How to Reverse Image Search on Google

In an increasingly visual online world, images serve as powerful tools for communication, inspiration, and information. From stunning wallpapers that adorn our digital screens to intricate digital art pieces that capture our imagination, the web is a vast gallery. But what happens when you encounter a compelling image and want to know more about its origin, its creator, or simply find similar visual content? This is where the invaluable technique of reverse image searching comes into play. Far from a niche technical skill, reverse image search is a versatile utility that empowers users to delve deeper into the visual landscape, offering insights that traditional text-based searches cannot.

For enthusiasts of high-resolution photography, graphic designers seeking creative ideas, or anyone curating thematic image collections, understanding how to effectively reverse image search is a game-changer. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, focusing primarily on Google’s robust capabilities across various devices, while also exploring alternative tools and highlighting how this skill can profoundly enhance your experience with platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com – a hub for diverse imagery, photography resources, and visual design tools.
What Is Reverse Image Search?
At its core, a reverse image search is a method of querying search engines using an image itself, rather than textual keywords. Instead of typing “beautiful nature wallpaper” into a search bar, you would upload or provide the URL of an existing nature image, and the search engine would then scour the internet to find instances of that exact image, visually similar images, and related information. It’s like turning the traditional search paradigm on its head, making the image the starting point of your exploration.
The technology behind reverse image search is sophisticated, relying on algorithms that analyze the visual characteristics of an image – its colors, shapes, textures, and patterns – to create a unique digital fingerprint. This fingerprint is then compared against billions of images indexed across the web. The results typically include not only exact matches but also various sizes of the same image, pages where the image appears, and other images that share visual similarities, allowing for a multifaceted investigation into its context and background.
Why Use Reverse Image Search?
The applications of reverse image search are incredibly diverse, extending far beyond simple curiosity. For users of Tophinhanhdep.com, who engage with a wide spectrum of visual content from aesthetic backgrounds to digital art, these applications are particularly relevant:
- Finding the Original Source or Creator: This is perhaps the most common and crucial use. If you discover a captivating image – perhaps a striking piece of abstract art or a beautiful landscape photograph – and want to give credit where it’s due, reverse image search can lead you directly to the original photographer, artist, or publisher. This is essential for ethical usage, especially for those involved in visual design or digital photography.
- Discovering More Information About an Image: An image can tell a story, but reverse image search can provide the full narrative. You might find out when and where a photo was taken, who is featured in it, or the historical context of a particular piece of visual design. This is especially useful for nature photography or historical images, allowing users to delve into the subject matter.
- Locating Higher Resolution Versions: Often, we encounter images online that are compressed or low-resolution. For those interested in high-resolution photography for wallpapers or backgrounds on Tophinhanhdep.com, a reverse image search can help you find larger, clearer versions of your favorite visuals, ensuring optimal quality for your projects or personal use.
- Identifying Plagiarism and Copyright Infringement: For content creators, photographers, and artists, reverse image search is a vital tool for protecting intellectual property. By uploading your own digital photography or graphic design work, you can ascertain if others are using your images without permission, enabling you to address potential copyright violations. This is a critical aspect for stock photo providers or those sharing unique editing styles.
- Catching “Catfish” or Verifying Authenticity: In personal contexts, reverse image search gained notoriety through shows like MTV’s “Catfish,” where it was used to expose individuals using fake profiles. If you’re suspicious about a profile picture or any image shared by an online acquaintance, a reverse search can reveal if the image is publicly available or belongs to someone else.
- Finding Similar Products or Visual Styles: Imagine you see an item in a photograph – a unique piece of furniture, a particular style of clothing, or even a specific font used in a graphic design. Reverse image search can help you find similar products to shop for, or explore related visual design elements and creative ideas, broadening your inspiration for mood boards or thematic collections.
