What is a Vector Image?
In the vast and ever-evolving landscape of digital imagery, understanding the fundamental building blocks of visual content is paramount. Whether you’re a professional graphic designer, an aspiring digital artist, a photographer looking to enhance your work, or simply an enthusiast curating beautiful wallpapers and backgrounds on platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, you’ve likely encountered the terms “raster” and “vector” images. While both are critical to displaying visuals on screens and in print, they operate on entirely different principles, leading to distinct advantages and applications. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into what a vector image is, how it functions, why it’s indispensable in modern design, and how its unique properties contribute to the diverse visual offerings found on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Understanding Digital Imagery: Raster vs. Vector
To truly grasp the essence of vector graphics, it’s essential to first understand the alternative: raster graphics. The distinction between these two forms of digital imagery is not merely technical jargon; it defines how images are stored, displayed, and ultimately, how they can be manipulated and used across various media.
The Pixelated World of Raster Images
Raster images, often referred to as bitmaps, are the most common form of digital imagery we encounter daily. When you take a photograph with your digital camera, download a wallpaper from Tophinhanhdep.com, or view an image online, you’re almost certainly looking at a raster image. These images are composed of a rectangular grid of individual colored squares called pixels (picture elements). Each pixel holds specific color information, and when millions of these tiny pixels are arranged together, they form a complete image.

The beauty of raster images lies in their ability to capture complex details, subtle color gradients, and photographic realism. This makes them ideal for photographs, detailed paintings, and any visual content requiring intricate shading and a wide spectrum of colors. Common raster file types include .jpg, .png, .gif, .tiff, and .bmp. Software like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and Photo-paint are popular editors for raster images, allowing for detailed manipulation down to the individual pixel.
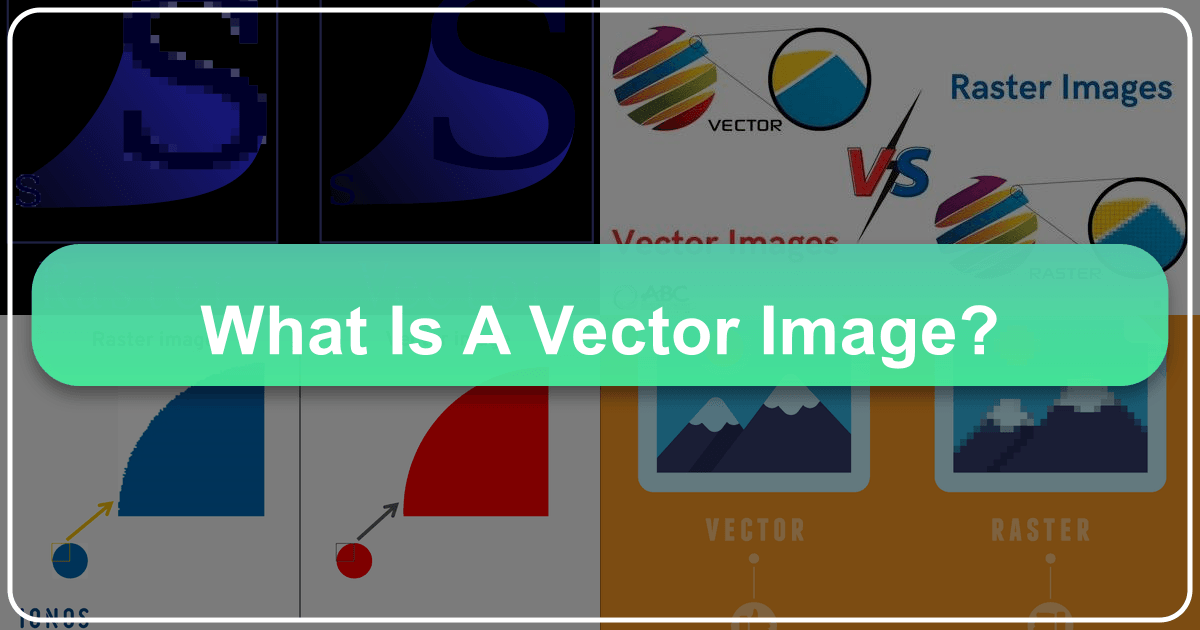
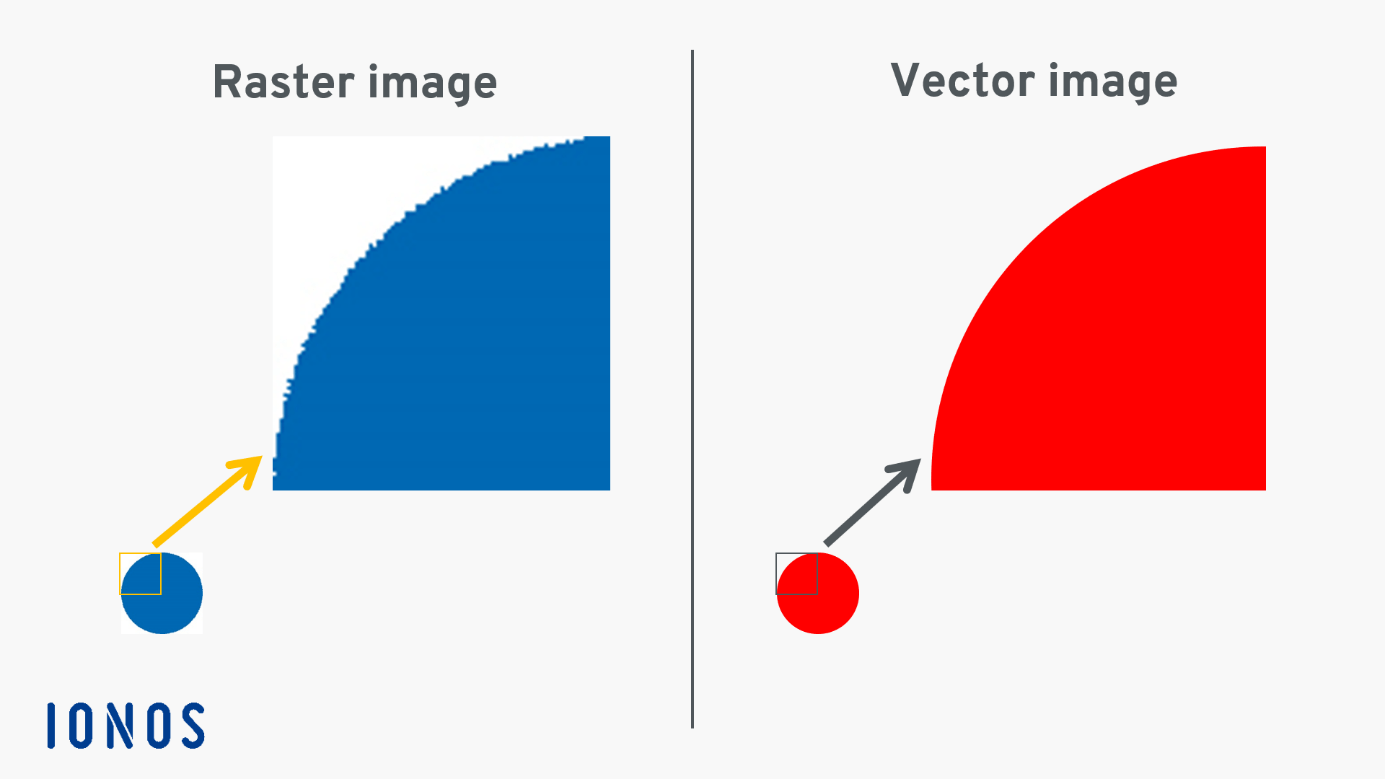
However, the pixel-based nature of raster images introduces a significant limitation: scalability. When you zoom in on a raster image or attempt to enlarge it beyond its original resolution, the individual pixels become visible. This phenomenon, known as pixilation, causes the image to appear blurry, jagged, and unprofessional. The image data is fixed at a certain resolution, meaning that increasing its size doesn’t add more detail; it merely stretches the existing pixels, compromising quality. Furthermore, high-resolution raster images, packed with millions of pixels, can consume substantial memory space.
