What is the CSS for Shrinking Image Size: Mastering Visuals for Tophinhanhdep.com

In the rich tapestry of the digital world, images are more than just visual elements; they are storytellers, mood setters, and crucial engagement drivers. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, dedicated to showcasing an extensive collection of Images, Photography, and Visual Design, the ability to control and optimize these visuals is paramount. From breathtaking Wallpapers and captivating Backgrounds to intricate Aesthetic compositions, stunning Nature shots, bold Abstract art, poignant Sad/Emotional imagery, and exquisite Beautiful Photography – every pixel counts.
However, the sheer diversity of devices and screen resolutions available today presents a significant challenge: how do we ensure that every image, regardless of its original size or format, looks perfect and loads quickly on every screen? The answer lies predominantly in CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) image resizing. It’s not merely about making an image smaller; it’s about intelligent scaling, preserving quality, enhancing user experience, and optimizing performance.
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the CSS techniques for shrinking and managing image sizes, ensuring that Tophinhanhdep.com’s vast visual library always shines. We’ll explore the fundamental properties, advanced scaling methods, considerations for background images, and the critical aspects of browser compatibility and accessibility, all through the lens of maximizing your visual impact.
The Fundamentals of CSS Image Resizing for Optimal Visuals
At its core, CSS image resizing is the process of adjusting an image’s displayed dimensions without necessarily altering its intrinsic file size or physical aspect ratio (unless explicitly desired). This adjustment is crucial for web performance and responsive design, especially for platforms rich in high-quality imagery.
Understanding Upsizing and Downsizing
There are two primary forms of image dimension manipulation:
- Upsizing: This involves increasing an image’s dimensions. While useful for displaying a smaller image on a larger canvas, a significant drawback is the potential loss of quality, leading to pixelation or blurriness. For High Resolution and Stock Photos on Tophinhanhdep.com, upsizing should generally be avoided unless the original resolution is exceptionally high, as it can degrade the “beautiful photography” aesthetic.
- Downsizing: This is the act of reducing an image’s dimensions. It’s invaluable for Optimizers and Compressors because it directly reduces file size, leading to faster loading times. Downsizing is essential for ensuring that Wallpapers and Backgrounds are web-friendly without compromising their visual integrity. When dealing with images for web, choosing the right format (like JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics with transparency, and newer, more efficient formats like WebP for optimal compression) in conjunction with appropriate downsizing, is key to striking the perfect balance between quality and file size. This directly relates to the Image Tools category of Tophinhanhdep.com, where efficient management of image formats and sizes is critical.
Why Image Resizing is Critical for Tophinhanhdep.com
The importance of CSS image resizing extends far beyond simple aesthetics. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, which thrives on visual content, it underpins many aspects of user satisfaction and site functionality:
- Improved Page Load Time: Images are often the heaviest elements on a webpage. Unoptimized or excessively large images can significantly slow down page load times. By properly resizing images using CSS, especially those within Thematic Collections or Mood Boards, we can drastically reduce the amount of data transferred, leading to a snappier, more enjoyable experience for visitors. Faster load times are also a critical factor in search engine rankings, directly impacting the visibility of your stunning Nature or Abstract image collections.
- Responsive Web Design: In an era where users access content from a myriad of devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktops), images must adapt seamlessly to varying screen sizes and resolutions. CSS resizing ensures that your Aesthetic photos, Digital Photography, or Graphic Design creations scale appropriately, providing a consistent and visually appealing experience on any device. This adaptability is foundational for a site like Tophinhanhdep.com, where visual presentation is everything.
- Visual Aesthetics and Layout Harmony: Correct image sizing is fundamental to maintaining a professional and polished appearance. It prevents images from overflowing their containers, causing overlaps, or appearing disproportionate, which can detract from the artistry of Photo Manipulation or the effectiveness of Creative Ideas. By ensuring images fit harmoniously within their designated spaces, CSS resizing elevates the overall Visual Design of Tophinhanhdep.com, making it more appealing and trustworthy to users seeking high-quality imagery.
