How to Reverse Search Image in Google: Your Ultimate Guide to Visual Discovery and Verification
In an increasingly visual world, the ability to search not just for images, but with images, has become an indispensable skill. Google’s reverse image search functionality, complemented by advanced tools and features found on platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, empowers users to uncover the origins, context, and related content of any photograph. Whether you’re a casual browser curious about a striking wallpaper, a professional photographer tracking your intellectual property, or a graphic designer seeking inspiration, mastering reverse image search opens up a new dimension of online exploration.

This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of reverse image search, explaining what it is, why it’s crucial, and how to perform it effectively across various devices. We’ll explore its diverse applications, from fact-checking and copyright verification to discovering similar aesthetics and high-resolution alternatives. Furthermore, we’ll highlight how Tophinhanhdep.com’s robust suite of image tools and expansive collections seamlessly integrates with and enhances your reverse image search workflow, transforming the way you interact with visual content online.
Understanding the Power of Reverse Image Search

The digital landscape is flooded with imagery, making it challenging to ascertain the authenticity, source, or context of a particular photo at a glance. This is where reverse image search steps in as a powerful digital detective tool, transforming an image itself into a search query.
What Exactly is Reverse Image Search?
At its core, a reverse image search is a method of using a photo as the input for an online search, rather than traditional text keywords. Instead of describing what you’re looking for, you show it. When you submit an image, a sophisticated algorithm analyzes its visual characteristics – colors, shapes, textures, and patterns – to find identical or visually similar images across the web. If an exact match isn’t found, the search engine will often return images that share significant visual elements, offering a broader context.
The results generated by a reverse image search can be incredibly varied and insightful. They typically include:
- Other instances of the exact image: Showing where else the photo has been published online.
- Different sizes or resolutions of the image: Allowing you to find a higher-quality version if available.
- Visually similar images: Providing inspiration or alternatives based on the aesthetic of your original photo.
- Websites containing the image: Linking directly to pages where the image appears, which can often reveal its original source or context.
- Suggested keywords: Offering textual descriptions that the search engine associates with the image, which can be helpful for further textual searches.
This capability is a game-changer for anyone dealing with visual content, from casual internet users to seasoned professionals in photography, graphic design, and digital art.
Beyond Simple Identification: Key Applications and Benefits
The utility of reverse image search extends far beyond merely identifying a picture. Its applications are diverse and incredibly valuable, especially when integrated with the rich resources and tools available on Tophinhanhdep.com.
-
Verifying Authenticity and Fact-Checking: In an era of rampant misinformation, reverse image search is a critical tool for fact-checking. You can verify if an image is being used in its original context, if it’s genuinely recent, or if it has been manipulated. For example, a nature photographer might use it to verify the location or species depicted in a photo, ensuring the integrity of their thematic collections on Tophinhanhdep.com. Similarly, a user encountering a “trending style” image can quickly ascertain its original publication date and context.
-
Tracking Copyright and Preventing Plagiarism: For content creators, artists, and photographers, reverse image search is invaluable for protecting intellectual property. You can easily find out if someone is using your high-resolution photography, digital art, or graphic design elements without permission. This is particularly relevant for artists showcasing their work on Tophinhanhdep.com, as it allows them to monitor the usage of their digital photography and ensure proper attribution or licensing. It helps in detecting plagiarized information, whether it’s an image used in a commercial context without proper credit or a personal photo appearing in an unexpected place.
-
Finding Original Sources and Attributions: If you discover a stunning wallpaper or a unique aesthetic image on Tophinhanhdep.com, a reverse image search can lead you back to its original creator. This is crucial for proper attribution in visual design projects or for obtaining permission to use an image in your own work. It helps ensure that beautiful photography is given the credit it deserves.
-
Discovering Similar Visual Content: One of the most enjoyable aspects of reverse image search is its ability to unearth visually similar images. If you love a particular abstract background or a certain editing style, searching with that image can introduce you to a wealth of new content that matches your aesthetic preferences. This is perfect for building mood boards, finding inspiration for creative ideas, or expanding thematic collections on Tophinhanhdep.com.