The Mathematical Elegance of Vector Graphics
In stark contrast to raster images, vector graphics are not built from pixels. Instead, they are constructed using mathematical equations that define geometric primitives like points, lines, curves, and polygons. Imagine a drawing where instead of coloring individual squares, you’re instructing a computer to “draw a line from point A to point B,” “create a circle with this radius at this center,” or “fill this enclosed shape with this color.” These instructions, based on vectors (which have an origin, direction, and length), are what constitute a vector image.
This mathematical definition means that a vector graphic is essentially a set of instructions rather than a fixed grid of color. When you open a vector file, the software interprets these mathematical formulas and renders the image precisely according to the stored coordinates. This dynamic rendering is the core reason for the vector image’s most significant advantage: infinite scalability without any loss of quality.
Visualizing the Difference: Zooming In
The fundamental difference between raster and vector images becomes strikingly apparent when you zoom in. On a raster image, zooming in reveals the pixel grid, leading to jagged edges and a loss of clarity. The image appears fragmented and distorted. Conversely, when you zoom in on a vector image, the lines and curves remain perfectly smooth and sharp. The mathematical equations simply recalculate and redraw the shapes at the new scale, maintaining pristine quality regardless of how large or small you make the image. There is no pixilation, no blurriness, only crisp, clean edges, which is crucial for high-resolution photography and visual design elements on Tophinhanhdep.com.
The Mechanics of Vector Graphics: How They Work
The technical foundation of vector graphics, though seemingly complex, is what grants them their unparalleled versatility and precision. It’s a fascinating system that empowers designers to create visuals that are both flexible and lightweight.
Points, Paths, and Mathematical Precision
At its heart, a vector image is a collection of geometric objects defined by mathematical vectors. A vector isn’t just a line; it’s an instruction that tells a computer how to draw that line, curve, or shape. Consider a simple red circle. In a vector file, this isn’t stored as a mosaic of red pixels. Instead, it’s defined by a mathematical formula that specifies its center point (e.g., coordinates X, Y), its radius, and its color (e.g., RGB value). When this information is processed, the software draws a perfect circle.
For more complex shapes, multiple vectors are used. A path, which forms the side of a shape, is created by connecting various anchor points. These points can have “handles” or “control points” that dictate the curvature of the line segment between them, allowing for smooth, organic shapes as well as sharp, angular ones. All of this information—the position of points, the direction and length of curves, and color fills—is precisely stored in the vector file as mathematical data. This geometric precision ensures that every element of the image is rendered with absolute accuracy, making it an ideal choice for the intricate graphic design and digital art showcased on Tophinhanhdep.com.
Scalability Without Quality Loss
The mathematical definition is the secret to vector graphics’ infinite scalability. When you resize a vector image, you’re not stretching pixels. Instead, you’re merely updating the mathematical formulas that define the image’s components. The software re-renders the image based on these new numerical values, redrawing all lines, curves, and shapes to fit the new dimensions perfectly. This means a logo designed as a vector graphic can be scaled down to a tiny icon on a website or blown up to cover a billboard without any degradation in quality. The edges remain crisp, and the colors stay true. This property is particularly valuable for businesses and brands that need their logos and branding to look consistent and professional across a vast array of applications, from business cards to large-scale signage, an aspect highly relevant to the visual design and creative ideas promoted by Tophinhanhdep.com.
Smaller File Sizes for Optimal Performance
Another significant advantage stemming from the mathematical nature of vector graphics is their typically smaller file size compared to raster images. Recording mathematical coordinates and instructions generally requires less memory than mapping out individual color information for millions of pixels. For instance, defining a large blue rectangle in a vector file might simply involve recording four corner coordinates and a color value. In a raster image, that same rectangle would require color data for every single pixel it encompasses.
This smaller file size is crucial for web designers and anyone concerned with digital performance. Images need to be lightweight to ensure fast loading times, which is vital for both a positive user experience and search engine optimization. Vector file types, especially Scalable Vector Graphics (.svg), are the industry standard for web icons, illustrations, and other graphics that need to load quickly and display crisply on various screen resolutions. Tophinhanhdep.com, which offers a wide range of images, understands the importance of optimized visuals, and vector graphics play a key role in achieving efficient loading without sacrificing aesthetic appeal.
