Mastering Image Optimization: How to Reduce the Size of Your Images for Better Performance and Visual Appeal

In today’s visually-driven digital world, images are paramount. From stunning wallpapers that adorn our desktops to captivating backgrounds for our mobile devices, aesthetic visuals, breathtaking nature scenes, intricate abstract art, emotional photography, and high-resolution masterpieces – images enrich our online experience and personal archives. However, the pursuit of visual excellence often comes with a significant challenge: file size. High-quality images, while beautiful, can be notoriously large, consuming valuable storage space, slowing down websites, and hindering efficient sharing. This is where the crucial skill of image optimization comes into play.
At Tophinhanhdep.com, where we curate a vast collection of diverse imagery, including wallpapers, backgrounds, and beautiful photography, we understand the delicate balance between visual fidelity and digital efficiency. Our platform serves as a hub for high-resolution photography, stock photos, and various digital photography styles, offering inspiration and tools for creators and enthusiasts alike. The ability to effectively reduce the size of an image without compromising its inherent beauty is not just a technical necessity; it’s an art that enhances user experience, improves website performance, and ensures seamless digital interaction. This comprehensive guide will delve into the multifaceted world of image size reduction, exploring its importance, methods, tools, and best practices, all within the context of maximizing the impact of the incredible visual content found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Understanding Image Compression: The Core of Digital Efficiency
Image compression is the process of reducing the file size of an image, typically by removing redundant or less critical data. This fundamental technique is essential for managing digital assets efficiently, impacting everything from website load times to the speed of file transfers.
The JPEG Phenomenon: A Foundation of Web Imagery
When discussing image compression, JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is often the first format that comes to mind. Named after the committee that established the standard in 1992, JPEG quickly became, and remains, a cornerstone of digital image storage. As of recent data, JPEG files account for a substantial portion of all image requests on the web’s most-trafficked sites, a testament to its widespread adoption and utility.

Key Characteristics of JPEGs:
- Widespread Adoption: JPEGs are universally supported across devices, from professional DSLR cameras and smartphones to web browsers and image editing software. This ubiquity makes it an ideal format for sharing and displaying photographs.
- Embedded Metadata: JPEG files often contain embedded color profiles and EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) metadata. This metadata can include valuable information such as camera model, aperture, shutter speed, date and time of capture, and even GPS locations for geo-tagged images. While useful, this metadata can also contribute to file size.
- Lack of Transparency Layer: Unlike formats like GIF or PNG, JPEG does not natively support a transparency layer. This means that if you need an image with a transparent background (e.g., a logo to overlay on various backgrounds), JPEG is not the appropriate choice.

How JPEG Compression Works: JPEG employs a form of “lossy” compression, meaning that it discards some of the original image data during the compression process. This makes the compression irreversible – you cannot fully reconstruct the original, uncompressed image from a lossy JPEG. However, the brilliance of JPEG lies in its ability to discard data that is least perceptible to the human eye.
The process involves a complex mathematical operation called a Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). During DCT, individual colored pixels are sampled and re-encoded. This results in a new file that can have a reduced resolution, lower quality, or both. The degree of compression is adjustable, allowing creators to find a balance between file size reduction and perceived image quality. This flexibility is crucial for photography and digital art showcased on platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, where high visual standards are maintained while ensuring optimal performance.
Why Optimize? The Benefits for Users and Creators
The question “why reduce JPEG size?” extends beyond mere technical curiosity; it addresses fundamental aspects of digital usability and efficiency. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, dedicated to providing high-quality visual content, optimization is not optional but essential.
- Faster Website Loading Times: In the digital age, speed is paramount. Slow-loading websites lead to higher bounce rates and frustrated users. Large image files are often the primary culprits behind sluggish performance. By reducing image sizes, Tophinhanhdep.com ensures that users can quickly browse through our extensive collections of wallpapers, backgrounds, and aesthetic photography without waiting for bloated images to load. This minimizes “latency”—the time it takes for data to transmit—and significantly improves the overall user experience.
- Reduced Bandwidth and Storage Costs: Images typically account for the largest proportion of data on an average website. For website owners and content creators, minimizing file sizes translates directly into reduced bandwidth usage and lower server storage costs. This economic benefit allows Tophinhanhdep.com to offer a wider variety of high-resolution images and maintain sustainable operations.
