Unlocking Scalable Visuals: A Deep Dive into What Are Vector Images with Tophinhanhdep.com
In the vast and dynamic world of digital imagery, where visuals speak louder than words, understanding the fundamental types of graphics is paramount. At Tophinhanhdep.com, we believe that empowering our users with knowledge about image technologies, from stunning “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds” to intricate “Graphic Design” projects, is crucial for creating truly impactful visuals. Among the myriad formats, vector images stand out as a cornerstone for versatility, clarity, and infinite scalability. This comprehensive guide will explore the essence of vector images, their underlying mechanics, their distinct advantages over raster graphics, and their diverse applications, all while highlighting how Tophinhanhdep.com can be your go-to resource for mastering these powerful visual assets.
The Fundamental Distinction: Vector vs. Raster Graphics
To truly appreciate vector images, it’s essential to first understand their counterpart: raster graphics. Most people interact with digital images daily, often without realizing the technical distinctions that govern their appearance and usability. Whether you’re browsing “Aesthetic” images, admiring “Nature” photography, or exploring “Abstract” art on Tophinhanhdep.com, you’re likely encountering a mix of both. The primary difference lies in how these image types are constructed and stored.
Understanding Raster Images: The Pixelated Canvas
Raster images, also known as bitmaps, are the most common type of digital image we encounter. Think of a photograph taken with a digital camera or your mobile phone – that’s a classic example of a raster image. These images are composed of a rectangular grid of individual colored squares called pixels (picture elements). Each pixel holds specific color information, and when millions of these tiny dots are arranged together, they form a complete image.

The sheer number of pixels dictates the image’s resolution and level of detail. A “High Resolution” photograph, for instance, contains millions of pixels, allowing for intricate details and smooth color transitions. This pixel-based structure makes raster graphics ideal for capturing the subtle nuances and rich color gradients of real-world “Photography.” Common raster file formats include .JPG (JPEG), .PNG, .GIF, .BMP, and .TIF.
However, the pixel-based nature of raster images comes with a significant limitation: scalability. When you enlarge a raster image beyond its original resolution, the individual pixels become visible, leading to a phenomenon known as “pixelation.” The edges appear jagged, and the image becomes blurry or “messy and unprofessional,” as described by IONOS. This is because the software is attempting to invent new pixel data, often by stretching existing pixels, which results in a loss of clarity and sharpness. For images that need to maintain pristine quality across various sizes – from a tiny web icon to a giant billboard – raster graphics fall short. This challenge often necessitates “Image Tools” like “AI Upscalers” on platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com to artificially increase resolution, though with varying degrees of success.