- Exploring Thematic Collections and Inspiration: If you have an image that perfectly captures a certain aesthetic, like a sad/emotional background or a vibrant abstract piece, a reverse image search can lead you to entire collections of similar imagery. This is invaluable for generating photo ideas, building mood boards, or staying abreast of trending styles on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Understanding the Underlying Technology
The magic behind reverse image search lies in advanced computer vision and machine learning algorithms. When you submit an image, the search engine doesn’t just look for an identical pixel-by-pixel match. Instead, it processes the image to extract key features, such as:
- Color Distribution: Analyzing the dominant colors and their patterns.
- Shape and Edges: Identifying objects, outlines, and structures within the image.
- Texture and Patterns: Recognizing repetitive elements or surface qualities.
- Composition: Understanding the spatial arrangement of elements.
These visual attributes are then converted into a numerical representation – a “vector” or “feature descriptor” – which acts as the image’s unique signature. This signature is then compared against a massive database of pre-indexed image signatures. When a close match is found, the associated information (websites, similar images, metadata) is retrieved and presented to the user. This intelligent approach allows for robust search results, even if the image has been cropped, resized, or slightly altered, making it a powerful tool for visual discovery and verification.
Performing Reverse Image Search on Google
Google remains the most popular and often the most effective platform for reverse image search due to its extensive image indexing and sophisticated algorithms. The methods vary slightly depending on whether you’re using a computer or a mobile device.

Reverse Image Search On A Computer
Performing a reverse image search on your desktop or laptop is straightforward, offering several intuitive methods to upload your visual query.
Uploading Images from Your Local Files
This is one of the most direct ways to search with an image you have saved on your computer:
- Navigate to Google Images: Open your preferred web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, etc.) and go to
images.google.com. - Locate the Camera Icon: In the search bar, you’ll see a small camera icon (representing “Search by image”). Click on it.
- Choose Your Upload Method: A pop-up window will appear, presenting two options:
- “Upload an image”: Click the “Choose file” button. This will open your computer’s file explorer, allowing you to browse and select the image you wish to search with.
- Drag and Drop: Alternatively, you can simply drag an image file from your desktop or a folder directly into the “Drop your image here” section of the pop-up.
- Initiate the Search: Once the image is uploaded (either by choosing the file or dragging it), Google will automatically begin processing and display your search results. These results typically include the image itself, suggested keywords, links to pages where the image appears, and visually similar images, which can be great for finding more aesthetic backgrounds or creative ideas for your visual design projects on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Searching with a Direct Image URL
If the image you want to search is already online and you don’t need to save it, you can use its URL:
- Obtain the Image URL: Right-click on the image you want to search (in a web browser) and select “Copy image address” or “Copy image URL.” (The exact wording might vary between browsers). If the image is the only content on the page, you might need to right-click and select “Open image in new tab” first, then copy the URL from the address bar.
- Navigate to Google Images: Go to
images.google.com. - Click the Camera Icon: As before, click the “Search by image” camera icon in the search bar.
- Paste the URL: In the pop-up window, select the “Paste image URL” tab. Right-click in the text field and choose “Paste,” or use the keyboard shortcut (Ctrl+V on PC, Command+V on Mac) to insert the copied URL.
- Perform the Search: Click the “Search by image” button. Google will then fetch the image from the provided URL and present its findings, helping you identify sources for high-resolution photography or discover new thematic collections.
Reverse Image Search On Mobile Devices
Reverse image searching on mobile devices has become incredibly convenient, primarily through Google’s dedicated apps and mobile browser functionalities.
Using the Google App (Chrome App, Google App)
The Google Chrome app and the standalone Google app offer the most streamlined experience for mobile reverse image searches on both Android and iOS devices. Safari, by itself, doesn’t natively support this without a workaround.
- Download and Open the App: Ensure you have either the Google Chrome app or the Google app installed on your smartphone. Open the app.