- Easier File Sharing: Sharing high-resolution images via email, messaging apps, or cloud services can be a cumbersome process due to file size limits. Optimized images are easier and quicker to upload and download, facilitating seamless sharing of beautiful photography or creative ideas amongst friends, colleagues, or social media followers.
- Better Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Search engines like Google prioritize fast-loading websites, incorporating page speed as a ranking factor. Optimized images contribute significantly to quicker load times, thereby boosting SEO rankings for platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com. This ensures that our stunning nature, abstract, and sad/emotional images are more discoverable to a wider audience seeking quality visual content.
- Maintaining Visual Integrity for Diverse Uses: While the goal is to reduce size, the underlying principle is to do so intelligently. For instance, a detailed nature photograph used as a desktop wallpaper needs less compression than a thumbnail for a blog post. Optimized images ensure that the visual point is effectively conveyed without users encountering pixelation or prolonged waits, striking that “happy medium” between file size and image quality that is so vital for the diverse content on Tophinhanhdep.com.
In essence, optimizing images is a critical step in building a responsive, cost-effective, and user-friendly digital presence. For Tophinhanhdep.com, it means delivering an uninterrupted and inspiring visual journey to every visitor.
Practical Strategies for Image Size Reduction
Reducing the size of an image involves a combination of techniques, each addressing different aspects of how image data is stored and displayed. Understanding these methods allows for targeted optimization, ensuring the best possible balance between file size and visual quality for the diverse range of images on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Resizing and Resolution: The First Line of Defense
One of the most straightforward and effective ways to reduce an image’s file size is to adjust its physical dimensions and resolution. Many images, especially those captured with high-end cameras or downloaded as high-resolution stock photos, are often much larger than they need to be for their intended use.
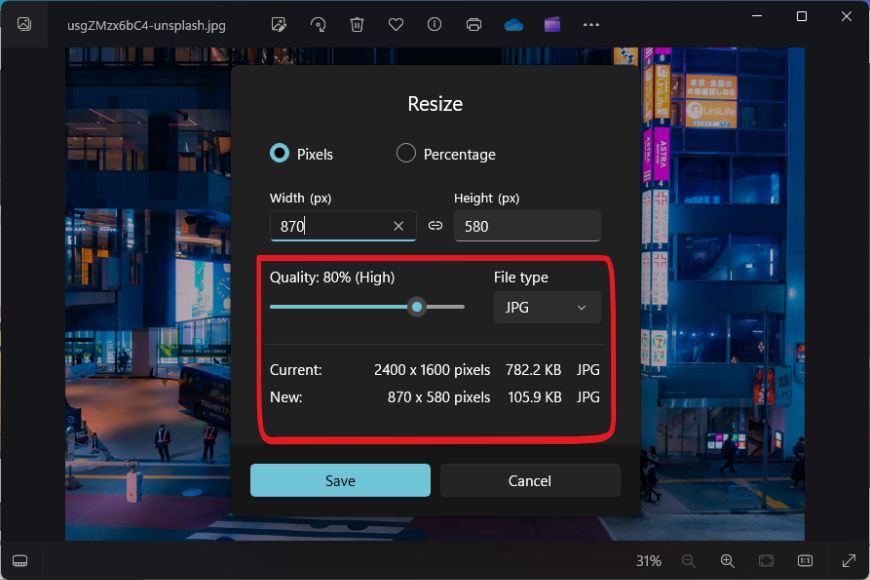
- Changing Picture Dimensions (Width and Height): The dimensions of a photo refer to its width and height in pixels. If an image is destined for a website banner that is 1200 pixels wide, uploading a 4000-pixel wide original is inefficient. Reducing the image to the exact display dimensions can dramatically cut its file size without any loss of displayed quality. Most image editing software, like Photoshop or GIMP, and even built-in OS tools (e.g., OS X Preview, Microsoft Photos App, Paint) offer simple “Resize Image” options to adjust these values. This is particularly relevant for the high-resolution photography featured on Tophinhanhdep.com, ensuring images fit various screen sizes without unnecessary overhead.