The Mathematical Beauty of Vector Images
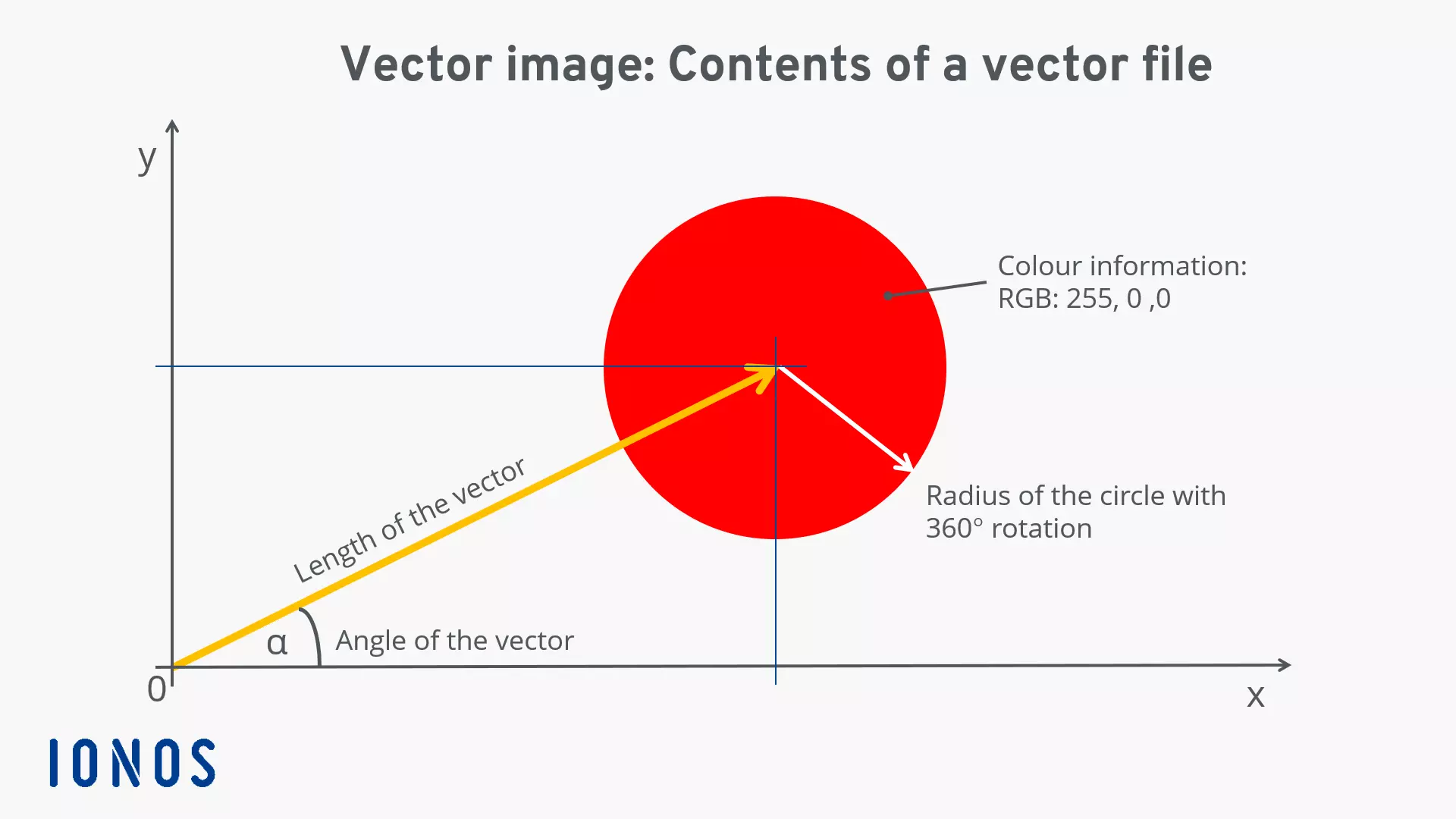
In stark contrast to raster graphics, vector images are not built from pixels. Instead, they are constructed using mathematical descriptions of geometric primitives such as points, lines, curves, and shapes. These mathematical statements define the exact position, direction, length, and color of each element within the image. For example, a circle isn’t stored as a grid of colored pixels, but rather as a mathematical formula defining its center point, radius, and fill color.
This mathematical foundation grants vector graphics their most powerful advantage: infinite scalability without any loss of quality. When a vector image is resized, the software simply recalculates the mathematical formulas to render the image at the new dimensions. The lines remain crisp, the curves stay smooth, and the colors retain their vibrancy, regardless of how large or small the image becomes. This makes vector graphics perfect for designs that need to be consistently displayed across a multitude of platforms and sizes, from a small icon on a smartphone to a massive banner in a trade show.
Moreover, vector files tend to be much smaller than raster files for simple designs, as they store mathematical commands rather than information for millions of individual pixels. Common vector file formats include .SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics), .AI (Adobe Illustrator), .EPS (Encapsulated PostScript), .PDF (Portable Document Format, often containing vector data), .CDR (CorelDraw), and .FH (Freehand Format). Understanding these formats is crucial for anyone involved in “Visual Design” or “Digital Art” looking to achieve professional and adaptable results.
How Vector Images Work: The Language of Mathematics in Visual Design
The operational principle of vector graphics can initially seem abstract, but it’s remarkably elegant and powerful. Imagine you’re drawing a shape not with a brush and paint (like pixels), but with a set of precise instructions that can be followed at any scale.
From Points and Paths to Perfect Shapes
At the heart of every vector image are mathematical formulas that describe geometric elements. A vector can be thought of as an arrow: it has an origin (a starting point on a coordinate graph), a direction, and a length. For example, to draw a simple line, the vector file stores the coordinates of its start and end points, along with information about its thickness, color, and whether it’s a solid or dashed line. For a more complex shape, like a curve, the software uses mathematical equations (often Bézier curves) that define how the line bends between multiple anchor points.