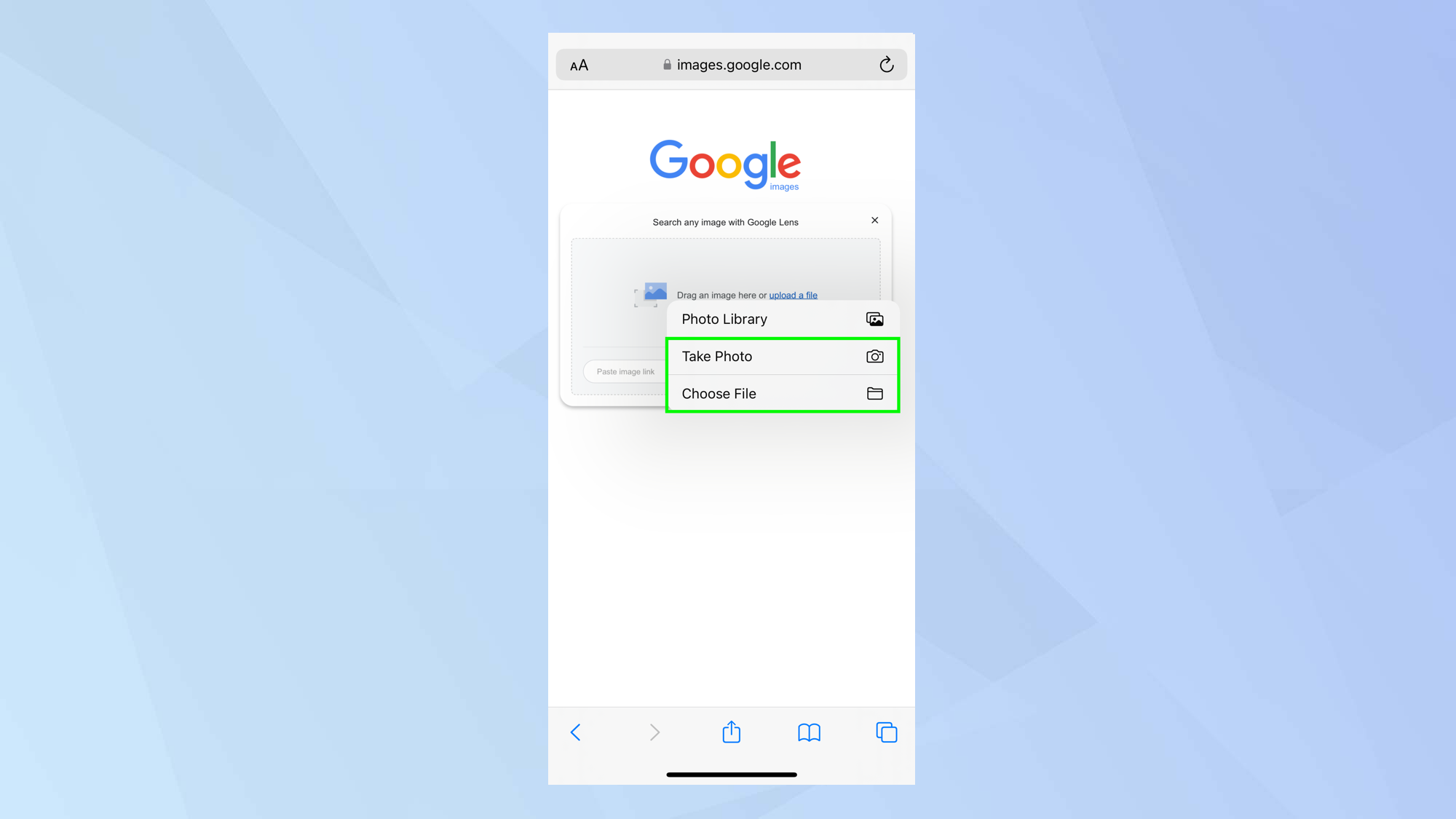
- Access the Camera Icon (Google Lens): In the search bar of the Google app (or if you navigate to images.google.com in Chrome), you’ll find a camera icon, which represents Google Lens. Tap this icon.
- Grant Permissions: If it’s your first time using it, the app will likely ask for permission to access your device’s camera and photo gallery. Grant these permissions.