- Adjusting Image Resolution (DPI/PPI): Image resolution is often expressed in DPI (Dots Per Inch) for print or PPI (Pixels Per Inch) for digital displays. For screens, 72 DPI is a common benchmark, as monitors typically display at this density. Images intended solely for web use rarely need a resolution higher than 72 PPI. Reducing the DPI from a print-ready 300 PPI to a web-optimized 72 PPI can significantly decrease file size, especially for the vast collection of digital photography and aesthetic backgrounds available on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Choosing the Right File Format: JPEG, PNG, WebP, and Beyond
The choice of file format dramatically influences an image’s size and its suitability for various applications. Different formats employ different compression algorithms and support different features. Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Image Tools” section often highlights converters, enabling users to switch between formats for optimal results.
- JPEG (.jpg or .jpeg): As discussed, JPEG is ideal for photographs and complex images with many colors and gradients. Its lossy compression excels at reducing photographic detail in ways that are least noticeable to the human eye, making it perfect for the beautiful photography, nature, and abstract images on Tophinhanhdep.com.
- PNG (.png): PNG (Portable Network Graphics) uses lossless compression and supports transparency. This makes it the go-to format for logos, icons, graphics with sharp edges, or images that require a transparent background. However, for complex photographs, PNG files can be significantly larger than JPEGs.
- WebP (.webp): Developed by Google, WebP is a modern format that offers superior compression compared to both JPEG and PNG, often resulting in smaller file sizes while maintaining comparable or even higher quality. It supports both lossy and lossless compression, as well as transparency and animation. WebP is increasingly supported by modern web browsers and is becoming the preferred format for web optimization.
- AVIF (.avif): Even newer than WebP, AVIF (AV1 Image File Format) often provides even greater compression efficiency. While it offers excellent quality-to-size ratios, its browser support is still growing compared to WebP.
- Other Formats (GIF, TIFF, BMP): GIF (.gif) is best for simple animations and images with limited color palettes (up to 256 colors) but not suitable for detailed photos. TIFF (.tiff) and BMP (.bmp) are typically uncompressed or use lossless compression, resulting in very large files, making them unsuitable for web use but sometimes necessary for high-quality print or archival purposes.
When to Convert: If you have high-resolution stock photos or digital art originally saved as large PNGs, converting them to JPEG (if transparency isn’t needed) or WebP can yield substantial file size reductions, a process facilitated by the “Converters” tool category on Tophinhanhdep.com.
The Power of Compression: Balancing Quality and Size
Beyond resizing and format choice, directly applying compression is a key strategy. This involves telling the software how aggressively to reduce the image data.
- Lossy vs. Lossless Compression:
- Lossy Compression: Permanently removes some image data, as with JPEG. The trick is to remove data that the average human eye won’t miss. Most image editors provide a “quality” slider (e.g., 0-100% or 1-12) when saving JPEGs. A higher quality setting means less compression and a larger file, while a lower setting means more compression and a smaller file, but with a greater risk of visible artifacts.
- Lossless Compression: Reduces file size by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancies in the image data without discarding any information. This means the original image can be perfectly reconstructed. PNG uses lossless compression. While it saves less space than lossy methods for photos, it’s crucial for images where every pixel detail matters, such as specific digital art or graphic design elements.
- Adjusting Quality Sliders: In tools like Photoshop or GIMP, when you save an image as JPEG, you’ll encounter a quality slider. This is your primary control over the lossy compression level. Finding the “happy medium” – where the file size is significantly reduced but the visual quality of the wallpaper or background image from Tophinhanhdep.com remains excellent – often requires a bit of experimentation. Many suggest that a quality setting between 70-85% for JPEGs strikes a good balance for web use.
- Impact on Aesthetic and Nature Photography: For the stunning aesthetic and nature photography found on Tophinhanhdep.com, careful compression is vital. Too much compression can introduce blockiness, banding, or blur, ruining the delicate details of a landscape or the subtle emotions in a sad/emotional image. The goal is always to achieve the smallest possible file size that still meets the required visual standard.
Stripping Unnecessary Metadata
Images often carry a payload of hidden information called metadata. While some metadata (like copyright info) is essential, much of it, such as camera details, lens information, exposure settings, and GPS location (EXIF data), is not needed for web display or general sharing.