Basic CSS Properties: Width, Height, Max-Width, and Max-Height
To effectively control image sizes, we start with a few foundational CSS properties:
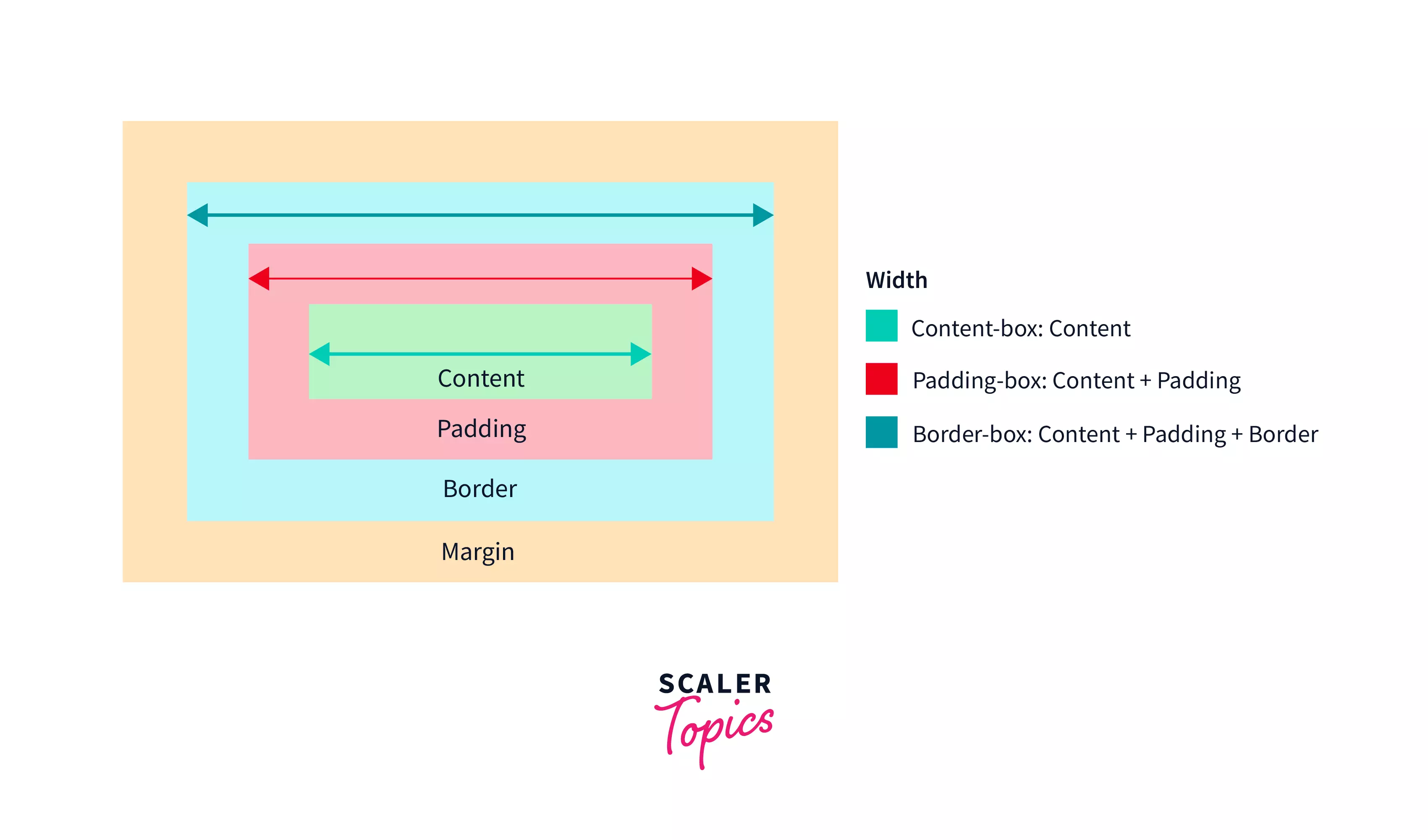
Controlling Dimensions with width and height
The width and height properties allow you to explicitly define the horizontal and vertical dimensions of an image. For instance, to set an image to a fixed size:
img {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}While straightforward, assigning both width and height with fixed pixel values can be problematic. If the specified dimensions do not match the image’s original aspect ratio (the ratio of its width to its height), the image will appear distorted or “squished,” ruining the Beautiful Photography. To prevent this, it’s generally recommended to set only one dimension, allowing the browser to automatically calculate the other to maintain proportionality.

The Power of max-width for Responsiveness
For truly responsive images, max-width is a game-changer. The most common and effective technique for shrinking images proportionally while maintaining their aspect ratio across different screen sizes is to apply:
img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}With max-width: 100%, the image will never exceed the width of its parent container. If the container shrinks, the image will scale down proportionally. height: auto ensures that the image’s height adjusts automatically to preserve its original aspect ratio, preventing distortion. This approach is vital for Wallpapers and Backgrounds that need to adapt gracefully to diverse devices, from large desktop monitors showing High Resolution imagery to small mobile screens displaying Aesthetic shots.