- Select Your Image Source:
- From Gallery/Camera Roll: Your recent photos will appear. Simply tap on the image you wish to search from your gallery.
- Take a New Photo: Tap “Search with your camera” (or a similar option) to open your phone’s camera. Point it at an object or image you want to search and take a picture. The app will then analyze it.
- From Search Results: If you’ve already performed a text-based image search within the Google app, tap on an image from the results, then look for the Google Lens icon (the camera icon) usually in the bottom-left corner of the image preview. Tapping this will initiate a reverse image search on that specific result.
- Explore Results: Google Lens is intelligent; it can often identify specific elements within an image (e.g., a shirt, a plant, a landmark). You can select different parts of the image to refine your search. The results will include visual matches, related products, and informative links, which is perfect for finding specific items for creative ideas or identifying subjects in nature photography.
The Desktop Site Workaround for Mobile Browsers
If you prefer not to use the dedicated Google or Chrome app, or if you’re using a browser like Safari on iOS that doesn’t natively support image uploads on its mobile version of Google Images, there’s a workaround:
- Open Google Images in Your Browser: Navigate to
images.google.comin your mobile browser. - Request Desktop Site: You’ll notice the camera icon is missing. To reveal it:
- On iPhone (Safari): Tap the “AA” icon on the left side of the address bar, then select “Request Desktop Website.”
- On Android (Chrome): Tap the three vertical dots (menu icon) in the top-right or bottom-right corner, then check the “Desktop site” box.
- The page will refresh, displaying the desktop version of Google Images with the familiar camera icon.
- Upload Your Image: Tap the camera icon. You’ll then be presented with “Paste image URL” and “Upload an image” options, similar to the desktop experience.
- Upload from Photo Library: Select “Upload an image,” then “Choose File,” and pick your image from your phone’s photo library.
- Paste URL: If the image is online, copy its URL from the web, then select “Paste image URL” and paste it into the field.
- View Results: After uploading or pasting, the search results will load, providing information, similar visuals, and sources, aiding in your quest for aesthetic backgrounds or photo ideas.
Recommended Third-Party Mobile Applications
While Google’s native solutions are powerful, several third-party apps specialize in reverse image search, often offering simplified interfaces or additional features:
- Google Lens (Android/iOS): While an official Google app, it’s worth reiterating its standalone power. It’s excellent for on-the-fly identification and shopping.
- Reversee (iOS): This popular free app streamlines the process for iPhone users, often bypassing the multi-step desktop site workaround. It quickly connects to Google, Bing, and TinEye for searches.
- Photo Sherlock (Android/iOS): Another highly-rated free app that allows users to pick images from their gallery or take new photos and search Google with ease, providing quick results for finding high-resolution photography or tracking down original art.
Leveraging Google Lens for Enhanced Image Search
New Google Lens Feature For Desktop In Chrome
Google Lens, initially a mobile-first feature, has been progressively integrated into the desktop version of Chrome, transforming how users interact with images on their computers. This enhancement allows for incredibly precise visual searches directly from your browser, making it a powerful tool for Tophinhanhdep.com users engaged in visual design or collecting image inspiration.
Google Lens on desktop is more than just a reverse image search; it’s an intelligent visual analysis tool. You can use it to:
- Identify Objects and Products: Select a specific item within an image (e.g., a plant, a piece of clothing, a landmark) to get information, find similar products to shop, or identify its species. This is fantastic for graphic designers looking for specific elements or individuals curating thematic collections based on objects.
- Extract Text: Lens can recognize text within an image, allowing you to copy it, translate it, or search for it. This can be invaluable for image-to-text functionality, helping you understand captions or information embedded in creative ideas.
- Visual Search Refinement: Once you search an image, Lens provides interactive results. You can highlight another area of the same image to perform a new, more specific search without starting over.
How to Use Google Lens on Desktop Chrome:
- Right-Click on an Image: When you encounter an image on any webpage in Chrome, simply right-click on it.
