How to Master Image Resolution Reduction for Optimal Performance
In the vast digital landscape, images are paramount. From stunning wallpapers and inspiring photography to crucial visuals for job applications or professional portfolios, the quality and performance of an image can significantly impact its effectiveness. High-resolution images, while offering unparalleled detail, often come with a hefty file size, leading to slower loading times, increased storage consumption, and compatibility issues across various platforms. This is where mastering the art of image resolution reduction becomes indispensable.
Understanding how to effectively reduce an image’s resolution—or more accurately, its pixel dimensions—is a skill that transcends casual browsing, touching upon core aspects of web design, digital photography, and efficient content management. Whether you’re a professional photographer curating a portfolio on Tophinhanhdep.com, a graphic designer optimizing assets, or simply looking to share a beautiful nature shot without bogging down your email, efficient image resizing is key. This comprehensive guide will demystify image resolution, debunk common myths, and provide practical methods, leveraging powerful tools available on platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, to ensure your visuals always perform at their best.
![]()
Understanding Image Resolution: Pixels, DPI, and the Web
Before diving into the “how-to,” it’s crucial to grasp what “image resolution” truly means and, perhaps more importantly, what it doesn’t mean, especially in the context of digital displays and the internet. Many users instinctively think of “resolution” as a singular metric defining an image’s overall quality and file size, but the reality is more nuanced.
What is Image Resolution?
At its core, image resolution refers to the amount of detail an image holds. It’s often expressed in terms of pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI).
- Pixels (Picture Elements): These are the tiny squares of color that make up a digital image. The total number of pixels in an image (e.g., 1920 pixels wide x 1080 pixels high) defines its pixel dimensions. This is a fundamental characteristic of any digital image.
- DPI (Dots Per Inch): This term is predominantly used in the printing world. It describes how many ink dots a printer will place within a one-inch line on a physical medium. Higher DPI generally means a sharper, more detailed print.
- PPI (Pixels Per Inch): Similar to DPI, PPI refers to the number of image pixels displayed per inch on a screen or included per inch in a print. For screens, a higher PPI means pixels are packed more densely, resulting in a smoother appearance, though the actual size of the pixels depends on the screen’s physical dimensions and zoom level.
The key takeaway here is that PPI/DPI primarily dictates the physical size an image will be printed or displayed at a certain magnification, without resampling (changing pixel count). A high PPI value for a given set of pixel dimensions will result in a smaller, more detailed print, while a low PPI will yield a larger, less detailed print.
The Misconception: Resolution vs. Pixel Dimensions for Web
Here’s where a significant and persistent misconception needs to be addressed, as highlighted by experts at Tophinhanhdep.com (and sources like Photoshop Essentials). Many believe that to optimize an image for the web, you must reduce its resolution to a “web resolution,” typically cited as 72 PPI. This belief is fundamentally incorrect.
For images displayed on a screen (like on Tophinhanhdep.com, social media, or a digital portfolio), the PPI/DPI value has virtually no impact on the image’s file size or its loading speed. The browser simply displays all the pixels present in the image, regardless of the PPI tag embedded within its metadata. A 6000x4000 pixel image with a 72 PPI setting will have the exact same file size and load time as the same 6000x4000 pixel image with a 300 PPI setting.
What does determine an image’s file size and, consequently, its loading speed on the web, are its pixel dimensions (width x height) and its compression level. A 6000x4000 pixel image contains 24 million pixels. A 1000x667 pixel image contains roughly 0.67 million pixels. The image with fewer pixels will inevitably have a smaller file size and load faster, regardless of its PPI setting.
The “72 PPI web resolution myth” likely stems from a time when monitors typically displayed at around 72-96 pixels per inch. However, modern screens vary widely in pixel density (e.g., Retina displays), making a fixed “web resolution” meaningless. When you resize an image for the web, your primary goal is to adjust its pixel dimensions to match the maximum display size required, then apply appropriate compression. For example, if an image will only ever be displayed at 800 pixels wide on a webpage, there’s no benefit to uploading a 6000-pixel-wide image, even if its PPI is set to 72. You’re still forcing the browser to download 6000 pixels of data it doesn’t need.