When you create a vector image, say a red circle, the software doesn’t “paint” individual red pixels. Instead, it records instructions like: “Draw a circle with its center at coordinates (X, Y), a radius of Z units, and fill it with color RGB (255, 0, 0).” When this image is displayed or printed, the rendering device (your screen or printer) uses these instructions to draw the circle perfectly, pixel by pixel, at the precise resolution required for that output. This process ensures that the path forming the side of the shape results in a smooth edge, no matter how closely you “zoom in,” as IONOS explains. This meticulous construction is what makes vector images indispensable for “Graphic Design” elements that demand crisp, clean lines and perfect outlines.
The Power of Scalability and Editability
The mathematical nature of vector graphics unlocks two primary advantages vital for any creative professional: unparalleled scalability and superior editability.
Infinite Scalability: As discussed, the ability to resize vector images without any loss of quality is their defining characteristic. A logo designed as a vector graphic can be flawlessly reproduced on a small business card, emblazoned on a website banner, or expanded to cover an entire building billboard, all from the same original file. This eliminates the need to create multiple versions of an asset for different output sizes, streamlining workflows and ensuring brand consistency across all touchpoints. For users seeking “High Resolution” images for various contexts, vector graphics provide an inherent solution that raster images can only mimic through complex “Image Optimization” or “AI Upscaling” processes.
Ease of Editing: Unlike raster images where editing often means manipulating groups of pixels, vector graphics allow for precise manipulation of individual elements. You can easily change the color of a shape, adjust the curvature of a line, move anchor points, or resize a specific component without affecting the rest of the image or degrading its quality. This makes iterative design processes, photo manipulation, and creative revisions significantly more efficient. A “Graphic Designer” using vector software can fine-tune every aspect of a design, ensuring it meets exact specifications. Furthermore, source vector files (.ai, .cdr, .svg) are fully editable, allowing designers to revisit and modify designs years after their initial creation, a distinct advantage when managing “Creative Ideas” and evolving design needs.
Common Vector Formats and Their Applications
Over the years, various vector file formats have emerged, each tailored for specific uses in the design and digital world. Understanding these formats is key to selecting the right tool for your project, whether you’re working on “Digital Art” or preparing files for print.
A Gallery of Vector File Types
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): This is an XML-based, open standard vector graphics format specifically designed for the web. SVG images can be styled with CSS and even animated with JavaScript, making them incredibly versatile for responsive web design. They are widely supported by modern web browsers and are perfect for icons, logos, diagrams, and other interactive web elements on Tophinhanhdep.com.
- AI (Adobe Illustrator Artwork): As a proprietary format developed by Adobe, AI files are the native format for Adobe Illustrator, the industry-standard vector editing software. AI files offer robust features for complex “Graphic Design,” digital illustrations, and branding projects, providing very high-quality images. While proprietary, many other vector programs (like Amadine mentioned in the reference) can import and sometimes edit AI files.
- EPS (Encapsulated PostScript): An older but still widely used vector format, EPS files are based on the PostScript programming language. They are a common choice for sending vector graphics to print houses, especially for professional print production. EPS can contain both vector and raster data, making it a versatile “container format.”
- PDF (Portable Document Format): While primarily known as a document format, PDF files can store vector graphics (as well as raster images and text). PDF has become a universal standard for sharing electronic documents and is frequently used for print-ready artwork because it preserves fonts, images, and layouts precisely across different systems. Many vector logos or illustrations intended for print are delivered as PDFs.
- CDR (CorelDraw Format): This is the native file format for CorelDRAW, another popular vector graphics editor. CDR files support uncompressed image data and a rich set of features, making them suitable for various design tasks for print and web.
- DXF (Drawing Exchange Format): Developed by Autodesk, DXF is primarily used for CAD (Computer-Aided Design) applications, allowing for the exchange of 2D and 3D design data between different CAD programs.
Where Vector Shines: Practical Uses in Design and Photography
Vector images are the workhorses behind countless visual assets we encounter daily, playing a critical role in “Visual Design” and complementing “Photography” across various mediums.
- Logos and Branding: This is arguably the most crucial application for vector graphics. A company’s logo needs to appear perfectly crisp on everything from a small app icon to a large company sign. Vector formats ensure that brand identity remains consistent and professional at any scale. For businesses creating a visual identity, Tophinhanhdep.com provides “Creative Ideas” and resources to inspire logo design.
