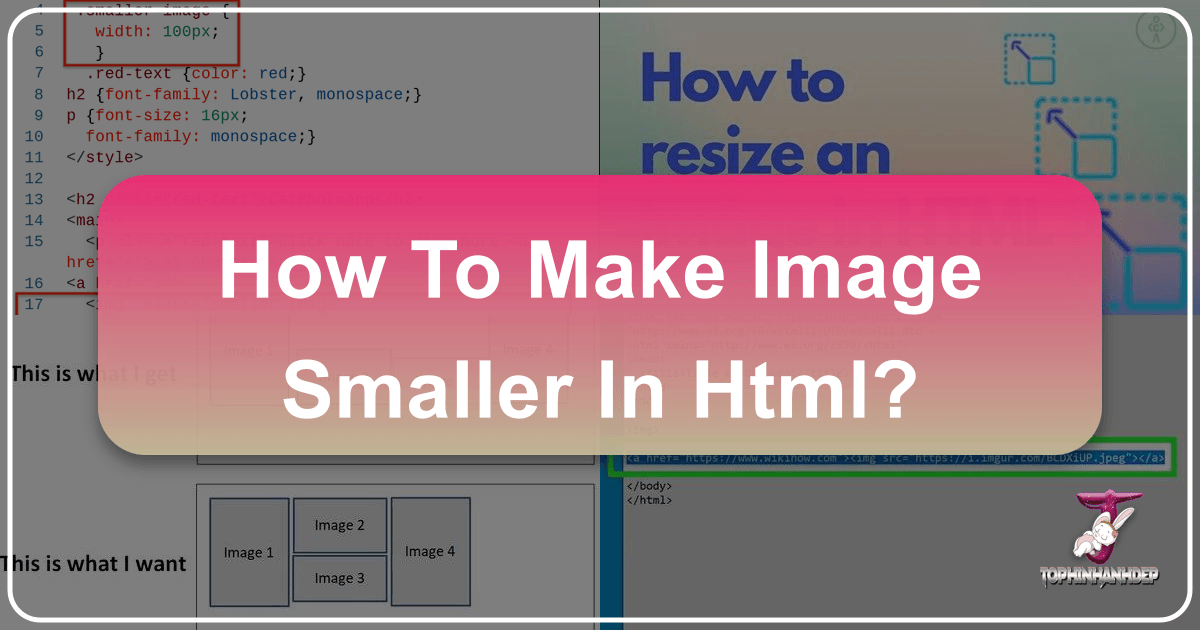
Using width and height Attributes in <img>
The most direct way to specify an image’s size in HTML is by using the width and height attributes directly within the <img> tag. These attributes take values in pixels (px) in HTML5, defining the exact dimensions the browser should render the image.
For example, if Tophinhanhdep.com wanted to display a smaller version of a beautiful landscape photograph, the HTML might look like this:
<img src="landscape-wallpaper.jpg" alt="A serene landscape wallpaper from Tophinhanhdep.com" width="400" height="300">Here, src points to the image file (e.g., “landscape-wallpaper.jpg”), and alt provides descriptive text for accessibility, crucial for both user experience and SEO, particularly for a content-rich site. The width="400" and height="300" attributes instruct the browser to display the image at 400 pixels wide and 300 pixels high.
Pros:
- Simplicity: Extremely easy to implement and understand.
- Layout Preservation: When
widthandheightare explicitly set, the browser knows the exact space required for the image before it even loads. This prevents layout shifts (or “jumps”) that can occur if the browser has to reflow content once the image dimensions are determined, leading to a smoother user experience, especially for users browsing Tophinhanhdep.com’s high-resolution images.
Cons:
- Fixed Size: These attributes define a fixed size, which isn’t ideal for responsive web design where layouts adapt to different screen sizes. A beautiful photograph that looks perfect on a desktop might appear too large or too small on a mobile device.
- Image Quality and Bandwidth Waste: This is the most significant drawback. Even if you set
width="400"for an image that is originally 2000 pixels wide, the browser still downloads the full 2000-pixel image. It then scales it down on the client-side. This results in wasted bandwidth (the user downloads more data than needed) and unnecessary processing on the user’s device, slowing down page load times. For Tophinhanhdep.com, where High Resolution Photography is a core offering, this can be detrimental to performance.

Applying Dimensions with CSS width and height Properties
A more flexible and often preferred method for sizing images involves using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). CSS offers greater control over presentation and separation of concerns, allowing for better maintainability and responsiveness.
You can specify image dimensions using the width and height CSS properties, either inline, in a <style> block, or in an external stylesheet:
<!-- HTML -->
<img src="abstract-art.jpg" alt="Abstract digital art from Tophinhanhdep.com" class="gallery-thumbnail">
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
.gallery-thumbnail {
width: 250px;
height: 180px;
}
</style>Pros:
- Centralized Styling: CSS allows for consistent styling across multiple images or entire sections of a website, making it easier to manage the Visual Design of Tophinhanhdep.com’s extensive collections.