Why Choose Vector? Advantages and Key Applications
Given their unique characteristics, vector graphics are the preferred choice for a multitude of design and visual communication tasks. Their advantages extend far beyond mere scalability, influencing efficiency, adaptability, and aesthetic quality across various mediums.
Logos, Branding, and Corporate Identity
Perhaps the most iconic application of vector graphics is in the realm of branding and corporate identity. A company’s logo is its most recognizable visual asset, and it needs to be adaptable for countless uses. From a tiny favicon in a web browser to a large banner at an event, a logo must maintain its integrity and clarity. Vector formats ensure this consistency. Designers can create a logo once in a vector program like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW, and it can then be exported for web, print, embroidery, signage, and more, always appearing sharp and professional. This ensures that the brand message is consistently delivered, regardless of the medium or scale.
Illustrations, Icons, and Digital Art
For illustrators and digital artists, vector graphics offer a powerful toolkit for creating clean, stylized visuals. Icons, infographics, technical drawings, and even complex digital paintings often leverage the precision of vectors. While raster images excel at photographic realism and soft gradients, vector graphics are perfect for crisp lines, solid color blocks, and graphics that require geometric accuracy. Modern vector software, however, has evolved to allow for sophisticated gradients, shadows, and textures, blurring the lines and enabling artists to achieve a wide range of styles, from flat design to more dimensional illustrations. Many of the abstract and aesthetic image collections on Tophinhanhdep.com likely incorporate vector elements or are entirely vector-based.
Web Graphics and Responsive Design
In the age of diverse devices and screen resolutions, responsive web design is non-negotiable. Vector graphics, particularly SVG files, are perfectly suited for this environment. An SVG icon or illustration will look flawless on a desktop monitor, a high-resolution tablet, or a small smartphone screen, without requiring multiple versions of the same asset. This not only ensures visual quality but also simplifies web development and optimizes loading times, as discussed earlier. For Tophinhanhdep.com, optimizing images for web display is critical, and understanding vector graphics contributes to providing a seamless user experience across all devices.
Print Media of All Sizes
When it comes to print, vector graphics are often the format of choice for anything that isn’t a photograph. Whether it’s a business card, a flyer, a poster, or a massive billboard, vector images will always deliver razor-sharp results. This is because printing presses interpret the mathematical data to produce incredibly precise lines and shapes. For projects combining text, illustrations, and photographs—like brochures or magazine layouts—designers often use vector elements for text and graphics, while photographs remain in raster format. The ability to guarantee print quality at any scale makes vector graphics indispensable for professional printing, including the production of high-resolution stock photos and themed image collections from Tophinhanhdep.com.
Common Vector File Formats and Ecosystem
Just as there are various file types for raster images (.jpg, .png), vector graphics also come in several formats, each with its own strengths and typical applications. Familiarity with these formats is essential for any designer or content creator working with digital visuals.
Adobe Illustrator (AI)
Adobe Illustrator is one of the most widely used professional vector graphics editing programs, and its native file format is .ai. AI files are proprietary to Adobe but are highly versatile for creating, editing, and saving vector artwork. They offer rich features for graphic design, illustration, and logo creation, and are often considered the “source file” for many vector projects due to their comprehensive data retention and editability. If you’re engaging in graphic design or digital art that might end up as a beautiful wallpaper or aesthetic background on Tophinhanhdep.com, an AI file might be your starting point.
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
SVG is an XML-based, open-standard vector image format specifically designed for the web. Being an open standard means it’s broadly supported across web browsers and can be manipulated using CSS and JavaScript, allowing for interactive and animated vector graphics. SVGs maintain perfect clarity at any resolution, making them ideal for responsive web design, icons, and illustrations. Their small file size also contributes to faster website loading times, which is a key consideration for performance-driven platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com.
Encapsulated PostScript (EPS)
EPS files are another common vector format, especially in the print industry. Based on the PostScript programming language, EPS files can contain both vector and raster data, making them a versatile “container” format. Historically, they were widely used for transferring vector artwork between different design programs and for professional printing. While still in use, newer formats like PDF and SVG have often replaced EPS for many applications, and support for EPS is being deprecated in some modern operating systems and applications.