Why and When to Reduce Image Resolution (or Pixel Dimensions)
Understanding the distinction between true resolution (PPI/DPI for print) and pixel dimensions (for digital display) clarifies why and when to reduce image size. The goal is almost always to reduce the total number of pixels while maintaining acceptable visual quality, rather than merely changing an arbitrary PPI value.
Enhancing Web Performance and User Experience
One of the most compelling reasons to reduce the pixel dimensions of images is to significantly enhance web performance. High-resolution images are often “too heavy” for websites, especially those with extensive visual content like the beautiful photography and aesthetic collections found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
- Faster Load Times: Smaller image files mean quicker downloads. This directly translates to faster page loading times, which is crucial for retaining visitors. Studies consistently show that users abandon websites that take too long to load.
- Improved Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Search engines like Google prioritize fast-loading websites. Optimized images contribute positively to your site’s speed, thereby improving its SEO ranking. This is vital for photographers and artists who want their work discovered online.
- Better Mobile Experience: A significant portion of internet traffic comes from mobile devices. These devices often have slower connections and less processing power than desktop computers. Optimized images ensure that content on Tophinhanhdep.com (or any site) loads quickly and smoothly on smartphones and tablets, providing a seamless user experience.
Meeting Specific Platform Requirements
Beyond general web performance, many online platforms impose strict file size or dimension limits for uploaded images. This makes resolution (pixel dimension) reduction a necessity.
- Job and Admission Portals: These often have stringent requirements for passport-sized photos or document scans, demanding specific pixel dimensions and file sizes (e.g., “photo must be 300x300 pixels and under 50KB”).
- Social Media: While social platforms often automatically compress images, uploading an already optimized image can prevent over-compression and preserve quality.
- Email Attachments: Sending large image files via email can be slow and may exceed recipient mailbox limits. Reducing pixel dimensions makes sharing digital photography and creative ideas effortless.
- Saving Storage Space: For photographers and digital artists working with vast collections of high-resolution images (e.g., stock photos, digital art), reducing the pixel dimensions of copies intended for web or client proofs can save significant storage space, both locally and on cloud services.
Impact on Different Image Types
The need for resolution reduction varies depending on the type and purpose of the image:
- Wallpapers and Backgrounds: Users browsing Tophinhanhdep.com for wallpapers might prefer very high-resolution images for their desktop screens. However, if these images are used as website backgrounds, optimized versions are crucial for performance.
- Digital Photography and Abstract Art: These often originate as very high-resolution files. For online display or portfolio sites, reducing pixel dimensions is essential to showcase work effectively without sacrificing loading speed.
- Nature and Aesthetic Images: Similar to photography, these images benefit greatly from optimization. Collections of “beautiful photography” or “thematic collections” on Tophinhanhdep.com need to be optimized for quick browsing.
- Graphic Design and Visual Design Assets: Graphic designers frequently need to provide clients with web-optimized versions of their digital art or photo manipulation projects.
In all these scenarios, the goal is to achieve the smallest possible file size that still delivers acceptable visual quality for its intended display context.
Practical Methods for Reducing Image Resolution
Now that we understand the ‘why’, let’s explore the ‘how’. There are numerous tools and techniques available for reducing image resolution (i.e., pixel dimensions), ranging from simple online utilities to professional desktop software. Tophinhanhdep.com provides access to a suite of image tools that can streamline this process significantly.