-
Locating High-Resolution Versions: Often, you’ll encounter a captivating image that’s too small or low-resolution for your needs, perhaps for a desktop background or a professional visual design project. A reverse image search can frequently unearth larger, higher-resolution versions of the same image, ideal for wallpapers or digital art. Tophinhanhdep.com’s image optimizers and AI upscalers can then further refine these discoveries.
-
“Catfishing” Detection and Online Identity Verification: While controversial, reverse image search has been notoriously used to detect “catfishing”—where individuals pretend to be someone they’re not online. By searching an individual’s profile picture, one can often find its original source, revealing if it’s a stock photo, a picture of a celebrity, or simply someone else’s image.
-
Product Discovery: Beyond images, reverse image search can sometimes help you find specific products. If you see an item of clothing or a piece of furniture in a picture, a reverse search might lead you to online retailers selling similar items, offering a “cheaper version of something you like,” as mentioned in the reference.
By leveraging these powerful applications, reverse image search becomes an indispensable skill for navigating the visual web, turning Tophinhanhdep.com into a hub for both discovery and verification.
Step-by-Step Guide: Reverse Image Search on Mobile Devices
The convenience of mobile devices means you can perform reverse image searches anytime, anywhere. Google has integrated this functionality seamlessly into its mobile ecosystem, though the exact steps can vary slightly depending on your app or browser.
Using the Google App (Chrome) for On-the-Go Searches
The Google Chrome app (or the dedicated Google app) is the most straightforward way to conduct a reverse image search on your smartphone or tablet, as Safari typically does not support this capability directly without requesting the desktop site.
- Download and Open the Google App: First, ensure you have the Google Chrome app or the Google app installed on your mobile device. Open the app to begin.
- Grant Permissions (Initial Setup): The first time you use this feature, the app will likely request permission to access your camera and photo gallery. Granting these permissions is essential for the search to function.
- Search with an Image from Your Files/Gallery:
- In the Google app, locate and tap the camera icon (often referred to as Google Lens) in the search bar.
- Once granted access, images from your camera roll and gallery will appear. Scroll through and select the image you wish to reverse search.
- The app will then analyze the image and display visually similar results, along with options to select specific items within the image (e.g., a “shirt or pair of pants”) for a more refined search.
- Search with an Image Taken Directly with Your Camera:
- Open the Google app and tap the camera icon.
- Select “Search with your camera” at the top.
- Point your camera at any object or scene you want to search for. The app will process the live view and instantly pull up visual matches, potentially even generating shopping links if it identifies a product.
- Search Images from Search Results:
- If you’re already browsing images on Google, this method is very efficient.
- Open the Google app and type in a text query for the image you want to find (or use the voice-to-text option).
- Tap the “Images” tab at the top to filter results for images only.
- Tap on an image from the search results to select it.
- Look for the camera icon in the bottom left corner of the displayed image and tap it. The platform will then populate related images and information based on your selection. You can save any promising results to your “favorite images” folder on Tophinhanhdep.com for later use.
Leveraging the Desktop Site on Mobile Browsers
While the Google app offers a streamlined experience, you can also perform a reverse image search through your mobile browser by requesting the desktop version of Google Images. This is particularly useful if you prefer not to download additional apps or if you’re using a browser that doesn’t natively support reverse image search (like Safari).