- Specificity and Overriding: CSS provides powerful mechanisms for applying styles based on different conditions (e.g., screen size, user interaction), offering more control than inline HTML attributes.
Cons:
- Same Bandwidth/Quality Issues: Similar to HTML attributes, simply setting
widthandheightin CSS doesn’t prevent the browser from downloading the full-sized original image. The scaling still happens client-side, leading to the same performance and quality compromises.
Maintaining Aspect Ratio and Responsiveness
When resizing images, especially for a site showcasing beautiful photography, preserving the original aspect ratio is crucial to avoid distortion. Stretching or squashing an image can severely detract from its aesthetic appeal. CSS provides elegant solutions for this:
Preserving the Aspect Ratio with height: auto or width: auto
To ensure an image maintains its original proportions, you should only specify one dimension (either width or height) and let the browser automatically calculate the other. Typically, width is set, and height is set to auto as most web layouts are width-constrained.
.responsive-image {
width: 100%; /* Makes the image take up 100% of its parent container's width */
height: auto; /* Automatically adjusts height to maintain aspect ratio */
}This approach allows images to adapt to their container while looking proportional.
Responsive Images with max-width
For truly responsive designs, preventing images from exceeding their original size while still scaling down for smaller screens is vital. This is where max-width shines:
.responsive-image-constrained {
max-width: 100%; /* Image will scale down, but never grow larger than its original width */
height: auto;
display: block; /* Prevents extra space below images */
}By setting max-width: 100%, the image will scale down to fit its parent container if the container is smaller than the image’s intrinsic width. However, it will never scale up beyond its original dimensions, preventing pixelation or blurriness that can occur when a smaller image is stretched to a larger size. This is particularly important for Tophinhanhdep.com’s Digital Photography, where maintaining crispness is key.
Beyond Basic Resizing: Advanced CSS Techniques and Cropping
Sometimes, simply resizing isn’t enough. Designers might need images to fill specific areas, crop gracefully, or serve as dynamic backgrounds. These advanced CSS techniques are vital for crafting intricate Visual Design elements and Photo Manipulation effects that enrich Tophinhanhdep.com’s aesthetic offerings.
Leveraging object-fit for Flexible Image Display
The object-fit CSS property offers powerful control over how an <img> or <video> element should be resized to fit its container, preserving its aspect ratio while potentially cropping or filling the space. This is a modern and highly effective tool for flexible image layouts.
.gallery-item-fit {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
object-fit: cover; /* Image covers the entire area, cropping if necessary, maintaining aspect ratio */
object-position: center; /* Centers the cropped image */
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}Common object-fit values include:
fill(default): Stretches or squashes the image to fill the container, potentially distorting the aspect ratio.contain: Resizes the image to fit entirely within the container, preserving its aspect ratio. Empty space might appear (like letterboxing).cover: Resizes the image to fill the container, preserving its aspect ratio. Parts of the image might be cropped to fit. Ideal for full-bleed sections, like aesthetic backgrounds on Tophinhanhdep.com.none: The image is not resized; its original size fills the area, potentially overflowing or leaving empty space.scale-down: The smaller ofnoneorcontain.
Combined with object-position, which controls the alignment of the image within its content box (e.g., object-position: right), object-fit provides precise control over how images are displayed, enabling sophisticated Photo Manipulation effects directly within the browser.
Mastering background-image for Aesthetic Control
For certain design elements, using images as backgrounds for other HTML elements (<div>, <section>, etc.) offers immense flexibility, especially for Wallpapers and Backgrounds. The background-image property, combined with background-size and background-position, allows for complex visual compositions.
.hero-banner {
background-image: url('nature-abstract.jpg');
background-size: cover; /* Scales the background image to cover the entire container */
background-position: center center; /* Centers the background image */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
width: 100%;
height: 400px; /* Fixed height for the banner */
}Key background-size values:
auto: Displays the image at its original size.lengthorpercentage: Sets explicit width and height (e.g.,200px 150pxor50% 75%).contain: Scales the background image to be as large as possible without cropping or stretching, ensuring the entire image is visible within the container.cover: Scales the background image to be as small as possible while still covering the entire container (cropping parts if necessary), maintaining its aspect ratio. This is a popular choice for full-width aesthetic backgrounds on Tophinhanhdep.com.
The background-image property is invaluable for creating dynamic visual layouts, where images are integral to the structure and mood, such as thematic collections or visual narratives on Tophinhanhdep.com.