Removing this non-essential metadata can offer a small, cumulative reduction in file size. While individually negligible, across hundreds or thousands of images, these savings can become significant. Many image optimization tools and online compressors, including those discussed in Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Image Tools” section, offer the option to strip EXIF data automatically.
By combining these practical strategies – thoughtful resizing, judicious format selection, intelligent compression, and metadata removal – creators can significantly reduce image file sizes, enhancing performance without sacrificing the visual impact that is the hallmark of Tophinhanhdep.com’s diverse image collections.
Essential Tools and Techniques for Image Optimization
The good news is that you don’t need to be a mathematical genius to optimize images. A wide array of tools, ranging from professional desktop software to convenient online platforms and powerful plugins, are available to simplify the process. Tophinhanhdep.com, with its focus on “Image Tools” (including Converters, Compressors, Optimizers, and AI Upscalers), serves as an excellent resource for exploring these solutions.
Desktop Software for Detailed Control
For those who require granular control over their image optimization process or frequently work with large batches of high-resolution images, dedicated desktop software remains an invaluable asset.
- Adobe Photoshop: A cornerstone of professional photography and graphic design, Photoshop offers robust image compression capabilities. When “Saving for Web (Legacy)” (found under File > Export) or simply “Exporting As” a JPEG, users can precisely adjust quality levels, select different file formats (including WebP in newer versions), and preview the file size in real-time. This level of customization is crucial for digital art and photo manipulation, allowing creators to fine-tune every aspect of their visual design. Adobe Bridge can also be used for large batch operations.
- GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): As a free and open-source alternative to Photoshop, GIMP provides extensive functionality for raster image editing, including comprehensive compression settings when exporting or saving files. It runs on most operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux), making it accessible for a broad range of users.
- Adobe Lightroom: Primarily a photo management and editing tool, Lightroom allows users to reduce file sizes during the export process. Options to adjust dimensions, resolution, and quality settings are readily available, along with the ability to set a maximum file size. This is particularly useful for managing large libraries of photography, from nature shots to aesthetic collections.
- ImageMagick: A powerful, open-source software suite designed for creating, editing, and converting bitmap images, ImageMagick is often used via the command line. It supports a vast array of formats and offers extensive scripting capabilities for resizing, compressing, and transforming images in bulk. It runs on Linux, Mac OS X, Windows, Android, and iOS, making it highly versatile for webmasters and developers.
- OS X Preview (Mac): For Mac users, the default Preview application offers a simple way to re-compress JPEGs. By exporting an image as a JPEG, a slider allows users to choose a quality level and preview the resulting file size, offering quick and easy optimization without needing third-party software.
- Microsoft Photos App / Paint (Windows): Windows users can leverage the built-in Photos app to resize and adjust image quality. Microsoft Paint, now redesigned, also provides straightforward options to resize photos by percentage or pixels. These tools are excellent for quick, basic reductions.
Online Tools and Plugins for Quick Optimization
For users who need fast, efficient image compression without installing software, or for automated website optimization, online tools and plugins are highly effective. Tophinhanhdep.com’s “Image Tools” category extensively covers “Compressors” and “Optimizers.”
- TinyPNG / TinyJPG: These popular web tools specialize in compressing PNG and JPEG files using “smart lossy compression.” They significantly reduce file sizes while aiming to maintain visual quality. Users can upload multiple images simultaneously and download them in bulk, making them ideal for quick optimizations for web content.
- JPEG-Optimizer / Compressor.io: Similar to TinyPNG, these online platforms provide user-friendly interfaces for compressing JPEGs and other formats. They often include options to set quality levels or automatically find the best compression ratio.
- Squoosh (by Google): A sophisticated, browser-based tool that allows users to compress images while comparing the quality difference in real-time. Squoosh supports modern formats like WebP and AVIF and can even work offline once loaded, making it a powerful tool for web developers optimizing images for various browsers.
- ShortPixel (for WordPress): For WordPress users, plugins like ShortPixel Image Optimizer automatically compress images upon upload. They also offer bulk optimization for existing images, conversion to WebP/AVIF, and options to serve optimized images from a CDN. WordPress itself has default JPEG compression rates (e.g., 82%), which can be adjusted. These plugins are invaluable for website owners showcasing wallpapers, backgrounds, and thematic collections from Tophinhanhdep.com.