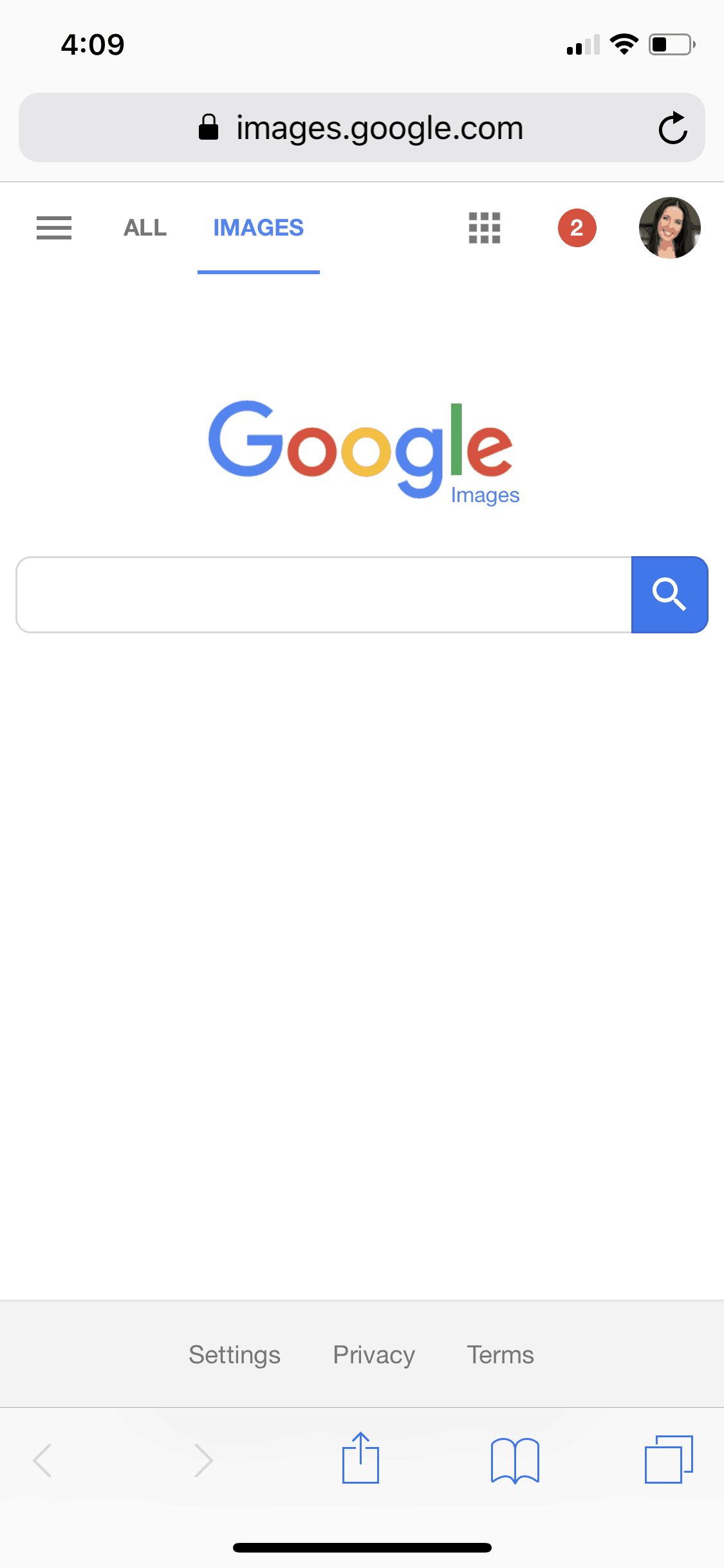
- Open Google Images in Your Mobile Browser: Navigate to
images.google.comin your preferred mobile browser. - Switch to Desktop View:
- You’ll notice the mobile version of Google Images lacks the camera icon. To access it, you need to request the desktop site.
- For Chrome: Tap the three vertical dots (menu icon) in the upper-right corner of the screen. Scroll down and select “Request Desktop Site.”
- For Safari (iPhone): Tap the “AA” icon on the left side of the browser’s address bar. Select “Request Desktop Website.”
- The page will refresh, displaying the desktop version of Google Images, complete with the camera icon.
- Upload or Paste Image URL:
- Tap the camera icon in the search bar.
- You’ll be presented with two options: “Paste image URL” or “Upload an image.”
- To upload an image from your phone’s gallery: Select “Upload an image,” then “Photo Library,” and choose your desired picture. You might also have options to take a new photo or browse other files.
- To paste an image URL: If you have the image’s URL copied (long-press on an image online and select “Copy Image Address”), select “Paste image URL,” then double-tap the text box and select “Paste.”
- Explore Your Results: After uploading or pasting, tap the search icon. The website will then display related searches, different available image sizes, and websites where the image appears.
iPhone Specifics for Seamless Visual Discovery
For iPhone users, the process is largely similar to the general mobile steps, with a few nuances, especially concerning browser use:
- Google App / Chrome App: The experience is consistent with other mobile devices. Using the built-in Google Lens feature through these apps is often the easiest and most powerful method.