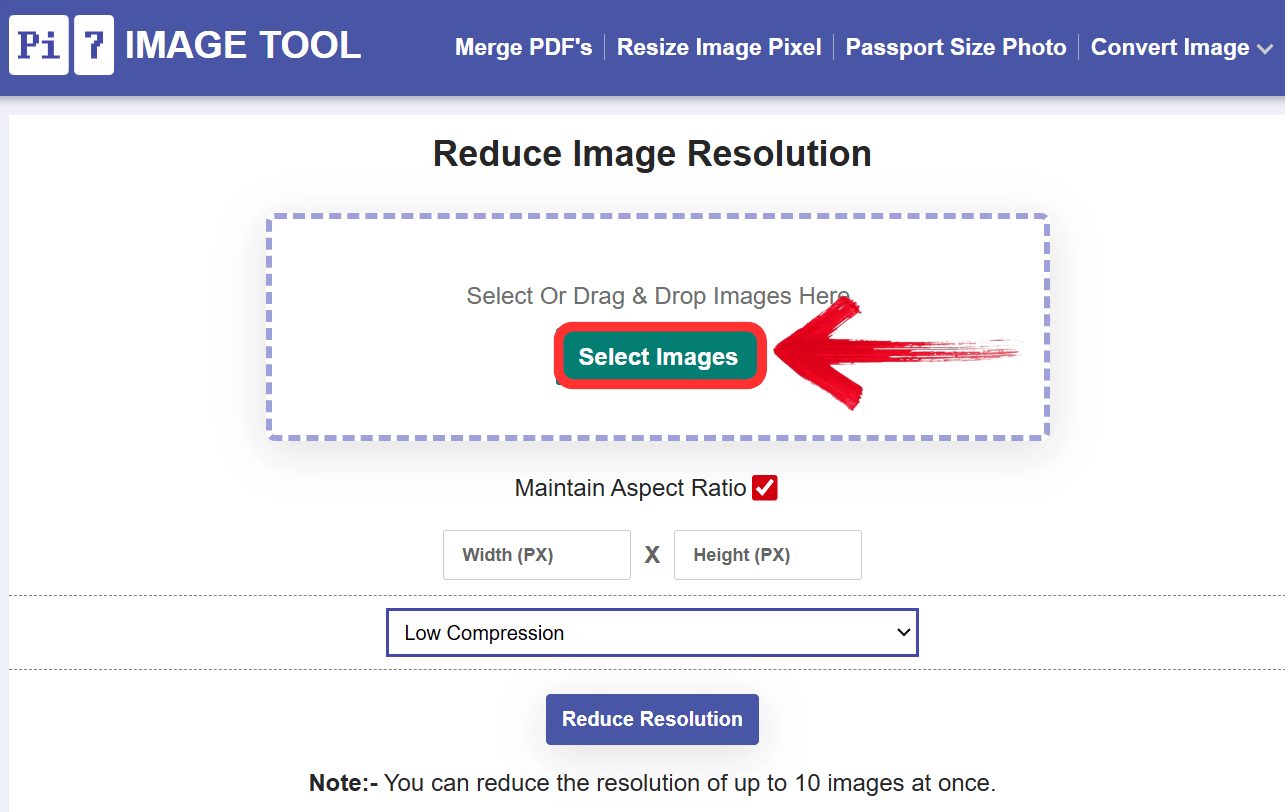
Using Online Image Tools (like Pi7 Image Tool on Tophinhanhdep.com)
Online image tools offer unparalleled convenience, requiring no software downloads or installations. They are accessible from any device with an internet connection, making them ideal for quick tasks or when you’re on the go. Tophinhanhdep.com, through its Pi7 Image Tool, provides an excellent example of such a utility.
Key Features of Tophinhanhdep.com’s Resolution Reducer Tool:
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces often involve simple drag-and-drop functionality for uploading images.
- No Downloads Needed: Being entirely web-based, you simply visit Tophinhanhdep.com, upload your images, and perform the reduction.
- Specify Desired Dimensions: Most tools allow you to input new width and height values in pixels, or even percentages. The Pi7 Image Tool specifically lets you define the desired width and height, ensuring your images meet precise requirements.
- Maintain Aspect Ratio: This critical feature prevents images from becoming distorted or stretched. Tophinhanhdep.com’s Pi7 Image Tool, for instance, offers a “Maintain Aspect Ratio” option, allowing you to change one dimension while the tool automatically adjusts the other proportionally.
- Bulk Image Processing: For photographers or content managers dealing with multiple images, bulk processing is a massive time-saver. The Pi7 Image Tool on Tophinhanhdep.com allows you to process up to 10 images simultaneously, saving valuable time and effort, and even points to a bulk resizer for 500+ images for even larger needs.
- Versatile Format Support: Tools like Pi7 Image Tool support various popular image formats, including JPG, PNG, and more, making them suitable for diverse needs.