AI-Powered Solutions: The Future of Image Optimization
The rise of artificial intelligence is revolutionizing image processing, including optimization. Tophinhanhdep.com’s emphasis on “AI Upscalers” points to this exciting frontier.
- Luminar Neo: As an example of advanced photo editing software, Luminar Neo integrates AI tools that not only help reduce image size but also preserve or enhance quality in the process. Its “Export Menu” allows for resizing and sharpening, with options to set desired dimensions. Key advantages include:
- AI-Powered Tools: Features like AI Sharpener and AI Upscaler can help maintain clarity even after compression or enlarge smaller images without significant loss of quality, which is crucial for high-resolution photography.
- Newbie-Friendly Interface: Makes complex tasks accessible.
- Batch Editing: Efficiently process numerous photos simultaneously, perfect for large collections of beautiful photography.
- Extensive File Format Support: Works with JPEG, PNG, TIFF, and more, allowing flexibility for online use or high-resolution printing.
- Quality Management: Offers precise control over quality settings during export to achieve the ideal balance between file size and image fidelity.
AI tools bridge the gap between aggressive compression and preserving intricate details, making them invaluable for creators working with diverse visual design and digital art projects. They represent the next generation of “Compressors” and “Optimizers” that Tophinhanhdep.com champions.
Whether you opt for the detailed control of desktop software, the convenience of online tools, or the cutting-edge capabilities of AI-powered solutions, the goal remains the same: to reduce image size effectively, ensuring that the visual stories, inspirations, and collections curated on Tophinhanhdep.com are delivered with speed and stunning clarity.
Optimizing for Diverse Visual Design and Photography Needs
Image optimization is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The ideal approach depends heavily on the intended use case, the target audience, and the platform where the image will be displayed. Tailoring your optimization strategy is crucial for various visual design projects, high-resolution photography, and digital art applications.
Tailoring Optimization for Different Platforms
Understanding the specific requirements of each platform ensures that your images look their best and perform optimally.
- For Websites and Blogs:
- Format Choice: WebP and AVIF are increasingly becoming the preferred formats due to their superior compression efficiency, leading to faster load times compared to JPEG and PNG. For images from Tophinhanhdep.com destined for web use, converting to these modern formats can make a significant difference.
- Exact Dimensions: Always resize images to the exact dimensions they will be displayed on the page. Uploading a 4000px-wide image when it will only render at 800px is wasteful.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading, a technique where images are loaded only when they enter the user’s viewport, rather than all at once when the page loads. This improves initial page load speed, especially for image-heavy pages featuring extensive photo ideas or thematic collections.
- Compression Level: For JPEGs, a quality setting of 70-85% often provides an excellent balance for web, ensuring the beautiful photography and creative ideas from Tophinhanhdep.com are showcased effectively without excessive file size.
- For Social Media:
- Platform-Specific Dimensions: Each social media platform (Facebook, Instagram, X, Pinterest, etc.) has recommended image dimensions and aspect ratios. Adhering to these guidelines prevents the platform from automatically compressing and potentially degrading your images.
- Format Considerations: JPEG is generally good for photos, offering smaller file sizes. PNG is better for graphics, logos, or images requiring sharp text or transparency. Test images on the platform after compression to ensure they don’t appear pixelated.
- Metadata: Social media platforms often strip metadata upon upload, so explicit removal before uploading isn’t strictly necessary but can still save a tiny bit of bandwidth.
- For Emails and Messaging:
- Strict Size Limits: Emails and messaging apps often have strict file size limits (e.g., 25MB for email attachments). Large images can cause delivery delays or prevent attachment altogether.
- Lossy Compression: Aggressive lossy compression is often acceptable for these use cases, as images are typically viewed on smaller screens or as thumbnails. Aim for file sizes under 1MB per image for efficient sharing of backgrounds or aesthetic pictures.
- Resizing: Resize images to fit typical email widths (around 600-800 pixels) to ensure quick loading, even on slower mobile networks.
- For Print:
- High Resolution: Print demands high resolution. Images intended for print should typically be 300 DPI (Dots Per Inch) or higher to ensure crisp, professional-looking results.
- Format Choice: TIFF (.tiff) or high-quality PDF are often preferred formats for print, as they preserve detail and color accuracy without heavy lossy compression. Uncompressed JPEGs or lossless PNGs can also be used.