The Hidden Costs of Client-Side Resizing: Performance and Quality
While HTML and CSS provide immediate visual control over image dimensions, relying solely on client-side resizing can incur significant performance and quality penalties, especially for a platform dedicated to rich visual content like Tophinhanhdep.com. Understanding these downsides is crucial for implementing truly optimized image strategies.
Impact on Page Load Speed and Bandwidth
The most critical drawback of client-side resizing is that the browser always downloads the original, often larger, image file first. Even if you instruct it to display an image at 400x300 pixels, if the original file is 2000x1500 pixels and 2MB in size, the user’s browser will still download the entire 2MB.
- Slower Page Loads: Downloading unnecessarily large files significantly increases page load times. This directly impacts user experience, leading to higher bounce rates and decreased engagement. For Tophinhanhdep.com, users expect fast access to galleries of high-resolution images; slow loading negates the visual appeal.
- Bandwidth Wastage: Every byte downloaded unnecessarily contributes to bandwidth consumption, both for the user (especially on mobile data plans) and for the server hosting Tophinhanhdep.com. This can translate to higher operational costs and a less accessible experience for users with limited data.
- Increased Processing on Client Devices: After downloading, the browser still needs to process and scale down the image. This requires CPU and memory, which can be particularly taxing on low-end devices, leading to a sluggish or unresponsive browsing experience. This is counterproductive to showcasing Beautiful Photography smoothly.
Preserving Visual Fidelity: When Browser Scaling Falls Short
While modern browsers do a decent job of scaling images, their algorithms are often optimized for speed over absolute quality. When a large image is aggressively scaled down by the browser, the final output might appear noticeably blurrier or less sharp than a meticulously pre-rendered smaller version.
- Loss of Sharpness: Detailed textures or fine lines in Nature or Abstract photography might lose their crispness when downscaled by the browser, diminishing the impact of the original artwork.
- Artifacts: In some cases, client-side scaling can introduce minor visual artifacts, especially with complex patterns or high-contrast areas. For Aesthetic and Sad/Emotional imagery where subtle details and mood are paramount, even small imperfections can be distracting.
For a website like Tophinhanhdep.com, which prides itself on the quality of its images, compromising visual fidelity due to client-side scaling is unacceptable. This necessitates moving beyond basic HTML/CSS controls to more advanced, server-side optimization techniques.
Optimizing Images the Tophinhanhdep.com Way: Server-Side and Smart Strategies
To truly “make images smaller” without sacrificing quality or performance, especially for a site rich in high-quality visual content, the most effective strategies involve server-side processing and intelligent content delivery. This is where Image Tools become indispensable, transforming raw Photography into web-ready assets.
Pre-Optimizing Images: The Role of Compressors and Converters
The fundamental principle of efficient image delivery is to serve an image that is already the correct size and format for its intended display. This requires proactive processing before the image even reaches the user’s browser.
- Image Compressors: Before uploading images to Tophinhanhdep.com, especially large RAW files from Digital Photography, they should be run through an image compressor. Tools (often found in the Image Tools category) can significantly reduce file size without a noticeable loss in perceived quality. This involves techniques like optimizing metadata, adjusting quality settings, and removing unnecessary data. The goal is to find the sweet spot between file size and visual fidelity.
- Image Converters: Different image formats are suited for different purposes.
- JPEG: Excellent for photographs (Wallpapers, Nature, Beautiful Photography) due to its efficient compression of continuous tones.
- PNG: Ideal for images with transparency or sharp edges (Abstract art, graphic design elements) as it uses lossless compression.
- WebP/AVIF: Next-generation formats that offer superior compression compared to JPEG and PNG, often with smaller file sizes and comparable quality. Tophinhanhdep.com should convert images to these modern formats for compatible browsers, with fallbacks to older formats for broader support. Image Tools like converters are essential for this.
- Resizing During Upload: Many content management systems or dedicated image services allow for automatic resizing of uploaded images into multiple dimensions (e.g., thumbnail, medium, large, full-size). This means that for a gallery of Aesthetic images, Tophinhanhdep.com can serve a small thumbnail version without making the user download the full high-resolution file.
AI Upscalers and High-Resolution Photography for Future-Proofing
While the focus is often on making images smaller, there are scenarios where upscaling is necessary, particularly when dealing with older or lower-resolution source material. Traditional upscaling often results in pixelation. However, advancements in AI Upscalers offer a solution.
- Enhancing Quality: AI Upscalers use machine learning to intelligently add detail and increase the resolution of an image, making it suitable for larger displays or print without significant quality degradation. For Tophinhanhdep.com’s collections, this means older or lower-res images can be brought up to modern standards, expanding the library of usable Photography.
- Preparing for Retina Displays: As screen resolutions continue to increase (e.g., Retina displays), images often need to be delivered at higher pixel densities to appear sharp. High Resolution Photography, combined with responsive image techniques (like
srcsetand<picture>elements in HTML), allows Tophinhanhdep.com to serve appropriate resolutions for different devices, ensuring images always look their best, whether they are nature wallpapers or abstract backgrounds.