- Integrated Compression: Many resolution reduction tools, including Pi7 Image Tool, offer simultaneous image compression. You can often choose between low, medium (best quality & small file size), and high compression (smallest file size) levels, allowing you to fine-tune the balance between file size and visual quality.
How to Use Tophinhanhdep.com’s Pi7 Image Tool:
- Navigate to the Tool: Visit Tophinhanhdep.com’s reduce image resolution page.
- Upload Images: Click “Select Images” or drag and drop up to 10 images into the designated area.
- Specify Dimensions: Enter your desired width and height in pixels. Ensure “Maintain Aspect Ratio” is checked to prevent distortion.
- Choose Compression (Optional): Select your preferred compression level (Low, Medium, High).
- Reduce Resolution: Click the “Reduce Resolution” button.
- Download: Once processed, download your optimized images.
The convenience of Tophinhanhdep.com’s integrated image tools extends beyond simple resolution reduction. Their “Image Tools” section features converters (PNG to JPEG, HEIC to JPG, Images to PDF), compressors, optimizers, and even AI upscalers, forming a comprehensive toolkit for digital asset management.
Desktop Software Solutions
For users who prefer offline control or require more advanced editing capabilities, various desktop software options are available across different operating systems.
- Microsoft Word (Windows/Mac): While not a dedicated image editor, Word can perform basic image compression. After inserting an image, clicking it reveals “Picture Tools” or a “Format” tab. Within the “Adjust” group, you’ll find “Compress Pictures.” You can select a target output, which reduces pixel dimensions and file size suitable for email or web. This is simple for quick document-related tasks, but lacks fine control.
- GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program - Windows/Mac/Linux): GIMP is a powerful, free, open-source image editor that provides functionality similar to Adobe Photoshop.
- Open your image in GIMP.
- Go to the
Imagemenu and selectScale Image. - In the pop-up box, you can type in new
WidthandHeightpixel values. Ensure the chain icon next to the dimensions is linked to maintain aspect ratio. - Click
Scaleto apply the changes instantly. GIMP offers greater control over resampling methods, which can impact output quality.
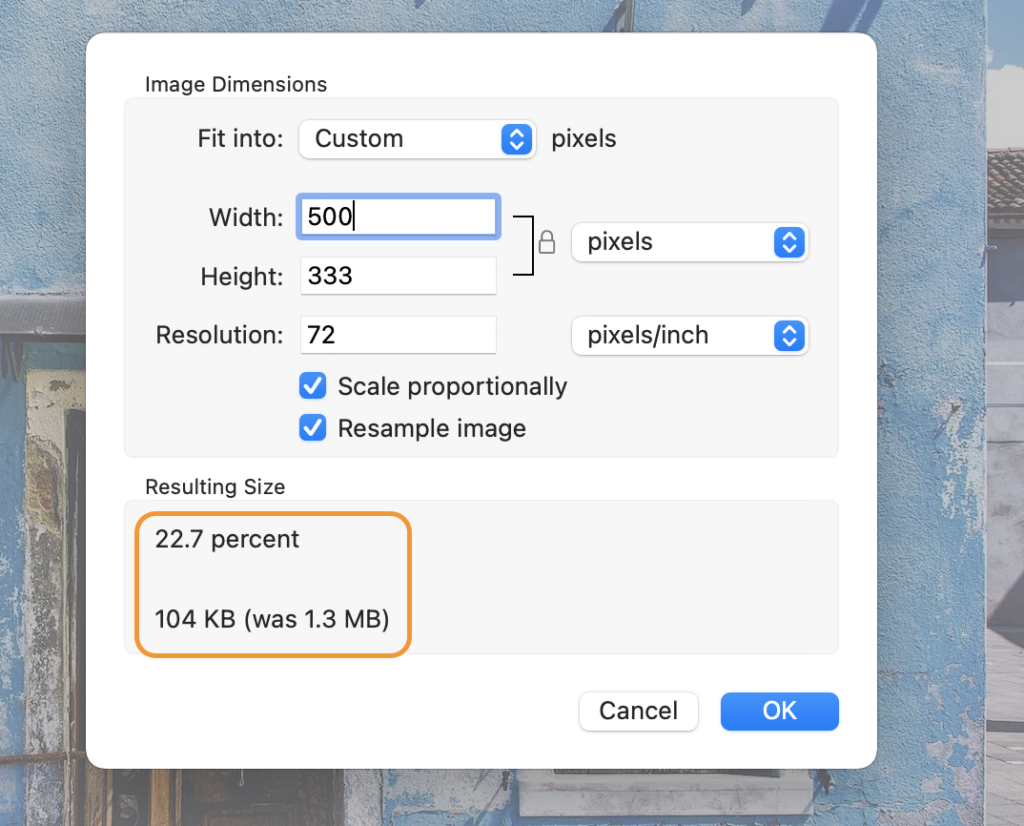
- Preview (Mac): macOS users have a built-in, lightweight tool in Preview.