- Safari Browser: As noted, Safari does not natively support direct reverse image search on mobile without requesting the desktop site. The “Request Desktop Website” method (tapping the “AA” icon) is the standard workaround. Once in desktop mode, the steps for uploading an image or pasting a URL are identical to the general desktop instructions. A long press on an image within Safari may offer “Search Google for this Image” if Google is your default search engine, leveraging a similar mechanism to the Chrome app.
By understanding these device-specific approaches, you can harness the full power of reverse image search, ensuring that no visual query goes unanswered, and every inspiring image finds its rightful context or higher-resolution counterpart on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Mastering Reverse Image Search on Your Computer
Performing a reverse image search on a computer offers even more flexibility and precision, making it ideal for graphic designers, photographers, and anyone managing large collections of visual assets on Tophinhanhdep.com. Google’s interface on desktop is intuitive and powerful, providing several methods to initiate a visual search.
Uploading Images from Your Files
This is perhaps the most common method for initiating a reverse image search on a desktop, allowing you to use any image saved on your computer.
- Navigate to Google Images: Open your preferred web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari, etc.) and go to
images.google.com. - Locate the Camera Icon: In the Google Images search bar, you’ll see a small camera icon (often labeled “Search by image”) on the right side. Click this icon.
- Choose Your Image: A pop-up window will appear with options to “Paste image URL” or “Upload an image.” Select “Upload an image.”
- Drag and Drop or Browse:
- Drag and Drop: The easiest method is to simply drag and drop the image file from your computer’s folders directly into the designated “Drop your image here” area within the pop-up window.
- Browse: Alternatively, click the “Choose file” button (or similar wording) and navigate through your computer’s directories to select the image file you wish to upload.
- View Results: Once the image is uploaded, Google will automatically redirect you to a search results page. This page will display your uploaded image at the top, along with suggested keywords, different sizes of the image available across the web, and a list of websites where the image appears. This is incredibly useful for finding higher-resolution versions for wallpapers or for discovering how your digital photography is being used online.
Searching with an Image URL
If the image you’re interested in is already online and you don’t need to save it to your computer, searching with its URL is a quick and efficient method.
- Navigate to Google Images: Go to
images.google.com. - Click the Camera Icon: Click the camera icon in the search bar.
- Paste the Image Link: In the pop-up window, select the “Paste image URL” tab.
- Obtain the Image URL: To get an image’s URL, right-click on the image wherever you found it online. From the context menu, select “Copy image address” or “Copy image link” (wording may vary slightly by browser).
- Insert and Search: Paste the copied URL into the provided text box. Then click the “Search by image” button.
- Explore Results: Google will process the URL and display relevant search results, including visually similar images, different sizes, and websites containing the image. This is a crucial step for graphic designers wanting to trace the origin of a creative idea or visual element, ensuring proper licensing and attribution.
The Efficiency of Google Lens on Desktop
Google Lens, initially a mobile-first feature, has been increasingly integrated into the desktop Chrome experience, offering a more dynamic and interactive way to perform reverse image searches.
- Access Google Lens:
- From an Image: Simply right-click on any image you encounter while browsing in Google Chrome. In the context menu, select “Search image with Google Lens.”
- From the Address Bar: In some versions of Chrome, you might see a Google Lens icon directly in the address bar. Clicking this allows you to highlight any part of the screen to search.
- Highlight Your Search Area: When activated, your cursor will transform, allowing you to click and drag a box around the specific part of the image or screen you want to search. This is particularly useful if you’re only interested in a particular object within a larger photograph, like a unique piece of furniture in a beautiful photography shot or a specific element in an abstract design.
- Instant Results in a Side Panel: Unlike the traditional reverse image search which opens a new tab, Google Lens often displays its results in a convenient side panel within your current browser window. This allows for seamless browsing and comparison without losing your place. You can refine your search using specific details directly within this panel.