- Illustrations and Digital Art: Many types of “Digital Art” and illustrations, especially those with clean lines, flat colors, or stylized aesthetics, are created using vector graphics. While raster allows for realistic color transitions (like painting on paper), vector offers precision and infinite scalability for stylized graphics, cartoons, and infographics. Modern vector software also allows for sophisticated effects like shadows and textures, bridging the gap between vector and raster appearances. Tophinhanhdep.com offers a wealth of “Image Inspiration & Collections” for artists working in this medium.
- Web Graphics and Icons: SVG is a powerhouse for web design. Vector icons and interface elements load quickly, scale perfectly on any screen resolution (from mobile to 4K monitors), and can be easily manipulated with CSS for interactive effects. This contributes to better user experience and responsive design, crucial for the “Aesthetic” and functional appeal of any website.
- Print Media: From brochures and business cards to posters, banners, and billboards, vector graphics are the preferred format for professional printing. They guarantee sharp lines and text, ensuring that printed materials always look polished and high-quality, regardless of their final size. This directly impacts the perceived quality of “Beautiful Photography” or “Sad/Emotional” illustrations presented in print.
- Mobile Application and UI/UX Design: User interfaces (UI) and user experience (UX) elements like icons, buttons, and navigation menus are often built with vector graphics. This keeps applications lightweight, ensures they look sharp on diverse device screens, and simplifies the design process for developers and designers who need to export assets in multiple sizes.
- Image Tools and Conversions: Tophinhanhdep.com offers a suite of “Image Tools” that interact with both vector and raster graphics. For instance, “Converters” can transform raster images into vectors (vectorization or image tracing), although this process often involves approximations and may not yield a perfect replica of complex photos. Conversely, vector images must be converted to raster format (rasterization) before they can be displayed on screens or printed, as display devices are inherently raster-based. “Optimizers” can then reduce the file size of these rasterized outputs for web use. While our “AI Upscalers” primarily enhance raster image resolution, the inherent scalability of vector graphics bypasses this need, making them a cornerstone for future-proof design.
Embracing Vector Graphics for Optimal Visual Impact on Tophinhanhdep.com
In a world increasingly dominated by diverse screen sizes and digital platforms, the ability to create and manipulate images that retain their quality across all contexts is invaluable. Vector graphics provide this essential capability, making them an indispensable tool for designers, artists, photographers, and anyone looking to create professional-grade visual content. Tophinhanhdep.com is dedicated to providing the resources and inspiration you need to harness this power.
Integrating Vector into Your Creative Workflow
Choosing between raster and vector graphics ultimately depends on your project’s specific needs. For “Beautiful Photography” or highly detailed “Nature” scenes, raster images remain the superior choice due to their ability to capture complex color gradients and photorealistic detail. However, for “Graphic Design,” “Digital Art,” logos, icons, illustrations, and any element requiring infinite scalability and crispness, vector graphics are the undisputed champion.
Software like Adobe Illustrator (a professional industry standard) or free alternatives like Inkscape and Amadine (for Mac, iPad, and iPhone users, as mentioned in the reference content) provide the tools necessary to create and edit vector images. Tophinhanhdep.com encourages its users to explore these powerful applications to unlock new dimensions in their creative projects. Whether you’re designing a new company logo, crafting a stylized illustration for a website, or preparing graphics for print, integrating vector-based thinking into your workflow will significantly enhance the quality and versatility of your output.
The Future of Scalable Imagery
The trend towards responsive design and high-resolution displays ensures that the importance of vector graphics will only continue to grow. As users demand sharper, faster-loading visuals across a multitude of devices, scalable vector assets become a critical component of successful “Visual Design.” From “Wallpapers” and “Backgrounds” that need to adapt to different screen ratios without distortion, to “Aesthetic” graphic elements that maintain their appeal at any size, vector images offer the ultimate solution for adaptability and visual excellence.
At Tophinhanhdep.com, we are committed to being your comprehensive platform for all things visual. Through our diverse “Images” collections, “High Resolution” “Photography” resources, innovative “Image Tools,” expert guidance on “Visual Design,” and inspiring “Image Inspiration & Collections,” we aim to equip you with the knowledge and assets to create, transform, and share stunning visuals. By understanding and utilizing the power of vector images, you can ensure your designs are not only beautiful but also infinitely adaptable and ready for the future of digital display. Embrace the mathematical precision of vector graphics and elevate your visual storytelling with Tophinhanhdep.com.