Leveraging Relative Units for Fluid Layouts
Beyond fixed pixel values, CSS offers relative units that provide greater flexibility and responsiveness:
- Percentage (
%): Sets a dimension relative to the parent element’s size. For instance,width: 50%;makes an image half the width of its container. This is excellent for Image Collections where images need to dynamically adjust within a grid layout. emandrem: These units are relative to font sizes.emis relative to the font size of the element itself (or its nearest parent with a defined font size), whileremis relative to the root<html>element’s font size. They are particularly useful for scaling images that are intrinsically linked to text size, enhancing overall readability and Visual Design.vhandvw: Viewport height and viewport width. These units are relative to the browser’s viewport dimensions.width: 100vw;means the image will take up 100% of the viewport width. This is perfect for creating full-screen Wallpapers or immersive Backgrounds that stretch across the entire screen, showcasing the grandeur of Nature or the complexity of Abstract art.
By combining max-width: 100% with height: auto and strategically using relative units, you can ensure that the diverse array of images on Tophinhanhdep.com maintains its high quality and aesthetic appeal, regardless of how or where it’s viewed.
Advanced Scaling Techniques for Dynamic Image Presentation
While basic width and height properties handle fundamental resizing, CSS offers more sophisticated tools to achieve dynamic and creatively controlled image scaling. These techniques are particularly useful for Digital Art, Photo Manipulation, and presenting Creative Ideas where precise visual effects are desired.
Harnessing the transform Property
The CSS transform property is incredibly powerful, allowing you to apply various transformations to HTML elements, including resizing, rotating, skewing, and translating. For scaling, we use the scale() function.
The scale() function modifies the size of an element. It can take one or two arguments:
scale(factor): Scales both the width and height by the samefactor. For example,transform: scale(1.3);would make the image 30% larger, whiletransform: scale(0.5);would shrink it to 50% of its original size.scale(scaleX, scaleY): Scales the width byscaleXand the height byscaleY. This allows for non-uniform scaling, which can intentionally distort an image but can also be used for unique Visual Design effects or Photo Manipulation.
Example: Imagine you have an image, like one from a Thematic Collection, and you want it to subtly grow on hover for an interactive effect:
.image-container img {
transition: transform 0.3s ease; /* Smooth animation */
}
.image-container img:hover {
transform: scale(1.1); /* Enlarges image by 10% on hover */
}This dynamic scaling can add a layer of interactivity and visual interest to Photo Ideas or Mood Boards, making the user experience more engaging.
Controlling Image Fit with object-fit
The object-fit property provides exquisite control over how an <img> or <video> element’s content should be resized to fit its container, crucial for maintaining the artistic integrity of Beautiful Photography or intricate Digital Photography. Unlike width and height which can distort, object-fit primarily helps manage content within a defined space, offering solutions for varied image dimensions. It’s particularly useful when you have a container of a fixed size and want images of different aspect ratios to fill it uniformly without distortion or awkward empty space.
The object-fit property accepts several key values:
contain: This value scales the image down (or up) proportionally to fit entirely within its container, preserving its aspect ratio. If the image’s aspect ratio differs from the container’s, there might be empty space (letterboxing or pillarboxing) around the image. This is ideal for ensuring all of an Aesthetic image is visible within a gallery thumbnail.cover: This scales the image proportionally to completely cover its container. If the image’s aspect ratio doesn’t match the container’s, parts of the image will be clipped (cropped) to ensure no empty space. This is often preferred for Backgrounds or Wallpapers where filling the entire area is more important than showing every detail of the Nature scene.fill: This is the default value. It scales the image to fill the container entirely, regardless of its aspect ratio. This will often stretch or squish the image, leading to distortion. Generally,fillshould be used with caution, as it can detract from the quality of High Resolution images.none: The image is displayed at its original size, ignoring the container’s dimensions. If the image is larger than the container, it will overflow and be clipped. This can be useful for Digital Art pieces where every pixel of the original needs to be respected, and cropping is not desired.scale-down: This value compares the rendered size of the image as ifnoneandcontainwere specified, and uses the smaller of the two. It’s a smart way to ensure an image is neither upscaled past its original size nor clipped.
Example:
Consider displaying various Sad/Emotional or Abstract images in a grid of square containers. Using object-fit: cover; would ensure each square is fully filled, even if some parts of the original image are cropped, creating a uniform, impactful gallery. Conversely, object-fit: contain; would show the entire image, but might leave white space around it if the aspect ratios don’t match, preserving all content.
.gallery-thumbnail img {
width: 200px;
height: 200px; /* Fixed square container */
object-fit: cover; /* Ensures image covers the entire square */
}This property becomes indispensable for Image Collections and Trending Styles where a consistent presentation across diverse photographic subjects is key to maintaining a professional aesthetic.