Dynamic Image Delivery for Adaptive Experiences
The ultimate strategy for image optimization involves dynamic, on-demand image delivery, often facilitated by an Image CDN (Content Delivery Network) or a dedicated image optimization service.
- Real-time Transformations: Instead of pre-generating every possible image size and format, these services allow Tophinhanhdep.com to request images with specific transformations (e.g.,
width=400,format=webp,quality=70) via URL parameters. The server then processes the original image in real-time and delivers the optimized version. This is incredibly flexible for responsive design and managing diverse Image Inspiration & Collections. - Content Negotiation: Such services can also automatically detect the user’s browser capabilities and network conditions, serving the most optimal image format (e.g., WebP for Chrome, JPEG for Safari) and resolution without any manual intervention from the developer.
- Caching: Optimized images are cached at edge locations around the globe, ensuring fast delivery to users regardless of their geographical location, which is vital for a global audience accessing Tophinhanhdep.com’s diverse range of images.
By employing these advanced techniques, Tophinhanhdep.com can overcome the limitations of client-side resizing, providing users with a seamless, high-quality, and fast visual experience across all devices.
Integrating Images for Impactful Visual Design and Inspiration
For a website like Tophinhanhdep.com, images are not just decorative; they are the core content. Therefore, how they are integrated into the Visual Design is paramount, extending beyond mere technical resizing to encompass creative vision, thematic cohesion, and user engagement.
Aesthetic Considerations for Wallpapers, Backgrounds, and Art
The sheer variety of images on Tophinhanhdep.com—from Wallpapers and Backgrounds to Aesthetic, Nature, Abstract, Sad/Emotional, and Beautiful Photography—demands a thoughtful approach to visual presentation.
- Contextual Sizing: The “right” size for an image is highly contextual. A full-bleed hero image functioning as a background wallpaper will naturally be larger than a small thumbnail in a gallery grid. Understanding the role each image plays in the overall Visual Design helps determine its ideal dimensions.
- Visual Hierarchy: Image sizes can be used to establish a visual hierarchy, drawing the user’s eye to primary content (e.g., a featured high-resolution photo) and away from secondary elements (e.g., related image suggestions).
- Color and Mood: Beyond size, the color palette and mood of images (e.g., calming Nature scenes, vibrant Abstract art, poignant Sad/Emotional photography) must be considered in relation to the overall site design. Sizing and cropping decisions can emphasize or de-emphasize elements within an image to enhance its intended emotional impact.
- Negative Space: Effective visual design often utilizes negative space around images, not just the images themselves. Proper sizing ensures images don’t feel cramped or overwhelming, allowing each piece of Beautiful Photography to breathe and be appreciated.
Curating Image Collections and Mood Boards for Creative Projects
Tophinhanhdep.com also serves as a source of Image Inspiration & Collections, catering to users looking for Photo Ideas, Mood Boards, Thematic Collections, and Trending Styles. This aspect emphasizes the creative rather than purely technical side of image management.
- Dynamic Gallery Layouts: Implementing responsive gallery layouts where images adapt gracefully to different screen sizes and aspect ratios is key. Techniques like CSS Grid and Flexbox, combined with
object-fit, allow for aesthetically pleasing and functional displays of diverse thematic collections. - Interactive Previews: Providing small, optimized thumbnails for quick browsing, with the option for users to view larger, higher-resolution versions upon interaction (e.g., click, hover), enhances the user experience. This strategy ensures fast initial loading while still offering access to the full detail of High Resolution Photography.
- Metadata and Searchability: For a vast collection of images, robust metadata (tags, descriptions, categories like “Aesthetic” or “Nature”) is as important as technical optimization. This allows users to effectively search and curate their own Mood Boards or find specific Photo Ideas, regardless of image size. Image-to-Text tools (from the Image Tools category) can aid in automatically generating descriptive alt text or tags, further improving searchability and accessibility.
- Showcasing Editing Styles: For Photography sections, presenting images alongside information about their Editing Styles (e.g., monochrome, vintage, vibrant HDR) can add value and context. Ensuring these example images are perfectly sized and optimized highlights the quality of the post-processing.
In conclusion, “making an image smaller in HTML” is a multi-faceted challenge that requires a holistic approach, especially for a content-rich platform like Tophinhanhdep.com. While basic HTML and CSS attributes provide initial control, true optimization for performance, quality, and aesthetic impact demands server-side processing, dynamic delivery, and a keen understanding of visual design principles. By embracing these strategies, Tophinhanhdep.com can continue to be a premier destination for stunning images, delivering inspiration and visual delight efficiently to its global audience.