- Select “Search image with Google Lens”: From the context menu that appears, choose this option.
- Crop or Highlight: A side panel will open on the right side of your browser. You can either let Lens analyze the entire image or, more powerfully, click and drag a box to highlight a specific part of the image you want to search.
- View Results: The side panel will immediately display search results based on your selection, including visually similar images, identified objects, related information, and external links. This seamless integration makes discovering new aesthetic backgrounds or finding sources for high-resolution photography incredibly efficient.
This desktop integration of Google Lens vastly expands the utility of reverse image search, blurring the lines between searching with an entire image and querying specific elements within it.
Exploring Beyond Google: Alternative Reverse Image Search Tools
While Google reigns supreme, a holistic approach to reverse image search often involves leveraging other specialized tools. Each platform offers unique strengths, indexing different parts of the web or employing distinct algorithms, which can sometimes yield results that Google might miss. For Tophinhanhdep.com users, exploring these alternatives ensures a comprehensive search for everything from stock photos to creative ideas.
Bing Reverse Image Search
Microsoft’s Bing offers its own capable visual search engine, often integrated with its main search functionality. It provides a clean interface and can be particularly useful for finding pages that include an image, as well as visually similar content.
How to Use Bing for Reverse Image Search:
- Access Bing Images: Go to
bing.com/imagesin your web browser. - Locate the Visual Search Icon: In the search bar, you’ll see a camera icon (sometimes labeled “Visual search” or a magnifying glass with a camera). Click it.
- Upload or Paste: Bing offers several ways to input your image:
- Browse: Click “Upload an image” or “Browse” to select a file from your computer.
- Drag and Drop: Drag an image directly into the search box.
- Paste Image or URL: You can paste an image directly from your clipboard or paste an image URL.
- Take Photo (Mobile): On mobile, Bing allows you to directly take a photo using your camera for immediate search.
- Review Results: Bing’s results are typically categorized into “Similar images,” “Pages including this image,” and “Related searches.” Unlike Google, Bing sometimes allows uploading multiple images at once, which can be useful for comparing several images from your mood boards or thematic collections on Tophinhanhdep.com. The “Pages Including” tab is particularly strong for tracing sources of stock photos or beautiful photography.
TinEye: The Original Image Detective
TinEye stands out as one of the pioneers in reverse image search and remains a top choice for its singular focus: finding where an image originated and where else it has appeared online. It prides itself on its “image recognition technology,” rather than relying on metadata or keywords, making it an excellent tool for copyright holders and those tracing image lineage.
How to Use TinEye for Reverse Image Search:
- Visit TinEye: Go to
tineye.com. - Upload or Paste: The homepage is minimalistic, featuring a search bar with an upload button and a field for pasting URLs.
- Upload: Click the upward-pointing arrow icon to browse and select an image from your computer.
- Paste URL: Paste the image’s URL directly into the search bar.
- Drag and Drop: You can also drag an image from an open browser tab directly onto the TinEye homepage.
- Analyze Results: TinEye meticulously searches its vast database (which includes billions of images) and presents all instances of your image it can find.
- Filtering Options: A key advantage of TinEye is its robust filtering options. You can sort results by:
- Best Match: Prioritizes images with the highest visual similarity.
- Most Changed: Shows images that have been most altered from the original.
- Newest/Oldest: Helps in dating an image or finding its first appearance.
- Image Size: Useful for finding high-resolution versions for your wallpapers or backgrounds.
- Collection/Website: Allows you to narrow down results to specific sources or websites.
- This makes TinEye exceptionally powerful for identifying plagiarism, finding higher-resolution versions, or tracing the evolution of a particular piece of digital art or photo manipulation. Many professionals consider TinEye an indispensable part of their image research toolkit.