Portable Document Format (PDF)
While primarily known as a document format, PDF files can also contain vector graphics. In fact, many vector design programs can save artwork as PDFs, preserving vector information. This makes PDFs excellent for sharing designs that need to be viewed and printed accurately across different systems, as they embed all necessary fonts and graphics. PDFs are a de facto standard for exchanging electronic documents and print-ready files, often used to display vector logos or detailed diagrams.
Popular Vector Editing Software
Beyond Adobe Illustrator, several other powerful tools are available for creating and editing vector graphics. CorelDRAW is another industry-leading vector graphics suite, offering a comprehensive set of tools for design, illustration, and layout, with its native .cdr format. For those seeking free and open-source alternatives, Inkscape is a highly capable vector editor that fully supports the SVG format and provides a robust feature set for digital artists. Tophinhanhdep.com encourages creative ideas and digital art, making these tools highly relevant for content creators.
Vector Graphics in the World of Tophinhanhdep.com: Enhancing Your Visual Journey
Tophinhanhdep.com is a hub for diverse visual content, encompassing everything from stunning photography to abstract designs and aesthetic wallpapers. Understanding vector graphics enriches both the creation and appreciation of this content, offering new possibilities for high-resolution imagery and visual design.
Crafting Dynamic Wallpapers and Backgrounds
While many wallpapers and backgrounds on Tophinhanhdep.com might be beautiful photography (raster images), a significant portion of aesthetic, abstract, and thematic collections can benefit immensely from vector graphics. Abstract patterns, geometric designs, minimalist backgrounds, and custom artistic elements are perfectly suited for vector creation. These vector-based wallpapers can be downloaded and used across devices with varying screen resolutions—from a phone to an ultra-wide desktop monitor—without ever losing their sharp, clean appearance. This ensures that users always get the highest quality visual experience, regardless of their display.
Integrating Vector Elements with High-Resolution Photography
The boundary between raster and vector is not always distinct; often, they are used in conjunction. For instance, a beautiful high-resolution photograph (raster) downloaded from Tophinhanhdep.com might be enhanced with vector-based graphic overlays, text, or decorative frames. Think of a stock photo with a clean vector logo, or a nature image featuring elegant vector-drawn botanical illustrations. This hybrid approach allows designers to combine the rich detail of photography with the crisp scalability of vector art, leading to sophisticated photo manipulation and creative ideas for various visual projects.
Utilizing Image Tools for Vector Conversion and Optimization
Tophinhanhdep.com recognizes the importance of image tools, including converters, compressors, and optimizers. For users working with existing raster images, “image vectorizers” (converters) can transform pixel-based artwork into scalable vector graphics. While this process might not be perfect for highly detailed photographs, it’s invaluable for logos, simple illustrations, and text-based designs that need infinite scalability. Furthermore, tools that optimize and compress images are crucial for all types of graphics, including vector formats like SVG, ensuring that even mathematically defined images are as lightweight as possible for web use, contributing to a seamless browsing experience for users seeking image inspiration and thematic collections.
Inspiring Visual Design and Creative Ideas
Ultimately, a deep understanding of vector graphics empowers creators to push the boundaries of visual design. From graphic design principles to digital art techniques, vector capabilities open up new avenues for creative expression. On Tophinhanhdep.com, the principles of vector graphics can inspire photo ideas, inform mood boards, and define trending styles. By recognizing the strengths of vector images—their precision, scalability, and smaller file sizes—designers and enthusiasts alike can make more informed choices about the visuals they create, share, and appreciate, ensuring that every image, whether a sad/emotional illustration or a vibrant abstract piece, achieves its full potential.
In conclusion, vector images represent a powerful and indispensable component of the digital design landscape. Their mathematical foundation provides unparalleled scalability, precision, and efficiency, making them the preferred choice for logos, illustrations, web graphics, and print media. For platforms like Tophinhanhdep.com, leveraging the unique advantages of vector graphics—both in standalone art and in conjunction with high-resolution photography—is key to delivering a rich, high-quality, and versatile visual experience for every user. Understanding “what is a vector image” is not just about technical knowledge; it’s about unlocking a world of creative possibilities in digital art and design.