Resizing Background Images for Immersive Experiences
Background images, commonly used for Wallpapers and Backgrounds on Tophinhanhdep.com, are handled differently in CSS than standard <img> tags. They are applied using the background property and offer their own set of properties to control their size and positioning, enabling the creation of truly immersive and responsive visual experiences.
The background-size Property
This property is dedicated to controlling how a background image is scaled relative to its container. It’s crucial for making a Nature or Abstract background fill the entire area beautifully.
auto: The default value. The background image will not be resized; it displays at its natural dimensions. This often results in repetition if the image is smaller than the container.cover: This scales the background image (while preserving its aspect ratio) to be as large as possible, such that the background area is completely covered by the image. Some parts of the image may be clipped to fit. This is the go-to for full-screen Wallpapers and Backgrounds, ensuring there are no empty spaces.contain: This scales the background image (preserving its aspect ratio) to be as large as possible without cropping or distortion, such that the entire image is visible within the background area. Empty space may appear if the aspect ratios don’t match. Useful when every detail of a Beautiful Photography background must be seen.<width> <height>: You can specify explicit dimensions, e.g.,background-size: 50% 100%;orbackground-size: 200px 300px;. This offers precise control but requires careful management to avoid distortion. Using percentages orvw/vhunits here can maintain responsiveness.
Example: To make a stunning Nature scene serve as a full, responsive background:
body {
background-image: url('nature-wallpaper.jpg');
background-size: cover; /* Ensures the image covers the entire viewport */
}background-repeat and background-position
These two properties complement background-size to give full control over background image presentation.
Controlling Tiling with background-repeat
This property dictates whether and how a background image tiles within its container, especially when the image is smaller than the element.
repeat: (Default) The image repeats horizontally and vertically to fill the background area. This can be used for subtle patterns or textures but is generally undesirable for large photographic backgrounds.no-repeat: The image appears only once. This is almost always used withbackground-size: cover;orcontain;for photographic backgrounds to prevent visual clutter.repeat-x: The image repeats only horizontally.repeat-y: The image repeats only vertically.
Positioning the Image with background-position
This property controls the initial position of the background image within its container. Values can be keywords (e.g., center, top, bottom, left, right), percentages, or length units.
center: Positions the image in the center of the container.top left,bottom right, etc.: Positions the image in a corner.50% 50%(same ascenter center): Positions the image centrally.
Example: To create a perfectly centered, non-repeating, full-coverage Wallpaper for Tophinhanhdep.com:
header {
background-image: url('abstract-background.webp');
background-size: cover; /* Make it cover the container */
background-repeat: no-repeat; /* Ensure it doesn't tile */
background-position: center; /* Center the image */
height: 100vh; /* Example: Make header full viewport height */
}This combination ensures that whether it’s a vibrant Digital Art piece or a serene Sad/Emotional landscape, the background image provides an immersive and visually consistent experience across all screen sizes.
Ensuring Cross-Device Harmony and Accessibility
Beyond the technical application of CSS properties, ensuring images function flawlessly across different environments and for all users is paramount. For a platform like Tophinhanhdep.com, this means every High Resolution image, Trending Style, or Beautiful Photography collection is accessible and compatible.
Browser Compatibility and Modern Image Formats
The web is a diverse ecosystem of browsers, and each may handle image formats and CSS properties slightly differently. While modern CSS properties like object-fit and advanced background-size values have broad support, it’s crucial to consider browser compatibility.
- Testing: It is essential to test how your resized images appear across a wide range of browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) and devices (desktops, tablets, various smartphones). This ensures that your carefully curated Image Collections and Creative Ideas are presented consistently to every visitor. While external testing platforms exist, for Tophinhanhdep.com, understanding common browser behaviors and leveraging developer tools for responsive design checks is often sufficient for most CSS-based resizing.
- Modern Image Formats: Embrace contemporary image formats like WebP and AVIF. These offer superior compression ratios and quality compared to older formats like JPEG and PNG, leading to even faster load times for your Wallpapers and Backgrounds. However, always provide fallbacks (e.g., a JPEG version) using the
<picture>element (discussed below) for browsers that may not yet fully support these newer formats, ensuring universal access to your Digital Photography. This directly aligns with the mission of Image Tools on Tophinhanhdep.com: Optimizers and Compressors.
Accessibility in Image Resizing
Web accessibility ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with your website. When resizing images, accessibility remains a crucial consideration.