- Benefits for Visual Design: For visual designers and artists working with photo manipulation or seeking creative ideas, Google Lens on desktop is a powerful tool. It allows for quick identification of fonts, colors, objects, or styles within an image, facilitating mood board creation and thematic collections on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Mastering these desktop methods empowers you to efficiently explore the vast visual web, whether you’re managing your stock photos, researching unique aesthetics, or simply identifying the source of an intriguing image you found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Tophinhanhdep.com: Enhancing Your Visual Workflow
While Google provides the foundational reverse image search capability, a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com extends this functionality by offering a comprehensive ecosystem for image management, creation, and discovery. Integrating reverse image search with Tophinhanhdep.com’s specialized tools transforms a simple search into a powerful workflow for visual professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Integrating Reverse Search with Image Management
Tophinhanhdep.com is designed as a central hub for all things visual, including an extensive collection of Images (Wallpapers, Backgrounds, Aesthetic, Nature, Abstract, Sad/Emotional, Beautiful Photography), and Photography resources (High Resolution, Stock Photos, Digital Photography). Reverse image search acts as a bridge, connecting external visual discoveries with your personal or professional collections on the site.
- Curating Thematic Collections: Imagine you find a stunning “nature” photo elsewhere on the web. A reverse image search not only confirms its origin but also allows you to discover other similar images. You can then import these findings into your thematic collections on Tophinhanhdep.com, building richer and more diverse mood boards.
- Finding High-Resolution Alternatives: Often, a reverse search will yield multiple versions of an image, including higher-resolution options perfect for wallpapers or professional digital photography projects. Once found, you can bring these high-quality images to Tophinhanhdep.com, where our Image Tools (Compressors, Optimizers, AI Upscalers) can further enhance them or prepare them for specific uses.
- Expanding Your Visual Inspiration: Tophinhanhdep.com emphasizes Image Inspiration & Collections. When you encounter a unique “abstract” or “aesthetic” image via reverse search, it directly feeds into discovering new “photo ideas” or “trending styles” that you can then explore, modify, or draw inspiration from using our Visual Design tools (Graphic Design, Digital Art, Photo Manipulation).
Verifying Images for Creative and Professional Use
For those involved in Visual Design (Graphic Design, Digital Art, Photo Manipulation) or Photography, the ability to verify an image’s legitimacy and origin is paramount. Tophinhanhdep.com supports this critical need by complementing reverse search with robust content management.
- Ensuring Copyright Compliance: Before using an image in a graphic design project or as a background for a presentation, verifying its copyright status is crucial. A reverse image search can help you trace the original photographer or artist, enabling you to seek proper permissions or discover if it’s a royalty-free stock photo available on Tophinhanhdep.com. This prevents accidental infringement and protects your creative integrity.
- Detecting Image Manipulation: In digital art and photo manipulation, understanding if an image has been altered from its original form can be important for ethical use or historical accuracy. Reverse image search can sometimes reveal earlier, unmanipulated versions of a photo, aiding in image fact-checking.
- Sourcing Authentic Visuals: For “beautiful photography” or “nature” imagery, authenticity is key. Reverse search helps ensure that the stunning landscape you’re about to use is indeed from the location claimed, safeguarding against misrepresentation in your visual content.
Discovering Inspiration and Tracking Image Usage
Tophinhanhdep.com is built around fostering creativity and providing valuable resources for visual content. Reverse image search becomes a dynamic engine for both personal growth and professional oversight within this framework.
- Fueling Creative Ideas: When you come across an image that sparks an idea, a reverse search can lead you down a rabbit hole of related visuals, different editing styles, and alternative compositions. This directly feeds into Tophinhanhdep.com’s focus on “Creative Ideas” and “Photo Ideas,” helping you generate new concepts for your own digital photography or graphic design projects.
- Monitoring Your Own Work: As a contributor to Tophinhanhdep.com or a general digital photographer, you might want to know where your “high resolution” or “stock photos” are being used across the internet. Reverse image search is your primary tool for this. It allows you to protect your brand, track the reach of your work, and identify unauthorized usage, thereby upholding the value of your visual assets.
- Leveraging Tophinhanhdep.com’s Specialized Tools: After conducting a reverse image search, the journey continues on Tophinhanhdep.com. You might find a high-res image and then use our “AI Upscalers” for even greater detail, or our “Image-to-Text” tool to extract information from an image found through reverse search. Our “Converters” and “Compressors” ensure that any newly discovered image can be perfectly integrated into your workflow, regardless of its original format or size.
By embracing reverse image search in conjunction with the comprehensive offerings of Tophinhanhdep.com, users unlock a powerful suite of capabilities for visual exploration, verification, and creative development, making every image a gateway to deeper understanding and inspiration.