- Open your image in Preview (right-click the file and choose “Open with” > “Preview”).
- Go to the
Toolsmenu and selectAdjust Size. - In the dialogue box, you can enter new
WidthandHeightpixel values. EnsureScale proportionally(represented by a lock icon) is enabled. - Click
OKto apply the changes. Preview allows you to view the estimated file size after adjustment.
General Best Practice for Desktop Tools: When manually reducing pixel dimensions, especially for very large images, Informatics Inc. suggests a “reduce by no more than half” rule. If you have a 3000-pixel image and need it to be 500 pixels, it might be better to reduce it to 1500 pixels, then to 750 pixels, and finally to 500 pixels, rather than one drastic jump. This iterative reduction can sometimes help prevent the image editor from making poor decisions when discarding pixels, reducing “noise” or artifacts. However, modern algorithms are often efficient enough to handle single-step reductions for most common scenarios. Always save your reduced image as a new file to preserve the original.
Integrating Reduction with Other Optimization Techniques
Reducing pixel dimensions is just one part of image optimization. For truly outstanding web performance and visual quality, it should be combined with other techniques:
- Compression: This involves reducing the amount of data in an image file.
- Lossy Compression (e.g., JPEG): Discards some image data permanently, resulting in smaller files but a slight loss in quality. Ideal for photographs.
- Lossless Compression (e.g., PNG): Reduces file size without discarding data, preserving perfect quality but with generally larger files than lossy. Ideal for graphics with sharp lines or transparency.
- Tophinhanhdep.com’s Pi7 Image Tool, for instance, offers compression options alongside resolution reduction.
- Choosing the Right File Format: Select the format best suited for your image: JPEG for photos, PNG for images with transparency or sharp graphics, and WEBP for modern web applications that prioritize efficient compression and speed. Tophinhanhdep.com’s converters can assist with format changes.
- Image Optimizers: Dedicated optimizers can further strip unnecessary metadata from image files without affecting visual quality, leading to marginal but cumulative file size reductions.
By combining pixel dimension reduction with smart compression and appropriate file formats, you can achieve the perfect balance between high-quality visuals and optimal performance, ensuring that your images, whether they are aesthetic photos, abstract art, or part of a trending collection on Tophinhanhdep.com, load quickly and beautifully for every visitor.
Conclusion
The digital age demands not just beautiful images, but also efficiently managed ones. Understanding how to intelligently reduce the resolution—or more precisely, the pixel dimensions—of your images is a critical skill for anyone engaging with visual content online. Dispelling the myth of the “72 PPI web resolution” allows us to focus on what truly matters: optimizing pixel count for the intended display size and applying effective compression.
Whether you’re streamlining a portfolio of “beautiful photography,” optimizing “stock photos” for client delivery, or ensuring that “aesthetic wallpapers” load swiftly on Tophinhanhdep.com, the principles remain the same. Embrace the convenience and power of online tools like the Pi7 Image Tool available on Tophinhanhdep.com for quick, bulk processing, or delve into desktop software for more intricate control. Pair these techniques with smart compression and the right file formats to achieve a harmonious balance between visual fidelity and digital performance.
Ultimately, Tophinhanhdep.com is dedicated to providing comprehensive resources, from stunning “images” and “photography” inspiration to practical “image tools” and “visual design” guides. By mastering image resolution reduction, you not only improve your digital footprint but also contribute to a faster, more enjoyable online experience for everyone, making your visual content truly stand out.