- Filtering Options: A key advantage of TinEye is its robust filtering options. You can sort results by:
Other Search Engines and Browser Extensions
Beyond Google, Bing, and TinEye, several other platforms and tools offer reverse image search capabilities, each with its own niche or approach:
- Yandex Images: The Russian search engine Yandex has a very strong image search function. Similar to Google, it allows users to upload images or paste URLs to find similar visuals and sources. Yandex is particularly good at facial recognition and can sometimes find results that other engines miss, making it valuable for verifying identities or finding related portrait photography.
- Baidu Images: China’s dominant search engine, Baidu, also includes reverse image search. While its interface is primarily in Chinese, it can be effective for searching images within the vast Chinese internet ecosystem. It’s mobile-friendly, allowing direct uploads from phones.
- Browser Extensions: Many developers have created browser extensions to simplify the process. Examples include:
- RedEye Reverse Vision (Chrome): This extension allows you to right-click on any image in your browser and instantly perform a reverse image search across multiple engines (Google, Bing, Yandex, TinEye) simultaneously. This is a massive time-saver for visual designers and content curators.
- Similar extensions exist for Firefox and other browsers, offering a quick shortcut to initiate searches without navigating to a dedicated website.
- ChatGPT and AI Integration: Newer developments like ChatGPT’s ability to “see” and interpret images, or other AI-powered tools like Ask Photos on Pixel phones, represent the next frontier. While not traditional reverse image search engines, they can take an image and provide contextual information, generate descriptions, or even suggest related creative ideas based on visual input. This blends the functions of image-to-text and visual search in innovative ways.
- Specialized Platforms (e.g., eBay’s Shopbot): Some platforms integrate reverse image search for specific purposes. eBay’s Shopbot, for example, allows users to upload an image of a product they’re looking for, facilitating visual shopping. This showcases how image search extends beyond general web content to specialized e-commerce and information retrieval.
These diverse tools mean that if one search engine doesn’t yield the desired results, another might hold the key. For comprehensive image research, particularly for finding unique aesthetic backgrounds, verifying stock photos, or gathering detailed photo ideas, combining these resources offers the best chance of success.
Harnessing the Power of Visual Search for Tophinhanhdep.com Users
For the vibrant community that gravitates towards Tophinhanhdep.com – a platform dedicated to exquisite imagery, professional photography, versatile image tools, innovative visual design, and boundless image inspiration – reverse image search isn’t just a technical trick; it’s a fundamental skill that unlocks a world of creative and practical possibilities. Understanding how to apply this powerful tool within the context of the website’s main topics can significantly enhance your experience and output.
Applying Reverse Image Search in Visual Design and Photography
The intersection of reverse image search with visual design and photography is rich with potential.
- Discovering Original Artists and Their Portfolios: If you encounter a piece of digital art or a stunning photograph that aligns with your aesthetic, a reverse image search can lead you directly to the artist’s portfolio. This is invaluable for graphic designers seeking inspiration, allowing them to explore an artist’s entire body of work, understand their editing styles, and even commission original pieces, contributing to a broader pool of creative ideas.
- Tracing Copyright and Usage Rights for Stock Photos: For professionals who frequently use stock photos or contribute their own high-resolution photography, verifying usage rights is paramount. A reverse image search can help ascertain if an image is freely available, under a specific license, or belongs to a stock photography site. This prevents inadvertent copyright infringement and ensures ethical practice in your visual design projects.
- Analyzing Photo Manipulation and Creative Techniques: When you see an image with a particularly striking photo manipulation or an innovative creative idea, reverse image search can help find discussions, tutorials, or breakdowns related to how that effect was achieved. This is a powerful learning tool for aspiring photographers and digital artists looking to refine their skills and expand their repertoire of editing styles.
- Ensuring Uniqueness for Graphic Design Projects: Before incorporating a found image into a graphic design, a quick reverse search can confirm its prevalence online. This ensures your designs stand out and aren’t using an overused or easily recognizable visual element, maintaining originality and impact.