- Alt Text: Always provide descriptive
alttext for all<img>elements. This text is read by screen readers for visually impaired users and displayed if an image fails to load. For Photography and Digital Art, thealttext should accurately convey the image’s content or purpose. Even for Aesthetic or Abstract images, a concise description is valuable. For images containing text, thealttext should ideally replicate that text. This connects to Image-to-Text tools, emphasizing the importance of text equivalence for visual content. - Readability of Embedded Text: If an image contains text, ensure that resizing, particularly extreme downsizing, does not render the text illegible. This is particularly relevant for Graphic Design elements that might be embedded as images. Maintain sufficient contrast and size.
- Focus on Content: While aesthetics are vital for Tophinhanhdep.com, the primary goal of an image should always be its content. Resizing techniques should support, not detract from, the image’s message or beauty.
The HTML <picture> Element for Adaptive Image Delivery
The <picture> element is an advanced HTML solution for delivering highly optimized and responsive images. It allows developers to provide multiple <source> elements, each specifying a different image file based on various criteria such as screen width, pixel density, or image format support. The browser then intelligently selects and loads the most appropriate image.
Example: Serving different versions of a High Resolution image for a Nature wallpaper:
<picture>
<!-- Serve WebP for modern browsers, different sizes for different screens -->
<source srcset="nature-wallpaper-large.webp 1200w, nature-wallpaper-medium.webp 800w"
type="image/webp" media="(min-width: 768px)">
<source srcset="nature-wallpaper-small.webp 400w"
type="image/webp" media="(max-width: 767px)">
<!-- Fallback for browsers not supporting WebP -->
<source srcset="nature-wallpaper-large.jpg 1200w, nature-wallpaper-medium.jpg 800w"
type="image/jpeg" media="(min-width: 768px)">
<source srcset="nature-wallpaper-small.jpg 400w"
type="image/jpeg" media="(max-width: 767px)">
<!-- Default img tag for maximum compatibility -->
<img src="nature-wallpaper-medium.jpg" alt="A beautiful nature landscape as a desktop wallpaper">
</picture>In this example, the browser will:
- Check for WebP support.
- Load the appropriate
.webpimage based on screen width. - If WebP is not supported, it will fall back to the
.jpgsources. - Finally, if none of the
<source>elements match or are supported, it will load the image specified in the<img>tag.
This method is crucial for Tophinhanhdep.com because it ensures that users receive the smallest, most optimized image file possible for their device and browser, without sacrificing the quality of the original Beautiful Photography or the impact of Thematic Collections. It’s a cornerstone of high-performance and future-proof Digital Photography on the web.
Conclusion
Mastering CSS for shrinking and managing image sizes is not just a technical skill; it’s an art form that directly impacts the aesthetic appeal, performance, and accessibility of any visual-centric platform, especially Tophinhanhdep.com. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the foundational properties like width, height, max-width, and height: auto, which form the bedrock of responsive image handling. We then ventured into advanced techniques such as the transform property for dynamic scaling and the object-fit property for precise control over how images conform to their containers, ensuring that Digital Art and Photo Manipulation retain their intended impact.
Furthermore, we delved into the nuances of resizing background images using background-size, background-repeat, and background-position, vital for crafting immersive Wallpapers and engaging Backgrounds that showcase Nature, Abstract, or Aesthetic themes beautifully across all devices. Finally, we emphasized the critical importance of browser compatibility, the adoption of modern image formats for optimization (Image Tools: Optimizers, Compressors), and the indispensable role of accessibility (e.g., alt text and readable embedded text). The <picture> element emerged as a powerful HTML tool for delivering truly adaptive images, catering to varying screen sizes and formats efficiently.
For Tophinhanhdep.com, a platform dedicated to Images (Wallpapers, Backgrounds, Aesthetic, Nature, Abstract, Sad/Emotional, Beautiful Photography), Photography (High Resolution, Stock Photos, Digital Photography, Editing Styles), Image Tools (Converters, Compressors, Optimizers, AI Upscalers, Image-to-Text), Visual Design (Graphic Design, Digital Art, Photo Manipulation, Creative Ideas), and Image Inspiration & Collections (Photo Ideas, Mood Boards, Thematic Collections, Trending Styles), these CSS techniques are not mere options but essential strategies. They ensure that every visual piece, from a serene Sad/Emotional shot to a vibrant Trending Style, is presented flawlessly, loads swiftly, and is accessible to a global audience.
By applying these CSS image resizing principles, Tophinhanhdep.com can continue to provide an unparalleled user experience, where the beauty and clarity of its visual content are always at the forefront. Embrace these techniques, experiment with creative ideas, and let your potential for stunning Visual Design soar. Happy coding and happy designing!