- Minimal Compression: Avoid excessive compression that can introduce artifacts, which become much more noticeable when printed. For professional prints of high-resolution stock photos or beautiful photography, lossless or very light lossy compression is recommended.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
While optimizing images, it’s easy to make mistakes that can negate the benefits or even harm the visual quality.
- Loss of Image Quality: The most common pitfall is over-compressing images, leading to visible degradation such as pixelation, blurriness, or artifacting. For the high-quality images on Tophinhanhdep.com, this can ruin the aesthetic appeal. Always preview the compressed image and adjust settings to find the optimal balance.
- Using the Wrong File Format: Employing a PNG for a complex photograph or a JPEG for a logo with transparency can lead to unnecessarily large files or undesirable visual outcomes. Understanding the strengths of each format is key.
- Metadata Loss: While often beneficial to remove, sometimes metadata (e.g., copyright information for professional photographers) needs to be preserved. Be aware of what your tools are stripping.
- Color Distortion: Heavy lossy compression can sometimes lead to subtle color shifts or washed-out tones, especially in images with delicate color gradients. Using high-quality compression tools and checking images across different displays helps mitigate this.
Best Practices for Consistent Optimization
Efficient image optimization should be an integrated part of any digital workflow, supporting consistent visual design and photo manipulation efforts.
- Test Before Saving: Always preview the compressed image alongside the original. Many tools offer a side-by-side comparison, making it easier to evaluate the quality-to-size trade-off.
- Use the Right Tool for the Job: Select tools appropriate for your needs. For batch processing many images for a new “Thematic Collections” page on Tophinhanhdep.com, a plugin like ShortPixel or a desktop batch resizer is ideal. For a single piece of digital art, Photoshop offers precise control.
- Backup Original Images: Always keep uncompressed, high-resolution originals. Once lossy compression is applied, the lost data cannot be recovered. Cloud storage or external drives are excellent for this.
- Batch Process When Handling Large Volumes: Manually optimizing dozens or hundreds of images is inefficient. Utilize bulk compression and resizing features in tools like Photoshop, Lightroom, PowerToys, or online compressors to streamline your workflow for extensive “Image Inspiration & Collections.”
- Optimize Regularly for Long-Term Efficiency: For dynamic websites like Tophinhanhdep.com, image optimization is an ongoing process. Regularly review and optimize new and existing image assets to ensure consistent performance and user experience.
By adopting these tailored strategies and best practices, creators can effectively manage image file sizes across all their projects. This not only optimizes performance but also ensures that the richness and beauty of the visual content – be it abstract art, beautiful photography, or inspiring wallpapers – from Tophinhanhdep.com are always presented in their best light.
Conclusion: The Art and Science of Visual Efficiency
In a digital landscape increasingly dominated by visual content, the ability to manage and optimize image file sizes is an indispensable skill for anyone involved in digital photography, visual design, or content creation. From the intricate details of high-resolution stock photos to the broad strokes of stunning wallpapers and backgrounds, every image benefits from thoughtful optimization.
At Tophinhanhdep.com, we understand that exceptional visual quality should not come at the cost of performance. Our mission is to provide an expansive library of images – ranging from aesthetic and nature photography to abstract and sad/emotional pieces – alongside the “Image Tools” necessary to make these visuals shine in any context. By embracing the strategies discussed in this guide – from understanding the nuances of JPEG compression and selecting appropriate file formats, to leveraging powerful desktop software, convenient online tools, and cutting-edge AI-powered solutions – you empower yourself to deliver captivating visuals with maximum efficiency.
Image optimization is truly an art and a science: the art of preserving beauty while applying the science of data reduction. Whether you’re optimizing images for faster website loading, seamless social media sharing, efficient email communication, or high-fidelity print, the principles remain consistent. Always prioritize testing, back up your originals, streamline your workflow with batch processing, and make optimization a regular practice.
By mastering how to reduce the size of your images, you contribute to a faster, more accessible, and ultimately more enjoyable digital experience for everyone. Tophinhanhdep.com is here to inspire your visual journey, and with these optimization techniques, you can ensure that every image you encounter or create leaves a lasting, positive impression. Embrace the power of visual efficiency, and unlock the full potential of your digital imagery.