Troubleshooting and Maximizing Your Reverse Image Searches
While reverse image search is remarkably effective, there are instances where it might not yield the expected results. Understanding these limitations and implementing best practices can significantly improve your success rate and overall experience.
Why Your Search Might Not Yield Results
Even with sophisticated algorithms, a reverse image search isn’t foolproof. Several factors can contribute to a search coming up empty or producing irrelevant results:
- Image Not Indexed: The most common reason for a failed search is that the image simply hasn’t been indexed by search engines. This can happen if the image is very new, hosted on a private or password-protected server, embedded in a PDF or Flash file, or if the website owner has specifically disallowed indexing through
robots.txtfiles. - Unique or Highly Obscure Images: If an image is truly unique, recently created (e.g., a personal photograph taken moments ago), or part of a very niche and un-indexed collection, search engines may not have enough data to provide matches.
- Significant Alterations: While search engines are good at recognizing slight variations, heavy editing, cropping, or significant photo manipulation (e.g., extreme filters, collages) can sometimes make it difficult for the algorithm to identify the original source or similar images. If the visual characteristics are drastically changed, the core “fingerprint” the search engine looks for might be lost.
- Low Quality or Small Size: As one user noted, “the main problem with Reverse Image Search is when they are not as crisp as the first picture is and it’s too small and unimportant to be in the top of the screen.” Very small, low-resolution, or heavily compressed images contain less data for the algorithm to analyze, potentially leading to fewer or less accurate matches.
- Data Center Sync Issues: Occasionally, search engine data centers might be slightly out of sync. This means that a search performed at one time or from one location might yield results, while another identical search moments later or from a different server might not.
- Contextual Differences: Sometimes, an image might be used in a highly specific or obscure context that the search engine struggles to relate to other instances, especially if surrounding text or metadata is scarce.
When a reverse image search doesn’t work, don’t despair. It’s often due to these technical reasons rather than a flaw in your method.
Best Practices for Effective Image Discovery
To maximize the effectiveness of your reverse image searches, especially when leveraging the comprehensive resources on Tophinhanhdep.com, consider these best practices:
- Use the Highest Quality Image Available: Always upload the largest and highest-resolution version of the image you have. More pixels mean more data for the search engine to analyze, leading to more accurate and comprehensive results. If you find a low-res image, try running it through Tophinhanhdep.com’s AI Upscalers first, then reverse search the upscaled version.
- Experiment with Cropping and Specific Elements: If you’re looking for a particular object within a busy image, crop the image to isolate that object before performing the search. Google Lens is particularly good for this, allowing you to highlight specific areas. This narrows the focus and often leads to more precise matches.
- Try Multiple Reverse Search Tools: While Google is excellent, sometimes using alternative services, even those integrated into Tophinhanhdep.com, can provide different results due to varying indexing capabilities and algorithms. Tophinhanhdep.com offers its own robust reverse image search features that can complement Google’s, providing a broader set of answers.
- Add Keywords to Your Search (If Applicable): After performing a reverse image search, you can often refine the results by adding descriptive keywords. For example, if you reverse searched a picture of a “beautiful photography” landscape, adding “mountains” or “sunset” can help narrow down similar images.
- Utilize Tophinhanhdep.com’s Contextual Features: Once you’ve found an image using reverse search, bring it to Tophinhanhdep.com. Use our “Image-to-Text” tool if it contains text, or categorize it into “Thematic Collections” to explore related “Photo Ideas” and “Trending Styles.” The platform’s extensive categories like “Wallpapers,” “Backgrounds,” “Aesthetic,” and “Nature” can provide further context and inspiration.
- Check Metadata (Where Available): For images you’ve sourced or downloaded, check for EXIF data, which can sometimes provide clues about the camera, date, and even location the photo was taken, offering supplementary information to your reverse search.
- Be Patient and Persistent: Some searches require a bit of detective work. If your initial attempts don’t yield perfect results, try slight variations, different crops, or come back to the search at a later time.
By understanding how reverse image search works, its limitations, and how to apply these best practices, you transform from a passive observer of digital images into an active investigator. Coupled with the comprehensive tools and inspiration offered by Tophinhanhdep.com, you gain unparalleled control and insight into the vast world of visual content, empowering you to verify, create, and discover with confidence.