- Finding Optimal Image Dimensions for Specific Uses: For wallpapers, backgrounds, or specific digital art installations, the exact dimensions and resolution of an image matter. Reverse image search, particularly with tools like TinEye, can efficiently locate all available sizes of an image, helping you find the perfect fit for your project and ensuring high-resolution quality.
Enhancing Image Collections and Inspiration
Tophinhanhdep.com thrives on inspiring its users with diverse image collections, from nature’s tranquility to abstract dynamism. Reverse image search amplifies this by turning a single image into a gateway for further exploration.
- Expanding Thematic Collections and Mood Boards: Start with one image that perfectly encapsulates a theme – perhaps a vintage aesthetic background, a sad/emotional portrait, or a specific nature scene. A reverse image search will unearth a wealth of visually similar images, allowing you to rapidly build extensive mood boards or expand your thematic collections. This is invaluable for visual designers planning a project or anyone curating a personal gallery.
- Discovering Trending Styles and Aesthetics: By reverse searching images that catch your eye – perhaps an abstract design or a unique photography style you’ve seen trending – you can quickly find other works within that style, identify key characteristics, and understand its popularity. This keeps your image inspiration fresh and relevant to current trends.
- Generating New Photo Ideas: If you have a photograph you admire, a reverse search can show you how other photographers have approached similar subjects, compositions, or lighting. This comparative analysis can spark new photo ideas and encourage experimentation with different digital photography techniques or editing styles.
- Curating High-Quality Wallpapers and Backgrounds: A user finds a breathtaking nature wallpaper but it’s too small for their ultrawide monitor. Reverse image search can help locate the same image in higher resolutions or discover alternative, equally stunning nature wallpapers from the same source or artist, ensuring Tophinhanhdep.com users always have access to premium visuals.
- Utilizing Image Tools with Found Visuals: Imagine you find an inspiring image but it’s low resolution. After using reverse image search to find the highest available quality, you can then leverage Tophinhanhdep.com’s image tools like AI upscalers to further enhance it, or use compressors and optimizers for web usage. If the image contains text you want to adapt, an image-to-text tool can extract it, showing how these tools integrate seamlessly with visual discovery.
Troubleshooting and Tips for Effective Searching
While reverse image search is powerful, it’s not without its nuances. Here are some tips to maximize your success and address common challenges:
- Start with the Best Quality Image: The clearer and less cropped your starting image, the better the search engine can analyze its features and provide accurate results. If you have multiple versions, try the highest resolution one first.
- Try Multiple Search Engines: As noted, Google, Bing, TinEye, and Yandex use different indexing methods and algorithms. If one doesn’t yield results, another might. For critical searches (e.g., copyright verification), always perform a multi-platform search.
- Refine Your Search with Google Lens: If you’re looking for something specific within a complex image, use Google Lens’s cropping feature to isolate the object of interest.
- Consider Image Alterations: If an image has been heavily edited, mirrored, or had significant elements added/removed, direct matches might be harder to find. Search for the most original-looking version if possible.
- “Why Reverse Image Search Sometimes Doesn’t Work?”: Sometimes, you might get zero results. This can happen if:
- The image is very new or obscure: It might not yet be indexed by major search engines.
- The website prevents indexing: Some sites use
robots.txtfiles or other methods to prevent search engines from crawling and indexing their images. - Data centers are out of sync: Rarely, temporary discrepancies in search engine databases can affect results.
- The image is truly unique and has never been shared online.
- Save Images Ethically: Always be mindful of copyright. Finding an image through reverse search doesn’t automatically grant you permission to use it. Always seek permission from the creator or verify its license.
By mastering reverse image search, users of Tophinhanhdep.com and anyone deeply invested in the visual world gain a powerful detective tool. It empowers you to navigate the vast ocean of online imagery with greater confidence, creativity, and ethical awareness, transforming passive viewing into active discovery and informed engagement with the digital canvas. Whether you’re hunting for the perfect aesthetic background, tracing the origins of a groundbreaking piece of digital art, or simply seeking inspiration for your next high-resolution photography project, reverse image search is your indispensable ally.